100% found this document useful (3 votes)
572 views19 pagesChemical Formulas and Compounds Guide
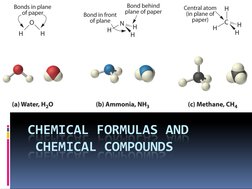
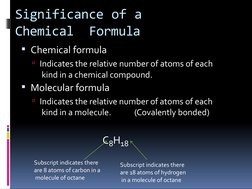
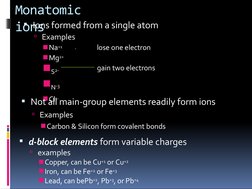
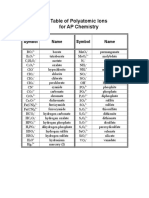
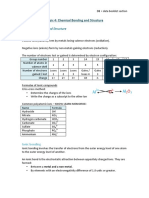
This document discusses chemical formulas and naming conventions for ionic and molecular compounds. It explains how to write formulas and name ionic compounds formed between ions as well as compounds containing polyatomic ions. The document also covers naming conventions for binary molecular compounds using prefixes to indicate the number of atoms present.
Uploaded by
Delano PeteCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (3 votes)
572 views19 pagesChemical Formulas and Compounds Guide
This document discusses chemical formulas and naming conventions for ionic and molecular compounds. It explains how to write formulas and name ionic compounds formed between ions as well as compounds containing polyatomic ions. The document also covers naming conventions for binary molecular compounds using prefixes to indicate the number of atoms present.
Uploaded by
Delano PeteCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd