Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sheeet 1
Uploaded by
Gurucharan ChhabraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sheeet 1
Uploaded by
Gurucharan ChhabraCopyright:
Available Formats
SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT
Aim Of the study The Regulatory Framework ( At Central Level )
Aim of the Study is to develop a waste management plan that works toward the sustainable,
preventative and comprehensive approach towards waste and thus to create Comprehensive Integrated MSW (Management National Urban Rules for
and Handling) Rules Revised Manual on Municipal Swachh Bharat Mission,
Solid Waste management Planning Process. Solid Waste Management, 2016 Sanitation Policy Special Waste
2000 and revised SWM, (SBM), 2014 (NUSP), 2008
Rules 2016
Key Focus Areas and Strategic Actions
• Municipal Solid Waste • Municipal Solid Waste • Policy prepared by the • Plastic Waste Hazardous Waste
(Management & Handling ) Management Manual 2000 Ministry of Urban Management Rules, (Management, Handling
Rules, 2000 by MoEFCC by MoUD and CPHEEO Development in 2008 2011 and revised in and Transboundary
• Revised SWM Rules, 2016 • Guidelines published by • Focus on re-orienting 2016 Movement) Rules, 2008
circulated in the year 2016 by MoUD through CPHEEO in institutions for developing • E-Waste with subsequent
MoEFCC the year 2016 city-wide approach to Management Rules, amendments in 2009
• Designates Urban Local Bodies • Provide implementation sanitation, covering all its 2011 and revised in
responsible for MSWM and lays guidelines for all aspects of aspects including Solid 2016
down the mandatory functions MSWM, including Waste Management
to be performed by various segregation, collection,
stakeholders transportation, treatment
• Separate rules for Construction and disposal
and Demolition waste 2016
Initiatives Of The Ahmedabad Municipal
Components of MSW management – different types of waste
Corporation In The SWM Sector
Information, Education and Communication
Methodology activities for Awareness among the Citizen of
Ahmedabad
• Guidelines for Swachh
STEP 1: ASSESSMENT OF CURRENT SITUATION AND GAP ANALYSIS Sanitation Mobile Court Bharat Mission (urban)
(2021)
AMC launched country’s first Sanitation Mobile Court on 4th • Ahmedabad Municipal
1.Legal & Policy Framework June, 2009
2.Institutional & Financial Set Up Corporation Solid Waste
3. Technical Aspects Management
4.Availability & Suitability of Land for Processing & Disposal
Preparing Ahmedabad's SWM Master Plan for • ROAD MAP FOR ZERO
5.MSW Generation, Collection & Transportation 2031 WASTE AHMEDABAD
6.Current Status of Dump Sites
Transfer Stations (under construction)
STEP 2: Six Transfer Stations of about 400 MT capacity each to be set
POLICIES, PROGRAMMES & LEGAL FRAMEWORK
up in Five Zones.
1.Identify National and State Policies/ Strategies and their Goals Effective Utilization of Garden / Green Waste Existing Treatment
2. State Level/Regional/District SWM Strategies/Policies Identify Overall Goals
for ULBs. AMC initiated a pilot project at Law Garden from 29th Plants and Dumping
3. Role of Central/State and Local Government September 2011. green waste will be converted into organic Sites
4.Institutions and Stakeholders Involved in MSWM Planning manure with the help of Organic Waste Convertor Machine of the
Excel Industries Ltd. and with project site management assistance
ROLE OF STAKEHOLDER CONSULTATION FOR MSWM by Gujarat Consumer Industries on PPP mode.
STEP 3:
PLANNING
STEP 4: PREPARATION OF DRAFT MSWM PLAN SWM PROFILE IN AHMEDABAD
1.Future Projections • Population Forecast • Anticipated Lifestyle
Changes • Change in Socio-economic Status
2.Rules, Regulations & Municipal Bye-Laws
3.Community Participation/IEC
4.Institutional & Financial Structuring
5.Storage, Collection (Door-to-Door & Street Sweeping),
Transportation
6.Identification of Land & Inclusion in City Master Plan
7.Selection of Process & Best Available Technology for Processing Geddam Renuka Sai
& Disposal GuruCharan Chhabra
Matta Arunima Rao
STEP 5: SCHEDULE FOR IMPLEMENTATION
Shreya Singhal
• Timeline • Manpower Requirement • Financial Viability
1.Measures to assess how clean a city is- Swach
Sarvekshan rankings, liveability index,, SDG parameters,
– what, who, when, how, why, which of the index;
2.Best practices – National 5 cities of similar size and
International 5 cities of similar size/context (role models)
Indian cities generating waste
Swachh Survekshan, conducted by MoHUA since
2016, is the world’s largest urban sanitation and Delhi topped the list of Indian cities with maximum waste
cleanliness survey. generation (30.6 lakh tonnes), and was followed by Greater
Mumbai at 24.9 lakh tonnes, Chennai at 18.3 lakh tonnes,
Greater Hyderabad at 16.4 lakh tonnes, Bengaluru at 12.8 lakh
Conducted under the ambit of the Swachh Bharat Mission
(Urban), the annual survey has managed to mobilise people, tonnes, Ahmedabad at 12.2 lakh tonnes, Pune and Surat
resources and authorities in an effort to prove that their city, of at 6.2 lakh tonnes, Kanpur at 5.5 lakh tonnes and Jaipur at 5.4
all cities in India, is the cleanest and that sustainable practices, lakh tonnes.
both by citizens and ULBs, are being encouraged and
promulgated.
2021 2019
Swachh Survekshan Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs 2016 World’s largest urban sanitation and Open Defecation Free - % of cities in the state are 10 6
cleanliness survey certified a. Water Plus b. ODF++ c. ODF+ d. ODF
Swachh Bharat Mission Urban Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs 2nd October 2014 To make a garbage - free city, a city % of cities in the state falling in the new SS-2021 Awards
completely free of garbage.” category of - a. Platinum (Divya) b. Gold (Anupam) c.
Silver (Ujjwal) d. Bronze (Udit) e. Aspiring (Aarohi)
Star rating protocol for Garbage free Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs 2018 24 components with two groups into ‘Important’ (1 & 3 3 star • Door to Door segregation
cities Star – 16 components and ‘Aspirational’ indicators (5 & 7 • Source Segregation
Star – 24 components) Garbage Free City for Star • Waste Processing
Rating - % of cities in the State • City Beautification
are certified a. 7 Star b. 5 Star c. • Onsite wet waste processing
3 Star d. 1 Star
Global Liveability Index WHO Published 173 cities covered 173 cities based on their living Stability-25 143 out of 173 Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai,
Economic Intelligence Unit conditions and, in general, citizen living Healthcare-20 Ahmedabad, and Bangalore.
standards Culture and Environmnet-25
Education-10
Infrastructure-20
Ease of Living Index Under Smart City Mission 2018 Municipal Performance Index examined The EOL index evaluates development outcomes across Bengaluru, Pune, Ahmedabad Services, Finance, Policy,
the sectoral performance of 111 four pillars — quality of life, economic ability, best cities in EoLI 2020 (Million Technology and Governance
municipalities. sustainability, and citizens perception survey — covering Plus Category)
49 indicators examined under 14 categories.
Total 111 Cities
Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) Niti Aayog’s SDG India Index – Baseline SDG 12 Aspirant (0–49), Gujarat worst performer rank 115 indicators incorporate 16
India Report 2018 Performer (50–64), 27th out of 28th. out of 17 SDGs, with a
Responsible consumption and production Front-Runner (65–99), qualitative assessment on Goal
Achiever (100). 17, and cover 70 SDG targets
GARBAGE FREE CITY ensures holistic evaluation across
entire SWM Chain
Best practices City generates more than 3800
TPD waste including 700 MT of construction
SOURCE SEGREGATION Indore and demolition waste.
Indore has become the cleanest city in
India by mastering segregation at source
and subsequent steps in the waste
management chain
The city is segregating its waste into six
categories:
1. Biodegradable,
2. Non-biodegradable (excluding
plastic),
3. Plastic,
4. Sanitary,
5. Domestic hazardous and
6. Electronic.
Steps taken by IMC to reform its waste management system
Land use- (routes, recycling sites,
waste to energy plants, disposal
sites, landfill sites -- existing and
proposed
RANKING’S GOVERNANCE YEAR OBJECTIVE INDICATORS RANKING’S POSITION INDICATORS
Ministry of Housing and Urban 2016 World’s largest urban sanitation Open Defecation Free - % of cities in the state Swachh Survekshan 10 12 service level progress
Swachh Survekshan
Affairs and cleanliness survey are certified a. Water Plus b. ODF++ c. ODF+ indicators
d. ODF Swachh Bharat Mission Urban 10TH
Swachh Bharat Mission Ministry of Housing and Urban 2nd October 2014 To make a garbage - free city, a % of cities in the state falling in the new SS-
Urban Affairs city completely free of garbage.” 2021 Awards category of - a. Platinum (Divya) Star rating protocol for Garbage free cities 3 star • Door to Door segregation
b. Gold (Anupam) c. Silver (Ujjwal) d. Bronze • Source Segregation
Garbage Free City for Star Rating - • Waste Processing
(Udit) e. Aspiring (Aarohi) % of cities in the State are certified • City Beautification
Star rating protocol for Ministry of Housing and Urban 2018 24 components with two groups into a. 7 Star b. 5 Star c. 3 Star d. 1 Star • Onsite wet waste processing
Garbage free cities Affairs ‘Important’ (1 & 3 Star – 16 components and
‘Aspirational’ indicators (5 & 7 Star – 24 Global Liveability Index 143 out of 173 Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai,
components) Ahmedabad, and Bangalore.
Ease of Living Index Bengaluru, Pune, Ahmedabad best Services, Finance, Policy,
Global Liveability Index WHO Published 173 cities covered 173 cities based on their living Stability-25 cities in EoLI 2020 (Million Plus Technology and Governance
Economic Intelligence Unit conditions and, in general, Healthcare-20 Category)
citizen living standards Culture and Environmnet-25
Education-10 Total 111 Cities
Infrastructure-20
Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) Gujarat worst performer rank 27th 115 indicators incorporate 16 out of
India out of 28th. 17 SDGs, with a qualitative
Ease of Living Index Under Smart City Mission 2018 Municipal Performance Index The EOL index evaluates development assessment on Goal 17, and cover 70
examined the sectoral outcomes across four pillars — quality of life, SDG targets
performance of 111 economic ability, sustainability, and citizens
municipalities. perception survey — covering 49 indicators
examined under 14 categories.
Sustainable Development Niti Aayog’s SDG India Index – SDG 12 Aspirant (0–49),
Goal (SDG) India Baseline Report 2018 Performer (50–64),
Responsible consumption and Front-Runner (65–99),
production Achiever (100).
Manek Chowk
Project Background
Manek Chowk is the very historic market place in the centre of the old
city. This market was chosen because of its transformational character,
this market transforms during three times a day during daytime it’s a
vegetable-fruit market and jewellery bazaar and in the night time its act
as a night food (Khani-pini bazaar).
ACTS, POLICIES, SCHEMES FOR SOLID WASTE GOVERNMENT ORGANISATIONAL
MANAGEMENT STRUCTURE FOR SOLID WASTE
MANAGEMENT
Phase I—public health and sanitation (1950–1980).
• Ministry of Food and Agriculture-offered soft loan to local bodies for promoting
1960 composting of urban solid waste
• Fourth Five year plan provide grant to state government for setting up MSW
1969- composting
74
• GOI introduced a modified scheme to revive urban waste composting facilities in
1974 cities with a population over 0.3 million.
• •GOI constituted first high power committee in fifth five year plan and committee
1975 covered eight area of waste management and made 76 recommendation.
Phase II—environmental safety
1986
• Environment (Protection) Act
• Hazardous Waste (Management & Handling) Rules, 1989
1989
• MSWM strategy paper by NEERI
1994
• High Power committee under the chairmanship of Prof. J.S Bajaj (Member,
Planning commission) was constituted Solid Waste Management is a state subject and it is the responsibility of the state
• Ministry of Health and family Welfare undertook national mission on environmental government to ensure that appropriate solid waste management practices are
introduced in all the cities and towns in the state.
health and sanitation
1995 However, SWM is a municipal function as under the 74th Constitutional
• Central Public health and Environmental Engineering organization (CPHEEO), Amendment, Disposal and management of Municipal Solid Waste is one of the 18
under the ministry of urban development and Poverty Alleviation drafted a policy functional domains of the Municipal Corporations and Nagar Panchayats. the
paper that detailed issues and funding requirements of SWM in India urban local bodies (ULB) that are directly responsible for it.
The ULBs are required to plan, design, operate, and maintain the SWM in their
• Bio-medical Waste (M&H) Rules respective cities/towns.
1998 • Supreme Court appointed Barman Committee
• Committee submitted the report in 1999
• •Ministry of Urban Development set up technology advisory group
1999 • •MoEF issued draft rule for Municipal Waste (Management and Handling)
RANKING’S GOVERNANCE YEAR OBJECTIVE INDICATORS
Phase III—MSWM and climate change (2000–onwards)
• Municipal Waste (Management and Handling ) Rules Ministry of Housing and Urban 2016 World’s largest urban sanitation and Open Defecation Free - % of cities in the state are
Swachh Survekshan Affairs cleanliness survey certified a. Water Plus b. ODF++ c. ODF+ d. ODF
• CPHEEO Manual on MSW
2000
• The Technology Advisory Group on Solid Waste Management 2005 Swachh Bharat Mission Urban Ministry of Housing and Urban 2nd October 2014 To make a garbage - free city, a city % of cities in the state falling in the new SS-2021
2005 Affairs completely free of garbage.” Awards category of - a. Platinum (Divya) b. Gold
• 12th Finance Commission (2005–2010)—Rs. 2,500 Cr for 423 Class I cities
(Anupam) c. Silver (Ujjwal) d. Bronze (Udit) e.
Aspiring (Aarohi)
2006 • National Environment Policy
Star rating protocol for Garbage Ministry of Housing and Urban 2018 24 components with two groups into ‘Important’ (1
• Strategy and Action Plan-Use of compost in cities free cities Affairs & 3 Star – 16 components and ‘Aspirational’
indicators (5 & 7 Star – 24 components)
2007 • 11th Five-Year Plan (2007–2012)—Rs. 2,210 Cr for MSWM
• National Urban Sanitation Policy (NUSP) Global Liveability Index WHO Published 173 cities covered 173 cities based on their living Stability-25
• Service Level Benchmarks (SLBs) in MSWM Economic Intelligence Unit conditions and, in general, citizen Healthcare-20
living standards Culture and Environmnet-25
2008 • Hazardous Waste (Management, Handling & Transboundary Movement)Rules
Education-10
• National Mission on Sustainable Habitat (NAPCC) Infrastructure-20
• The National Action Plan for Climate Change
• 13th Finance Commission (2010–2015)—Establishing standards for delivery of
2009 Ease of Living Index Under Smart City Mission 2018 Municipal Performance Index The EOL index evaluates development outcomes
• essential services
examined the sectoral performance across four pillars — quality of life, economic
• Plastic Waste (M&H) Rules of 111 municipalities. ability, sustainability, and citizens perception
• E-Waste (M&H) Rules survey — covering 49 indicators examined under
2011 14 categories.
• Draft Bio-medical Waste (M&H) Rules
• Swachh Bharat Mission
2014 Sustainable Development Goal Niti Aayog’s SDG India Index – SDG 12 Aspirant (0–49),
(SDG) India Baseline Report 2018 Performer (50–64), Geddam Renuka Sai
• Solid Waste Management Rules, Responsible consumption and Front-Runner (65–99),
2016 • production Achiever (100). GuruCharan Chhabra
Plastic Waste Management Rules,
• Bio-Medical Waste Management Rules, Matta Arunima Rao
• E-Waste Management Rules, Shreya Singhal
• Hazardous and Other Wastes (Management and Transboundary Movement) Rules,
• Construction and Demolition Waste Management Rules, 2016.
Best Case Studies
SOURCE TECHNOLOGICAL
SEGREGATION 3. Bangalore , Karnataka INNOVATION
1. Indore Bengaluru, the preeminent IT city of India, uses the power of
• Accountability
zeroes and ones to solve its myriad waste management woes.
The city is segregating its waste into six Bengaluru is the third most populous city and fifth most populous • Service assurance:
categories: agglomeration in India. It generates about 6,100 tonne of waste daily • Hassle-free garbage collection
1. Biodegradable, (452 g per person per day). Given the importance of the technology
2. Non-biodegradable (excluding
• Mess-free transfer:
sector to the city, the approach that Bengaluru has taken to deal with •
plastic), Discipline and rigidity
its mounting waste problem is also tech-based. Technological
3. Plastic, innovation has transformed the city's waste management system,
• Transport affirmation
4. Sanitary, which has become transparent, reliable and easy to monitor.
5. Domestic hazardous and
6. Electronic.
• Door-to-door collection of garbage
• the campaign ‘Do Bin Har Din’ (two • Information, Education and
bins everyday). Communication (IEC) is the key to
• IMC has engaged more than 800 self- behaviour change.
help groups (SHGs), comprising more • Participation of all, development
Framework than 8,000 women, to spread Takeaways for all
awareness • Indore focused on achieving 100
• Zero-waste tags are awarded to those per cent segregation at source, to • WASTE-WISE CITIES Best
markets and colonies which excel at break the chain. practices in municipal solid
waste management. • More than 8,000 women from waste management.
• IMC deploys one resource person marginalised communities have
THE JOURNEY OF WASTE SANITARY WASTE • Pune Municipal
with each garbage collection vehicle been given gainful employment.
IN SURAT CITY 4. PUNE MANAGEMENT
Corporation.
• Indore Municipal
The Red Dot Campaign in Pune shows the Corporation
light in handling sanitary waste, a significant • https://
MATERIAL feat in the waste management sector. www.suratmunicipal.gov.i
Pune Municipal Corporation (PMC) is divided n/CleanSurat/Home/
PROCESSING into five zones and 42 wards. It underwent a WasteMgtRulesAndActionP
lans
2. Surat process of delimitation on July 1, 2021, and
added 23 villages to its jurisdiction, making
it the largest Municipal Corporation of
Maharashtra. Reportedly, the city generates
BEST CASE STUDIES
nearly 2,258 tonnes of waste per day. It has AND SECTOR WISE
achieved 95 per cent segregation with the
help of self-help group SWaCH Seva
Sahakari Sanstha Maryadit, Pune
• Anudan Scheme: This scheme prioritised
community-level participation in solid waste
management. To maintain cleanliness,
payments at the rate of 60 paise and 65 paise
per sq. m respectively are made to residential
and non-residential societies.
Takeaways • centralised and then a decentralised process
of waste collection and disposal were
implemented
• Surat was ranked the second cleanest city in Geddam Renuka Sai
India by Swachh Survekshan 2020. It has also The Red Dot Campaign is one of the best GuruCharan Chhabra
received a 5-star garbage-free city tag IEC programme in India for making Matta Arunima Rao
• decentralised solid waste management, people aware about their responsibility
Shreya Singhal
Surat is divided into eight zones and 89 with regard to handling sanitary waste.
sanitary wards.
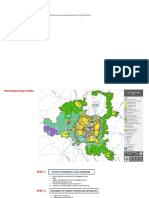
Landfill Sites – Comprehensive
Existing Treatment Plants and Dumping Sites Development Plan 2021
Type of Quantity Plant capacity Inferences:
Sno. Process technology Plant location
Waste (tpd) (TPD) • There is are Concentration of Three Processing plants Near to the Landfill Site- Gyaspur. Which are of Ahmedabad Enviro -
Material Recovery Nepra material Recovery Cand D waste -1000 TPD, Bharuch Enviro Infrastructure Ltd.- Windrow Composting- 300 TPD- Wet Type, Nepra material
1 Dry 100 100 Recovery Facility- Material Recovery Facility- 100 TPD , and Jindal Urban Waste Management Ltd.
Facility Facility
Material Recovery • The Old and the New Landfill sites are on the Southwest and South of AMC Boundary, as the city has south-west Monsoon
2 Dry 100 VASTRAL RTS 100
Facility wind Direction, The Prevailing wind is most often from the west for 7.0 months.
Material Recovery • In the Centre of the city Victoria Garden ; Waste to Compost of which Windrow Composting Processes wet type with 1 TPD
3 Dry 100 VATVA RTS 100
Facility capacity.
Material Recovery
4 Dry 100 SHAHWADI RTS 100
Facility
Material Recovery
5 Dry 100
Facility
SOLA RTS 100 Map of Plant location and Dumping sites
Material Recovery
6 Dry 100 KANKARIA RTS 100
Facility C and D WASTE
Material Recovery Windrow Composting The Ahmedabad Municipal Corporation (AMC) has now come up with a
7 Dry 100 Naroda 100
Facility novel solution to reduce large quantities of green waste dumped at
Material Recovery Facility
8 Wet 300 Windrow Composting Excel Industries 300 Dump Sites Pirana. The civic body will set up waste converter machines at
Lokmanya Tilak Garden (Victoria Garden) and Kankaria to produce
Bharuch Enviro
9 Wet 300 Windrow Composting 300 compost out of green waste. The two machines would be set up under a
Infrastructure Ltd.
Creative Eco Recycle pilot project based on public private partnership (PPP) model and the
10 Wet 400 Windrow Composting 400 civic body would bear the maintenance cost.
Port Pvt. Ltd.
11 Dry 1000 C and D WASTE Ahmedabad Enviro 1000
Victoria Garden ; Waste
12 Wet 1 Windrow Composting 1
to Compost
The machine to be set up at the garden will have the
Victoria Garden capacity to process two tons of waste at a time at
Inferences: a cost of Rs11 lakh. On the other hand, the
• The Red Highlighted are Not Spatially Found and the Highest Capacity machine to be set up at Kankaria will cost Rs4.5
KANKARIA lakh, which will have the capacity of a ton. The
Processing Plants.
RTS civic body plans to process 1,300 kg of waste a
• There is one C and D waste Processing Plant by Ahmedabad Enviro in the South
day, out of which the output will be 35 per cent.
West of the AMC. VASTRAL RTS “They intend to have 7-8 batches in a day, each
AMC Dump Yard processing 150 kg. Each batch will take 35 • Dnaindia
Total of 850 minutes to produce compost,” • Timesofindia.
• CEPT Portfolio M 2017
containers • Smart city- Ahmedabad
• Solid Waste
SOLA RTS
Management System in
Naranpura Dump Yard
Ahmedabad City – 2013
VATVA • Ahmedabad Municipal
RTS Corporation- Sanitary
Landfill Site
Ahmedabad Enviro Aslali Ambuja Dump • Google Earth
Bharuch Enviro Infrastructure Ltd.
Nepra material Recovery Facility
Jindal Urban Waste Management Ltd.
Existing Treatment
Plants and Dumping
Land Fill Site- Gyaspur Excel Industries Sites
• Capacity = 11.50 Lacs Metric Tones (i.e. 1.15
million tones), where daily off load 500 metric
Pirana Landfill Site KANKARIA RTS
tones of inert waste from waste processing
plants for coming 6 years.
• Total area used is 12.88 Hectares (32.8271 Kankaria Lake was constructed in 1451 by Sultan Qutb-
acres). ud-Din. The lake has a circumference of around 1.4 miles. A
• Total construction cost of this site is Rs 13 lakefront was developed in 2008 by spending Rs 36 Crore
Crores (i.e. Rs 130 million / i.e. $ 2.796 million which has many public attractions like Zoo, Toy Train,
1$=Rs 46.50). Kids City, Tethered Balloon Ride, Water Rides and Water
• Average size of shell = 262 m x 239 m = Park, Food Stalls and entertainment facilities.
62,618 Sq. M. (redesigned).
• Height of shell = 21.0 m – 8.0 m below G/L • Legacy Solid Waste is
(clear depth) + – 6.0 m above G/L in earthen being disposed &
bunds + – 7.0 m above earthen bunds in heap accumulated at Pirana
form HDPE Liner 1.5 mm thick. dumping site having total
• Air Space volume available for waste
area of about 84 acres for Geddam Renuka Sai
• accommodation = 13.45 Lacs CMT GuruCharan Chhabra
a long back.
• Density of compacted waste = 0.85 MT/CMT.
Matta Arunima Rao
• 65 acres of land is accumulated with heaps of garbage having 15-20 meter height at various Shreya Singhal
locations.
You might also like
- ECC ExampleDocument8 pagesECC Examplegrurocket100% (1)
- John DeereDocument568 pagesJohn DeereMMM-MMMNo ratings yet
- Municipal Solid Waste Management - IIIDocument412 pagesMunicipal Solid Waste Management - IIIsairam2103No ratings yet
- MSW - 2 - 2016 Municipal Solid Waste Management Rules - 2016 - Vol-2Document604 pagesMSW - 2 - 2016 Municipal Solid Waste Management Rules - 2016 - Vol-2nimm196267% (3)
- Municipal Solid Waste Management - IIDocument751 pagesMunicipal Solid Waste Management - IIsairam2103No ratings yet
- Solid Waste Management Associated With The Development of 3R Initiatives: Case Study in Major Urban Areas of VietnamDocument9 pagesSolid Waste Management Associated With The Development of 3R Initiatives: Case Study in Major Urban Areas of VietnamMuhammad FahriNo ratings yet
- No Copyright ProbablyDocument12 pagesNo Copyright ProbablyMukul AnandNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Waste Management Strategy For ArRiyadh City PDFDocument40 pagesComprehensive Waste Management Strategy For ArRiyadh City PDFfedericoNo ratings yet
- Week 3Document74 pagesWeek 3Manvi YadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Jagna CorrectedDocument14 pagesChapter 6 - Jagna Correctedmichael harridNo ratings yet
- Country Presentation On Nepal - Leadership Capacity Building Program On Sustainable and Improved Sanitation Strategies For PolicymakersDocument18 pagesCountry Presentation On Nepal - Leadership Capacity Building Program On Sustainable and Improved Sanitation Strategies For PolicymakersADBI EventsNo ratings yet
- AIP Activity 2019 - Waste and Pollution Management DivisionDocument3 pagesAIP Activity 2019 - Waste and Pollution Management DivisionDebah Diaz Baclayon WaycoNo ratings yet
- Waste Management: Xudong Chen, Yong Geng, Tsuyoshi FujitaDocument9 pagesWaste Management: Xudong Chen, Yong Geng, Tsuyoshi FujitaluisNo ratings yet
- City Government of Makati MS Report No. 2002 02H Executive SummaryDocument5 pagesCity Government of Makati MS Report No. 2002 02H Executive SummaryJessica BonifacioNo ratings yet
- Solidwaste Management Plan: Legal RequirementsDocument17 pagesSolidwaste Management Plan: Legal RequirementsnathNo ratings yet
- Plan FormulationDocument34 pagesPlan FormulationReena RajdeepNo ratings yet
- Sanjeevi 2015Document14 pagesSanjeevi 2015Bimael Quispe ReymundoNo ratings yet
- Name of Report:: Guidelines On Environmental Management of C&D Waste Management in IndiaDocument39 pagesName of Report:: Guidelines On Environmental Management of C&D Waste Management in IndiaSarangNo ratings yet
- Comments Env MGMT 07.03.17 PDFDocument39 pagesComments Env MGMT 07.03.17 PDFhimanshu vermaNo ratings yet
- Priortization of Urban Sanitaiton in Urban Policies and LegislationDocument3 pagesPriortization of Urban Sanitaiton in Urban Policies and LegislationYogendra ChitrakarNo ratings yet
- Overview of WASH AssessmentDocument12 pagesOverview of WASH Assessmentteodoro,jr. quintanaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Waste Management in New DevelopmentsDocument62 pagesGuidelines For Waste Management in New DevelopmentsrtertertNo ratings yet
- DSWD Strategy 2028: SerbisyoDocument77 pagesDSWD Strategy 2028: SerbisyoAbe riveraNo ratings yet
- Week3 - LEGISLATIVE TRENDS AND IMPACTS 1Document33 pagesWeek3 - LEGISLATIVE TRENDS AND IMPACTS 1Alma AinaNo ratings yet
- Legislative Trends and Impacts: Marfiah Ab - Wahid - PHDDocument28 pagesLegislative Trends and Impacts: Marfiah Ab - Wahid - PHDamylaNo ratings yet
- Malabon SWM Ms2002-02g EsDocument6 pagesMalabon SWM Ms2002-02g EsrahmaNo ratings yet
- Solid Waste Management in India 2018Document28 pagesSolid Waste Management in India 2018tsrinivasan5083No ratings yet
- Aom 002 SWMDocument7 pagesAom 002 SWMJonson PalmaresNo ratings yet
- SBM Guideline PDFDocument68 pagesSBM Guideline PDFKekhrie LhousaNo ratings yet
- Day3 Topic1 JAIF Presentation LorenzoDocument32 pagesDay3 Topic1 JAIF Presentation Lorenzogarthraymundo123No ratings yet
- Environmental Challenges: Ishfaq Showket Mir, Puneet Pal Singh Cheema, Sukhwinder Pal SinghDocument11 pagesEnvironmental Challenges: Ishfaq Showket Mir, Puneet Pal Singh Cheema, Sukhwinder Pal SinghNuriyahNo ratings yet
- Output-Based Aid For Municipal Solid Waste Management in NepalDocument2 pagesOutput-Based Aid For Municipal Solid Waste Management in NepaljakariaNo ratings yet
- Abu Dhabi City Municipality: Case StudyDocument6 pagesAbu Dhabi City Municipality: Case StudySaber AbdelaalNo ratings yet
- Organic Waste ManagementDocument70 pagesOrganic Waste ManagementAlejandro MagnoNo ratings yet
- Developing A Monitoring and Evaluation Framework To Integrate and Formalize The Informal Waste and Recycling Sector: The Case of The Philippine National Framework PlanDocument14 pagesDeveloping A Monitoring and Evaluation Framework To Integrate and Formalize The Informal Waste and Recycling Sector: The Case of The Philippine National Framework PlanJohn Gilbert GopezNo ratings yet
- Annotated Outline 10yr PlanDocument13 pagesAnnotated Outline 10yr PlanJerwinson InfantaNo ratings yet
- Strategy and Framework For Municipal Solid Waste ManagementDocument45 pagesStrategy and Framework For Municipal Solid Waste ManagementVictor NwachukwuNo ratings yet
- Road Traffic Noise Management in Queensland Through The Element Leadership ProcessDocument9 pagesRoad Traffic Noise Management in Queensland Through The Element Leadership ProcessMohammed Zuber InamdarNo ratings yet
- Hotel & Branded Apartments - TDDocument16 pagesHotel & Branded Apartments - TDabdulazeez88No ratings yet
- PnacyerDocument22 pagesPnacyerDEBANG EDCES R.No ratings yet
- Omnicane IntegratedReport 2016Document106 pagesOmnicane IntegratedReport 2016azsigncNo ratings yet
- Country Presentation On Bangladesh - Leadership Capacity Building Program On Sustainable and Improved Sanitation Strategies For PolicymakersDocument20 pagesCountry Presentation On Bangladesh - Leadership Capacity Building Program On Sustainable and Improved Sanitation Strategies For PolicymakersADBI EventsNo ratings yet
- Overview of JICA's Initiatives in Solid Waste Management Sector in BangladeshDocument14 pagesOverview of JICA's Initiatives in Solid Waste Management Sector in BangladeshAzwat007No ratings yet
- Life Cycle Assessment of Potential Municipal Solid Waste Management Strategies For Mumbai, IndiaDocument13 pagesLife Cycle Assessment of Potential Municipal Solid Waste Management Strategies For Mumbai, IndiaAnjuli MangerNo ratings yet
- WAC News June 2005Document4 pagesWAC News June 2005UN-HABITAT NepalNo ratings yet
- Webinar FTI-UPNVY - 28 Oct 2022, KHW - FinalDocument18 pagesWebinar FTI-UPNVY - 28 Oct 2022, KHW - FinalMuhammad FakhrizalNo ratings yet
- Urban Sanitation: VBS-CPR: A Joint ProjectDocument8 pagesUrban Sanitation: VBS-CPR: A Joint ProjectAbhinav KumarNo ratings yet
- The National Action Plan For Municipal Solid Waste ManagementDocument42 pagesThe National Action Plan For Municipal Solid Waste ManagementSharang PatelNo ratings yet
- SuniDocument2 pagesSuniSunil GuledguddNo ratings yet
- SWM On Dumping Ground jp8EB6dLFJDocument5 pagesSWM On Dumping Ground jp8EB6dLFJKavya ModiNo ratings yet
- SNAM 2020 Annual ReportDocument412 pagesSNAM 2020 Annual Reportjli165No ratings yet
- 02 PDFDocument202 pages02 PDFMai PavillionNo ratings yet
- Part 1Document96 pagesPart 1AUTOGREENNo ratings yet
- MSW - 1 - 2016 Munisicpal Solid Waste Rules-2016 - Vol IDocument96 pagesMSW - 1 - 2016 Munisicpal Solid Waste Rules-2016 - Vol Inimm1962No ratings yet
- Odisha Booklet Final PDFDocument8 pagesOdisha Booklet Final PDFBhushanPatilNo ratings yet
- JRA - SudafricaDocument32 pagesJRA - SudafricasilfrontierNo ratings yet
- Full Report SAPPDocument88 pagesFull Report SAPPIvan Amaral ManhiqueNo ratings yet
- Eco Task Force: Integrated Waste Management Subcommittee Annual ReportDocument9 pagesEco Task Force: Integrated Waste Management Subcommittee Annual ReportsustainableunhNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh FSM Review PDFDocument20 pagesBangladesh FSM Review PDFSandeepan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Solid Waste Management Sector in Pakistan: A Reform Road Map for Policy MakersFrom EverandSolid Waste Management Sector in Pakistan: A Reform Road Map for Policy MakersNo ratings yet
- Compendium of Best Practices in Road Asset ManagementFrom EverandCompendium of Best Practices in Road Asset ManagementNo ratings yet
- 05052017NPXTZXJEAnnexure DocumentofEIADocument362 pages05052017NPXTZXJEAnnexure DocumentofEIAGurucharan ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Draft Documents TTZAuthority Agra OnDocument240 pagesDraft Documents TTZAuthority Agra OnGurucharan ChhabraNo ratings yet
- VRINDAVAN ECO-CITY IN MAKING: Working Together For Sustainable DevelopmentDocument9 pagesVRINDAVAN ECO-CITY IN MAKING: Working Together For Sustainable DevelopmentGurucharan ChhabraNo ratings yet
- 0914 Part B DCHB MathuraDocument310 pages0914 Part B DCHB MathuraGurucharan ChhabraNo ratings yet
- 0914 Part A DCHB MathuraDocument380 pages0914 Part A DCHB MathuraGurucharan ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Sheet DistributionDocument2 pagesSheet DistributionGurucharan ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document9 pagesPresentation 1Gurucharan ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Existing Treatment Plants and Dumping SitesDocument2 pagesExisting Treatment Plants and Dumping SitesGurucharan ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Studio: 26 August 2022: Review 1: Infrastructure Plan Part 1Document35 pagesStudio: 26 August 2022: Review 1: Infrastructure Plan Part 1Gurucharan ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Terra CycleDocument7 pagesTerra CycleAngela de Mesa100% (1)
- TM1553 John Deere 4475, 5575, 6675, 7775 Skid Steer Loaders Technical ManualDocument9 pagesTM1553 John Deere 4475, 5575, 6675, 7775 Skid Steer Loaders Technical ManualtteelsarsNo ratings yet
- NSWMC Framework PDFDocument51 pagesNSWMC Framework PDFJefferson LimjucoNo ratings yet
- Rubric OutlineDocument3 pagesRubric Outlineapi-454215451No ratings yet
- Green HighwaysDocument27 pagesGreen HighwaysAnjali chilakalaNo ratings yet
- 0001 Site Road Report Web PDFDocument53 pages0001 Site Road Report Web PDFAri CleciusNo ratings yet
- Project On Green ChemistryDocument39 pagesProject On Green ChemistryHardik Shukla80% (5)
- Waste-to-Energy in The PhilippinesDocument54 pagesWaste-to-Energy in The PhilippinesEleazar Ante TalabongNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact of Tourism (2021)Document19 pagesEnvironmental Impact of Tourism (2021)Super PBNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Environmental Laws and PolicieDocument24 pagesPart 1 Environmental Laws and PolicieNoel Cagigas FelongcoNo ratings yet
- 2007 scWO PDFDocument10 pages2007 scWO PDFRodolfo Angulo OlaisNo ratings yet
- Hs Qemi Qemifloc VH 1007Document3 pagesHs Qemi Qemifloc VH 1007Wilmer CarrascoNo ratings yet
- Corporate Social Responsibility Governance, Outcomes, and FinancialDocument10 pagesCorporate Social Responsibility Governance, Outcomes, and FinancialnasirNo ratings yet
- 4th Quarter-HELE 4 TDDocument11 pages4th Quarter-HELE 4 TDChrislyn Gabucan GomonitNo ratings yet
- Doing Waste Tire Pyrolysis PlantDocument4 pagesDoing Waste Tire Pyrolysis PlantpyrolysisoilNo ratings yet
- K-G-Y ResearchDocument39 pagesK-G-Y ResearchYewuhalashet FisshaNo ratings yet
- Emergency Response Plan: Yara Dallol Potash Project, Danakil Depression, EthiopiaDocument26 pagesEmergency Response Plan: Yara Dallol Potash Project, Danakil Depression, EthiopiaNaba majeadNo ratings yet
- Solid Waste Management PNGDocument4 pagesSolid Waste Management PNGMichael BeroberoNo ratings yet
- FDM Bref 0806Document682 pagesFDM Bref 0806Ahmed WafiqNo ratings yet
- Proposal File On Our ProjectDocument66 pagesProposal File On Our ProjectAdmin OperationsNo ratings yet
- Environmental Pollution 2Document23 pagesEnvironmental Pollution 2Dulon ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Yellow BookDocument362 pagesYellow BookMonica Genadio100% (1)
- 4.0 EMS ObjectivesDocument6 pages4.0 EMS Objectiveslpamgt_674780425No ratings yet
- Smart Digital Dustbin: Dustbin (SDD) - Keywords-Incinerated Solid WastesDocument6 pagesSmart Digital Dustbin: Dustbin (SDD) - Keywords-Incinerated Solid WastesUma TamilNo ratings yet
- Ethical ConsumerismDocument17 pagesEthical ConsumerismDavid SelvaNo ratings yet
- Quiz in Science 5Document6 pagesQuiz in Science 5Abbie Hyacinth GetalagaNo ratings yet
- Technical Report Draft 1Document15 pagesTechnical Report Draft 1api-631662367No ratings yet
- Wylie A3Document2 pagesWylie A3Wylie A. BaguingNo ratings yet