Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Female Reprod. System
Uploaded by
reza fastabik0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views33 pagesThe document provides an overview of the anatomy of the female reproductive system. It describes the internal organs which include the ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, and vagina. It then discusses each of these organs in more detail, focusing on their structure, location within the body, and key functions. It also briefly outlines the external genitalia. The purpose is to educate on the basic anatomy of the female reproductive system.
Original Description:
Original Title
female reprod. system
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides an overview of the anatomy of the female reproductive system. It describes the internal organs which include the ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, and vagina. It then discusses each of these organs in more detail, focusing on their structure, location within the body, and key functions. It also briefly outlines the external genitalia. The purpose is to educate on the basic anatomy of the female reproductive system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views33 pagesFemale Reprod. System
Uploaded by
reza fastabikThe document provides an overview of the anatomy of the female reproductive system. It describes the internal organs which include the ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, and vagina. It then discusses each of these organs in more detail, focusing on their structure, location within the body, and key functions. It also briefly outlines the external genitalia. The purpose is to educate on the basic anatomy of the female reproductive system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 33
ANATOMY OF
THE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
M. Mansyur Romi
Dwi Cahyani Ratna Sari
Department of Anatomy, Embriology & Antropology
Faculty of Medicine Gadjah Mada University
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
Consists of :
The internal genitalia
Within the lesser pelvis
The external genitalia
In front of and below the pubic arch
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
THE INTERNAL ORGANS
Ovaries
Uterine tubes
Uterus
Vagina
OVARIES
Paired
Homologous with testis
Attached to broad ligament by
mesovarium
Anchored to uterus by ovarian ligament
Attached to pelvic wall by suspensory
ligament
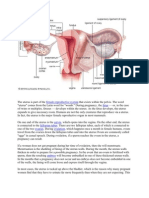
Anterior view of the female internal genital organs.
Note anastomosis between the ovarian and uterine
arteries and between the vaginal branch of uterine
artery and vaginal artery. These communication
occur between the layers of the broad ligament
OVARIES
Ovarian follicles
Primordial follicles
Primary follicle
Secondary (antral) follicle
Tertiary follicle
Atretic follicles
OVARIES
The numbers of human oocyte
At 5 months gestation 7 millions
At birth 1 million
Puberty 40.000
Of the 40.000 oocytes remaining at
puberty only about 400 undergo
ovulation during the reproductive years
UTERINE TUBES
Uterine (Fallopian) Tubes
10 - 12.5 cm long,
Is divisible into 4 parts, from lateral to
medial :
Fimbriated end (infundibulum) (3mm)
ampulla (widest, 1cm, fertilization)
Isthmus (narrow lumen 0,1- 0,5 mm)
intrauterine or intramural portion
CLINICAL ASPECTS OF
THE UTERINE TUBES
Endoscopy
Hysteroscopy
Salpingoscopy
Salpingography & hysterosalpingography
Tubal inflamation
Pyosalphinx
Hydrosalphinx
Tubal pregnancy
UTERUS
Hallow, thick-walled & muscular organ
In the lesser pelvic
Between urinary bladder & rectum
Size in adult non-pregnant
7,5 cm long
5,5 cm in breadth at its widest
2,5 cm thick
DIVISION OF THE UTERUS
Uterine body (corpus uteri)
Uterine cavity
Cervix (cervix uteri)
Cervical canal
UTERUS
UTERINE POSITION
Anteversion : between axes of vagina
and cervix
Anteflexion : between the cervix and
corpus uteri
UTERINE LIGAMENTS
Broad ligament:
attaches to either side of pelvic cavity
Uterosacral ligament:
connect to sacrum
Cardinal (lateral) ligaments:
between pelvic wall and cervix – vagina
Round ligaments:
extends to external genital
VAGINA
Female copulatory organ
Fibromuscular tube lined by non-keratinized
stratified epithelium
vestibule (cleft between the labia minora) to
uterus
7.5 - 10 cm long
Folding as rugae
Fornices:
Annular recess between the cervix and
vagina
posterior fornix: the deepest
THE EXTERNAL ORGANS
Mons pubis
Labia majora pudendi
Labia minora pudendi
vestibule
Clitoris
THE EXTERNAL ORGANS
vaginal orifice (introitus)
Hymen vaginae
external urethral orifice (urinary meatus)
Bulbs of the vestibule
Greater vestibular glands (glands of
bartholin)
You might also like
- 40 TS1M1 Sex and Sexuality-Vol. 2 (Praeger 2006)Document289 pages40 TS1M1 Sex and Sexuality-Vol. 2 (Praeger 2006)bfdscaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Female ReproductionDocument108 pagesAnatomy of The Female ReproductionDaisy HamdaliNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System UpdatedDocument84 pagesFemale Reproductive System UpdatedAtie IzzatiNo ratings yet
- DAMS CRS - Obstetrics & Gynaecology (DAMS Comprehensive Review Series) - DAMSDocument46 pagesDAMS CRS - Obstetrics & Gynaecology (DAMS Comprehensive Review Series) - DAMSAbhisek ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemSyed Isamil100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Reproductive SystemDocument93 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Reproductive SystemMelizza Fajardo BañanoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec 22 (FGOs)Document49 pagesAnatomy Lec 22 (FGOs)Humraz100% (1)
- 4. week ovulation, fertilization, implantation (١)Document41 pages4. week ovulation, fertilization, implantation (١)Maisy JohnNo ratings yet
- OB - TransesDocument112 pagesOB - TransesAldwin BagtasNo ratings yet
- Gynecological Disorders1Document308 pagesGynecological Disorders1Ayoola BolajiNo ratings yet
- Fibroids ADocument242 pagesFibroids Anautilus81100% (1)
- Female Reproductive System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesFemale Reproductive System Anatomy and PhysiologyIkea Balhon100% (3)
- Project Ease Biology Module 13Document30 pagesProject Ease Biology Module 13Kebb Patrick Enar75% (4)
- Manuscriptm1 203 Grp26 12gDocument61 pagesManuscriptm1 203 Grp26 12gRuthangela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Fallopian Tube & OvaryDocument89 pagesAnatomy of Fallopian Tube & OvaryAsma AijazNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument43 pagesReproductive SystemDoc Zay VillafuerteNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument75 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemProf Lina Ramli67% (3)
- Goboy, Louise Germaine U. BSN 210 Self-Assessment QuestionsDocument2 pagesGoboy, Louise Germaine U. BSN 210 Self-Assessment QuestionsLouise Germaine100% (1)
- Normal Anatomy and Physiology of Female PelvisDocument58 pagesNormal Anatomy and Physiology of Female PelvisVic RobovskiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Reproductive SystemDocument91 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Reproductive SystemApril BenaventeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument14 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyIvee BustaNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb: Organization FunctionDocument33 pagesUpper Limb: Organization FunctionAhmed Nabiel El-Jaliel100% (1)
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension Case StudyDocument77 pagesPregnancy Induced Hypertension Case StudyJoe Anne Maniulit, MSN, RN84% (49)
- Anatomy, Embryology and Uterine AnomailesDocument45 pagesAnatomy, Embryology and Uterine AnomailesMesk BanatNo ratings yet
- Operative Review TAHBSODocument22 pagesOperative Review TAHBSOGinger Enireht HTaibNo ratings yet
- Licenta Finala DamlaDocument49 pagesLicenta Finala DamlaDamla Kaykusuz100% (3)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocument67 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive Systemannu panchalNo ratings yet
- 4NUR-8.1 Case 4 - Gynecologic Nursing (Written Report)Document30 pages4NUR-8.1 Case 4 - Gynecologic Nursing (Written Report)lhedavenNo ratings yet
- GynaDocument22 pagesGynaIGA ABRAHAMNo ratings yet
- Presented By, P.Jeyanthi, M.SC (N) I Year Apollo CONDocument67 pagesPresented By, P.Jeyanthi, M.SC (N) I Year Apollo CONPaul AndersonNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument6 pagesBIOLOGYCLANSIE BUXTON CHIKUMBENo ratings yet
- ANATOMIDocument43 pagesANATOMIWidayuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Female Reproductive SystemDocument31 pagesAnatomy of Female Reproductive Systemhiba jawedNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyKristine Alejandro100% (1)
- ADETUTU Seminar in Fallopian TubeDocument17 pagesADETUTU Seminar in Fallopian TubeBamgbose OpeyemiNo ratings yet
- Maternal & Child Nursing ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY SECTION 1Document102 pagesMaternal & Child Nursing ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY SECTION 1emma rose lutella100% (1)
- 41 Female Reproductive AnatomyDocument14 pages41 Female Reproductive Anatomyruaa firasNo ratings yet
- Female RSsystem 2Document90 pagesFemale RSsystem 2icliftonguytonNo ratings yet
- Curs 2 - 3 Histoanatomy of COW Ovaries and Uterus FW Si CLDocument93 pagesCurs 2 - 3 Histoanatomy of COW Ovaries and Uterus FW Si CLB.L.C.SNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Female GenitaliaDocument70 pagesAnatomy Female GenitaliaHeni KurniawatiNo ratings yet
- 3 - Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis - Female Internal Genitals - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument10 pages3 - Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis - Female Internal Genitals - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfmimatechcontabilidadNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology CorrectedDocument15 pagesAnatomy and Physiology CorrectedSANCHAYEETANo ratings yet
- REWIEW OF FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM NewDocument49 pagesREWIEW OF FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM NewnamitaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Female Reproductive Organs: Dr.M.Mahalakshmi Assistant Professor Government Chengalpattu Medical CollegeDocument20 pagesAnatomy of Female Reproductive Organs: Dr.M.Mahalakshmi Assistant Professor Government Chengalpattu Medical Collegepranu6789No ratings yet
- Gynecological Disorders.Document282 pagesGynecological Disorders.Salman KhanNo ratings yet
- Session 4 Lecture 1 Part 1Document25 pagesSession 4 Lecture 1 Part 1avin xsroNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Female Reproductive SystemDocument63 pagesAnatomy of The Female Reproductive SystemMahmoud Abu Al AmrainNo ratings yet
- Female RSystemDocument71 pagesFemale RSystemicliftonguytonNo ratings yet
- Female Pelvic VisceraDocument73 pagesFemale Pelvic VisceraAnania EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- DR Mohtaseb Slide 4 EmbryologyDocument40 pagesDR Mohtaseb Slide 4 Embryologyapi-249972919No ratings yet
- Presentation On: Female Reproductive SystemDocument54 pagesPresentation On: Female Reproductive SystemLetsShop BbsrNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Embryology of The Female Genital Tract & Anatomy of Female Pelvis & Fetal SkullDocument11 pagesLecture 2 - Embryology of The Female Genital Tract & Anatomy of Female Pelvis & Fetal SkullBrandonRyanF.MosidinNo ratings yet
- Uterus AnatomyDocument7 pagesUterus AnatomyJoseph RadislaoNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System (Yuni)Document36 pagesFemale Reproductive System (Yuni)Ayi Abdul BasithNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Repeat LtcsDocument9 pagesCase Study - Repeat LtcsAnna SantosNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Female Reproductive SystemDocument62 pagesAnatomy of The Female Reproductive SystemBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 3Document12 pagesAssignment # 3usaeed00000No ratings yet
- Urogenital SystemDocument33 pagesUrogenital SystemimaninjaloenkosiniNo ratings yet
- Student Name: ALI HASSAN RAZA STUDENT I D: 2018304027Document6 pagesStudent Name: ALI HASSAN RAZA STUDENT I D: 2018304027Sayed AsifNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Functions of The UterusDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Functions of The UterusAnthony jesusNo ratings yet
- Gynecological Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument39 pagesGynecological Anatomy & Physiologynursereview100% (3)
- Caesarean Section: Advanced Maternal and Child Health Nursing NSC504Document60 pagesCaesarean Section: Advanced Maternal and Child Health Nursing NSC504tsega tilahunNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Women HealthDocument47 pagesIntroduction To Women HealthDarren LimNo ratings yet
- UterusDocument34 pagesUterushammad992No ratings yet
- Mayo MaDocument23 pagesMayo Madextroid12No ratings yet
- LECT 2anatomy and Physiology of Pregnancy 2Document45 pagesLECT 2anatomy and Physiology of Pregnancy 2Umer RafiqNo ratings yet
- Physics: PW - AITS - NT-20Document14 pagesPhysics: PW - AITS - NT-20Shivanshu ShivamNo ratings yet
- Gametogenesis and Fertilization: The Circle of SexDocument85 pagesGametogenesis and Fertilization: The Circle of SexAdityanair RA1711009010128No ratings yet
- Review 2007Document96 pagesReview 2007Japheth CanalesNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of ECTOPIC PREGNANCYDocument2 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY of ECTOPIC PREGNANCYrye100% (2)
- Camca Prelim Reviewer 2Document11 pagesCamca Prelim Reviewer 2Danna MedranaNo ratings yet
- TWINKL Knowledge OrganiserDocument2 pagesTWINKL Knowledge OrganiserDearbhla HubbardNo ratings yet
- Case-Presentation Final Nagd Ni ShetDocument7 pagesCase-Presentation Final Nagd Ni ShetMary Beth AbelidoNo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument13 pagesInstructional Planning Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatAlyssa AlegadoNo ratings yet
- Current Practices and Controversies in Assisted ReproductionDocument404 pagesCurrent Practices and Controversies in Assisted Reproductionalessia_chiriu8567No ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science ReviewerDocument25 pagesGrade 10 Science ReviewertinaNo ratings yet
- Genbio2 q2 Mod1.1 Reproduction-And-DevelopmentDocument9 pagesGenbio2 q2 Mod1.1 Reproduction-And-DevelopmentHazel AbitriaNo ratings yet
- HSG PresentationDocument18 pagesHSG Presentationashikin92No ratings yet
- Lab Report 4 SBCDocument27 pagesLab Report 4 SBCNisha Lauren Vishvanath100% (1)
- Cot First QuarterDocument15 pagesCot First QuarterRowena Torres DahiligNo ratings yet
- DC ManuscriptDocument13 pagesDC ManuscriptKaye Honeylee ManibogNo ratings yet
- The Finale: Multiple Choice: Anatomy & Physiology Coloring WorkbookDocument3 pagesThe Finale: Multiple Choice: Anatomy & Physiology Coloring WorkbookJonash Morales0% (1)
- Case Study #1: AbortionDocument42 pagesCase Study #1: AbortionJhoanne DelloroNo ratings yet
- Hysterosalpingography A Re - Emerging Study With CDocument7 pagesHysterosalpingography A Re - Emerging Study With CTuyul Yelsi 1No ratings yet
- Medical Terminology Reproductive SystemDocument130 pagesMedical Terminology Reproductive SystemsheshNo ratings yet
- Sejawat - Idn - Sistem Gastrointestinal, Urinaria, ReproduksiDocument91 pagesSejawat - Idn - Sistem Gastrointestinal, Urinaria, ReproduksiAinaya Miftia Asy'aristaNo ratings yet
- How Do Organism ReproduceDocument40 pagesHow Do Organism ReproduceNakshatra PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Female CattleDocument16 pagesAnatomy of Female CattleSaid AliNo ratings yet
- AJCC 8thed TNMDocument34 pagesAJCC 8thed TNMPrarthna PatelNo ratings yet