Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Operations Research
Operations Research
Uploaded by
Madhu yp0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views7 pagesThe document discusses four different solution methods for assignment problems: the enumeration method, simplex method, transportation method, and Hungarian method. It provides details on each method, including that the enumeration method lists all possible assignments and chooses the minimum cost option, while the Hungarian method reduces the cost matrix to have at least one zero in each row and column to find an optimal assignment. The transportation method can also be used but may result in degenerate solutions without adding dummy variables.
Original Description:
Original Title
Operations research
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses four different solution methods for assignment problems: the enumeration method, simplex method, transportation method, and Hungarian method. It provides details on each method, including that the enumeration method lists all possible assignments and chooses the minimum cost option, while the Hungarian method reduces the cost matrix to have at least one zero in each row and column to find an optimal assignment. The transportation method can also be used but may result in degenerate solutions without adding dummy variables.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views7 pagesOperations Research
Operations Research
Uploaded by
Madhu ypThe document discusses four different solution methods for assignment problems: the enumeration method, simplex method, transportation method, and Hungarian method. It provides details on each method, including that the enumeration method lists all possible assignments and chooses the minimum cost option, while the Hungarian method reduces the cost matrix to have at least one zero in each row and column to find an optimal assignment. The transportation method can also be used but may result in degenerate solutions without adding dummy variables.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
Operations research
course code: 20MBA24
Topic: solution methods of a
assignment problem
Faculty name : Hamsalekha
Designation : assistant professor
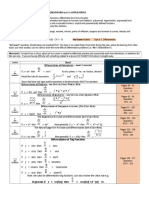
SOLUTION METHODS OF ASSIGNMENT
PROBLEM
An assignment problem can be solved by any of the following methods
• Enumeration method
• Simplex method
• Transportation method
• Hungarian method
1. Enumeration Method : In this method, a list of all possible
assignments among the given resources (men,
machines, etc.) and activities (jobs, sales areas, etc.) is prepared. Then
an assignment that involves the
minimum cost (or maximum profit), time or distance is selected. If two
or more assignments have the same
minimum cost (or maximum profit), time or distance, the problem has
multiple optimal solutions.
2. Simplex Method : Since each assignment problem
can be formulated as a 0 or 1 integer linear
programming problem, such a problem can also be
solved by the simplex method. The general
mathematical
model of the assignment problem involves n × n
decision variables and n + n or 2n equalities. Thus,
for any
assignment problem that involves 5 workers/jobs, there
will be 25 decision variables and 10 equalities.
Solving such an assignment problem manually is
difficult.
3. Transportation Method : Since an assignment problem
is a special case of the transportation problem, it
can also be solved by using MODI method. However,
every basic feasible solution of a general assignment
problem that has a square matrix of order n should have m
+ n – 1 = n + n – l = 2n – 1 assignments. But due to
the special structure of this problem, none of the solutions
can have more than n assignments. Consequently,
solutions will be degenerate. To remove degeneracy, (n – 1)
number of dummy allocations (deltas or epsilons)
will be required in order to proceed with MODI method.
Thus, the problem of degeneracy at each solution
makes the procedure computationally inefficient for
solving an assignment problem.
4. Hungarian Method : The Hungarian method
(developed by Hungarian mathematician D. Konig) is
an
efficient method of finding the optimal solution of an
assignment problem without making a direct
comparison of every solution. The method works on the
principle of reducing the given cost matrix to a
matrix of opportunity costs. Opportunity costs show the
relative penalties associated with assigning a resource
to an activity. Hungarian method reduces the cost matrix
to the extent of having at least one zero in each row
and column so as to make optimal assignments.
SL number Title of the Name of Publisher Edition and
book author name year
1 Operation and H.A Taha Pearson 2012
research publication
introduction
2 Operation J.K sharma M C millian 2014
research publications
Thank you
You might also like
- Project On Linear Programming ProblemsDocument29 pagesProject On Linear Programming ProblemsVinod Bhaskar67% (129)
- l3 DifferentiationDocument4 pagesl3 Differentiationapi-287224366100% (2)
- Assignment ProblemDocument20 pagesAssignment Problemmanojpatel5187% (15)
- Assignment ProblemDocument29 pagesAssignment Problemvenky364No ratings yet
- New Proposed Method For Solving Assignment Problem and Comparative Study With The Existing MethodsDocument5 pagesNew Proposed Method For Solving Assignment Problem and Comparative Study With The Existing MethodsEsther SeguraNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Assignment Problems: StructureDocument34 pagesUnit 5 Assignment Problems: StructureAnkit KashyapNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Methodology of Operations ResearchDocument5 pagesDiscuss The Methodology of Operations Researchankitoye0% (1)
- CA02CA3103 RMTAssignment ProblemDocument11 pagesCA02CA3103 RMTAssignment ProblemErnest SendezaNo ratings yet
- Mba or Unit-Iii NotesDocument12 pagesMba or Unit-Iii NotesAmruta PeriNo ratings yet
- Assignment ProblemDocument7 pagesAssignment ProblemkesmatNo ratings yet
- Or Theory NotesDocument11 pagesOr Theory Noteshsrinivas_7No ratings yet
- Explain The Types of Operations Research Models. Briefly Explain The Phases of Operations Research. Answer Operations ResearchDocument13 pagesExplain The Types of Operations Research Models. Briefly Explain The Phases of Operations Research. Answer Operations Researchnivinjohn1No ratings yet
- The Multiobjective Multidimensional Knapsack Problem: A Survey and A New ApproachDocument24 pagesThe Multiobjective Multidimensional Knapsack Problem: A Survey and A New ApproachVigneshwar NatesanNo ratings yet
- Assignment ProblemsDocument10 pagesAssignment ProblemsBalsam Qusay MohammedNo ratings yet
- Define Operations Research: Applications of Management ScienceDocument5 pagesDefine Operations Research: Applications of Management ScienceShinjiNo ratings yet
- SEM 2 MB0032 1 Operations ResearchDocument13 pagesSEM 2 MB0032 1 Operations Researchalokmitra_upNo ratings yet
- Saurabh Upadhyay Ashish Singh Dhruv Patil Irfan BengaliDocument26 pagesSaurabh Upadhyay Ashish Singh Dhruv Patil Irfan BengaliLion KenanNo ratings yet
- Branch and Bound Algorithms - Principles and ExamplesDocument30 pagesBranch and Bound Algorithms - Principles and Examplessaeed-21No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Deriving Solutions From A Linedeear Optimization Model PDFDocument40 pagesChapter 3 - Deriving Solutions From A Linedeear Optimization Model PDFTanmay SharmaNo ratings yet
- University School of Business (MBA) : SUBJECT NAME: Decision Science-II Subject Code: 20bat652Document9 pagesUniversity School of Business (MBA) : SUBJECT NAME: Decision Science-II Subject Code: 20bat652najla fedawiNo ratings yet
- Velammal Engineering College Department of Cse Design and Analysis of Algorithm Unit V Notes Decision Trees (2 Marks)Document29 pagesVelammal Engineering College Department of Cse Design and Analysis of Algorithm Unit V Notes Decision Trees (2 Marks)Aravindhan RNo ratings yet
- Explain The Difference Among Decision ProblemDocument5 pagesExplain The Difference Among Decision ProblemBipul Chandra KarNo ratings yet
- AOT - Lecture Notes V1Document5 pagesAOT - Lecture Notes V1S Deva PrasadNo ratings yet
- COMS3005A ComplexityDocument18 pagesCOMS3005A ComplexityPuseletso NakanaNo ratings yet
- DAA Unit 5Document29 pagesDAA Unit 5A Raghava Chowdary maddipatiNo ratings yet
- Interval Linear Assignment Problems: Sarangam MajumdarDocument3 pagesInterval Linear Assignment Problems: Sarangam MajumdarShita Juliana PutriNo ratings yet
- New Row Maxima Method To Solve Multi-Objective Transportation Problem Under Fuzzy Conditions A. J. Khan and D. K. Das Volume - 1, Number - 1 Publication Year: 2012, Page(s) : 42 - 46Document5 pagesNew Row Maxima Method To Solve Multi-Objective Transportation Problem Under Fuzzy Conditions A. J. Khan and D. K. Das Volume - 1, Number - 1 Publication Year: 2012, Page(s) : 42 - 46International Journal of Creative Mathematical Sciences and Technology100% (1)
- Optimization Models HUSTDocument24 pagesOptimization Models HUSTLan - GV trường TH Trác Văn Nguyễn Thị NgọcNo ratings yet
- Adsa QBDocument5 pagesAdsa QBHacker RanjanNo ratings yet
- Maths ProjectDocument23 pagesMaths ProjectAjay Vernekar100% (1)
- CONTENTSDocument6 pagesCONTENTSvivek.dogra.5095No ratings yet
- The Karmarkar Revolution: 1.1 Classical Portrait of The FieldDocument2 pagesThe Karmarkar Revolution: 1.1 Classical Portrait of The FieldDominicNo ratings yet
- Math138 Group 6 Written Report Pursue Parity Color and ProveDocument6 pagesMath138 Group 6 Written Report Pursue Parity Color and ProvePERATER, JELLY A.100% (1)
- Lower Bound TheoryDocument3 pagesLower Bound TheorytayNo ratings yet
- Elementary Theory and Application of Numerical Analysis: Revised EditionFrom EverandElementary Theory and Application of Numerical Analysis: Revised EditionNo ratings yet
- Application of A Dual Simplex Method To Transportation Problem To Minimize The CostDocument5 pagesApplication of A Dual Simplex Method To Transportation Problem To Minimize The CostInternational Journal of Innovations in Engineering and ScienceNo ratings yet
- Assignment and Transportation ProblrmDocument20 pagesAssignment and Transportation ProblrmHarish SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Overview of Some Solved NP-complete Problems in Graph TheoryDocument11 pagesOverview of Some Solved NP-complete Problems in Graph TheoryAndika Dwi NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Assignment ProblemDocument19 pagesAssignment ProblemSaket NandanNo ratings yet
- COUNTINGDocument51 pagesCOUNTINGJustine ReyesNo ratings yet
- Mba Semester Ii MB0048 - Operation Research-4 Credits (Book ID: B1301) Assignment Set - 1 (60 Marks)Document18 pagesMba Semester Ii MB0048 - Operation Research-4 Credits (Book ID: B1301) Assignment Set - 1 (60 Marks)geniusgNo ratings yet
- The Assignment Problem: SMS 4674 / SMS 3392 Operational ResearchDocument33 pagesThe Assignment Problem: SMS 4674 / SMS 3392 Operational ResearchMuhammad Hafiz Bin Yusoff100% (1)
- Vol10 Iss4 258-265 Ones Assignment Method For SolvingDocument8 pagesVol10 Iss4 258-265 Ones Assignment Method For Solvinggopi_dey8649No ratings yet
- Travelling Salesman ProblemDocument2 pagesTravelling Salesman ProblemkashiqirphanNo ratings yet
- 75 Sample ChapterDocument10 pages75 Sample ChapterkannambiNo ratings yet
- Metaheuristics Introduction 2Document81 pagesMetaheuristics Introduction 2IREM SEDA YILMAZNo ratings yet
- Maths ProjectDocument20 pagesMaths ProjectChirag JoshiNo ratings yet
- Dynamic ProgrammingDocument10 pagesDynamic Programmingiqra.id.aukNo ratings yet
- Wa0012.Document30 pagesWa0012.pandadiptimayee99No ratings yet
- Vijay Maths ProjectDocument54 pagesVijay Maths ProjectVijay MNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Programming: Applicability Possible Types of Constraint Set Methods For Solving The Problem ExamplesDocument4 pagesNonlinear Programming: Applicability Possible Types of Constraint Set Methods For Solving The Problem ExamplesLewis SitorusNo ratings yet
- BookTeghem TL PDFDocument24 pagesBookTeghem TL PDFAnNo ratings yet
- Theory: Assignment ProblemsDocument5 pagesTheory: Assignment Problemsnilkanth bhattNo ratings yet
- Potential of Quantum Finite Automata With Exact AcceptanceDocument15 pagesPotential of Quantum Finite Automata With Exact Acceptancelexleo1000No ratings yet
- Hungarian MethodDocument5 pagesHungarian MethodnunukantaNo ratings yet
- Daa Unit-5Document29 pagesDaa Unit-5pihadar269No ratings yet
- Discrete Maths Lecture Note (Chapter 1-3)Document19 pagesDiscrete Maths Lecture Note (Chapter 1-3)Gemechis GurmesaNo ratings yet
- CD-compiler Designe AkashDocument70 pagesCD-compiler Designe AkashElon muskNo ratings yet
- Ex 6.1. Linear Programming (Diet Problem)Document5 pagesEx 6.1. Linear Programming (Diet Problem)aaronkimNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Questions in Chapter 1: Section 1Document30 pagesSolutions To Questions in Chapter 1: Section 1taani_annNo ratings yet
- BSCMA1001 Week1 Assignment SolutionDocument16 pagesBSCMA1001 Week1 Assignment SolutionL.ABHISHEK KUMARNo ratings yet
- Mhtcet Iseet Mathematics BookDocument20 pagesMhtcet Iseet Mathematics BookRaven Russo50% (2)
- John Nolt LogicsDocument336 pagesJohn Nolt LogicsgorkolNo ratings yet
- ECE 279 Exp. 1 To Exp 10Document29 pagesECE 279 Exp. 1 To Exp 10Shruti KumariNo ratings yet
- Saccheri, Giovanni Girolamo PDFDocument3 pagesSaccheri, Giovanni Girolamo PDFcreeshaNo ratings yet
- Bisection Method Calculator - High Accuracy CalculationDocument3 pagesBisection Method Calculator - High Accuracy CalculationSusrianti JamalNo ratings yet
- Lab 05-Set Operations: Objective Current Lab Learning Outcomes (LLO)Document5 pagesLab 05-Set Operations: Objective Current Lab Learning Outcomes (LLO)hexaNo ratings yet
- MCSE 003 Previous Year Question Papers by IgnouassignmentguruDocument80 pagesMCSE 003 Previous Year Question Papers by IgnouassignmentguruIGNOU GURUNo ratings yet
- C - PointersDocument29 pagesC - PointersCommerceca HODNo ratings yet
- Algorithm Design Paradigms (Dynamic Programming)Document68 pagesAlgorithm Design Paradigms (Dynamic Programming)dasdNo ratings yet
- Debre Markos University Burie Campus: Logic in Computer Science Group AssignmentDocument14 pagesDebre Markos University Burie Campus: Logic in Computer Science Group AssignmentMezigebu MeleseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Recursion PDFDocument38 pagesChapter 11 Recursion PDFGirmaNo ratings yet
- Northwestern Mindanao State College of Science and Technology Labuyo, Tangub City Set ADocument2 pagesNorthwestern Mindanao State College of Science and Technology Labuyo, Tangub City Set AIs JulNo ratings yet
- Binary Search TreeDocument20 pagesBinary Search TreeShiva ThavaniNo ratings yet
- First Order Logic: Artificial Intelligence COSC-3112 Ms. Humaira AnwerDocument15 pagesFirst Order Logic: Artificial Intelligence COSC-3112 Ms. Humaira AnwerKhizrah Rafique0% (1)
- 2 Distributive LatticesDocument20 pages2 Distributive LatticesAravind KumarNo ratings yet
- Hypothetical PropositionDocument31 pagesHypothetical PropositionJerwin BautistaNo ratings yet
- IT 2 - LETS CHECK-Practice Exercises 1 and 2Document4 pagesIT 2 - LETS CHECK-Practice Exercises 1 and 2vnestacio00No ratings yet
- DBMS - Unit 3 - Notes (Relational Calculus)Document22 pagesDBMS - Unit 3 - Notes (Relational Calculus)ABCNo ratings yet
- EE351Chap3-2.0 - Transfer FTN & SFGsDocument19 pagesEE351Chap3-2.0 - Transfer FTN & SFGsSardar Hamid ullahNo ratings yet
- HE151434 - Nguyen Thanh Lam - SE1616 - Homework1Document5 pagesHE151434 - Nguyen Thanh Lam - SE1616 - Homework1Zoro BladeNo ratings yet
- Infinite Sequences of Primes of Form 4n-1 and 4n+1Document2 pagesInfinite Sequences of Primes of Form 4n-1 and 4n+1inventionjournalsNo ratings yet
- Chapter Ten: Fuzzy Logic ControlDocument25 pagesChapter Ten: Fuzzy Logic ControlCharlette Alessi InaoNo ratings yet
- Tarski's World TextbookDocument144 pagesTarski's World TextbookFlavio G. Martínez CruzNo ratings yet
- Week 15 - ClusteringDocument25 pagesWeek 15 - ClusteringRoyer Rojano100% (2)
- Module 1 Lesson 1.2. Graphical MethodDocument9 pagesModule 1 Lesson 1.2. Graphical MethodMaddyyyNo ratings yet
- Discrete Structure SyllabusDocument2 pagesDiscrete Structure SyllabusMausam Pokhrel100% (1)