Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tectonic Plates
Uploaded by
Sky0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views10 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views10 pagesTectonic Plates
Uploaded by
SkyCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
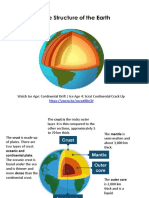
TECTONIC PLATES
What is a Tectonic Plate?
• A tectonic plate (also called lithospheric plate) is
a massive, irregularly shaped slab of solid rock,
generally composed of both continental and
oceanic lithosphere.
• Tectonic plates probably developed very early in
the Earth's 4.6-billion-year history, and they have
been drifting about on the surface ever since-like
slow-moving bumper cars repeatedly clustering
together and then separating.
• Plate size: greatly varies from hundreds to
thousands of kilometers across
• Plate thickness: ranging from less than 15 km for
young oceanic lithosphere to about 200 km or
more for ancient continental lithosphere (for
example, the interior parts of North and South
America).
7 MAJOR TECTONIC PLATES
MINOR TECTONIC PLATES
• Most of the boundaries between individual
plates cannot be seen, because they are hidden
beneath the oceans. Yet oceanic plate
boundaries can be mapped accurately from
outer space by measurements from GEOSAT
satellites. Earthquake and volcanic activity is
concentrated near these boundaries.
How Tectonic Plates Move?
TYPES OF PLATE BOUNDARY
REFERENCES
• California Earthquake Authority (2020). Understanding Plate Tectonic
Theory. Retrieved from
https://www.earthquakeauthority.com/Blog/2020/Understanding-Plate-Tecto
nic-Theory#:~:text=There%20are%20seven%20major%20plates,plate%20a
t%2039%2C768%2C522%20square%20miles
. February 7, 2022
• EARTHHOW (2022). 7 Major Tectonic Plates: The World’s Largest Plate
Tectonics. Retrieved from https://earthhow.com/7-major-tectonic-plates/.
February 7, 2022
• United States Geological Survey (n.a). What is a Tectonic Plate?. Retrieved
from https://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/tectonic.html. February 7, 2022
• All images are retrieved from Google
You might also like
- Major Tectonic Plates Move via ConvectionDocument3 pagesMajor Tectonic Plates Move via ConvectionSkyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.1 Plate TectonicsDocument23 pagesLesson 2.1 Plate TectonicsAvery BugarinNo ratings yet
- Tectonic Plates ReportDocument13 pagesTectonic Plates ReportJulio Paolo BautistaNo ratings yet
- G10 Q1 L7 Plate Tectonic TheoryDocument18 pagesG10 Q1 L7 Plate Tectonic TheoryMark GalangNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Structure of The EarthDocument71 pagesLecture 3 Structure of The EarthFuad AlAsadNo ratings yet
- Lecture #1 & 2 The Dynamic EarthDocument77 pagesLecture #1 & 2 The Dynamic EarthezansahizzahNo ratings yet
- Theory of Global Plate TectonicsDocument11 pagesTheory of Global Plate TectonicsHannylet OcateNo ratings yet
- Earth's Structure and Plate Tectonics ExplainedDocument79 pagesEarth's Structure and Plate Tectonics ExplainedHyres Almerina AlturasNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument41 pagesPlate TectonicsJohn100% (1)
- Enviro Geo Notes 3 CompressedDocument26 pagesEnviro Geo Notes 3 CompressedAlaiza mae BongcayNo ratings yet
- MODULE-1-2-3-4 - GeologyDocument24 pagesMODULE-1-2-3-4 - GeologyLIM KESSAH MARIENo ratings yet
- Geo Dina MikaDocument41 pagesGeo Dina MikaAKHMAD MUTTAQINNo ratings yet
- Earth and PlateTectonicsDocument34 pagesEarth and PlateTectonicsJohn BenedictNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics: How Earth's Surface MovesDocument32 pagesPlate Tectonics: How Earth's Surface MovesAmy Sara100% (1)
- DepEd Training on Communicating Earthquake HazardsDocument38 pagesDepEd Training on Communicating Earthquake HazardsJHON PATRICK MALINAWANNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics.: Egat Lominded & Bronte GilsonDocument22 pagesPlate Tectonics.: Egat Lominded & Bronte Gilsonmagie kohNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic2Document27 pagesPlate Tectonic2eduardocarlbituin15No ratings yet
- ENV203/GEO205: Intro to Geography Lectures 07-08Document26 pagesENV203/GEO205: Intro to Geography Lectures 07-08Abtahee Farhan Labib Ador 1921868642No ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument15 pagesPlate TectonicsTomato PotatoNo ratings yet
- Earth's Internal ForcesDocument22 pagesEarth's Internal ForcesAmreka HoseinNo ratings yet
- The Lithosphere Lesson 2Document30 pagesThe Lithosphere Lesson 2Hannah C. MillareNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument24 pagesPlate TectonicsMicah BlazaNo ratings yet
- Science 4Document2 pagesScience 4Prince Jonah LisaNo ratings yet
- L3 - Geosphere TectonicsDocument51 pagesL3 - Geosphere TectonicsbhaveshreddygunNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document32 pagesModule 1hannahloraineee norombabaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Plate Tectonics (Theories)Document10 pages1.2 Plate Tectonics (Theories)Lawrence AnDrew FrondaNo ratings yet
- 5 - Plate TectonicsDocument29 pages5 - Plate TectonicsrichardarisyabutNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics 122447Document12 pagesPlate Tectonics 122447mkwa811No ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics: Name: Krisia Marie Amac Bsge 3ADocument5 pagesPlate Tectonics: Name: Krisia Marie Amac Bsge 3AMark Rienzo HingpisNo ratings yet
- SCI 10 Tectonic PlatesDocument15 pagesSCI 10 Tectonic PlatesLynne Joie Laroza TapayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction To EGEDocument46 pagesLecture 1 Introduction To EGEbhargav reddyNo ratings yet
- Physical Geology02Document233 pagesPhysical Geology02Siari Ann Iligan100% (1)
- Tectonic EarthquakeDocument25 pagesTectonic EarthquakeMark Aaron AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument52 pagesPlate TectonicsTrembletonNo ratings yet
- EAS 1600 Lab 08 Fall 2018 "Plate Tectonics" ObjectivesDocument20 pagesEAS 1600 Lab 08 Fall 2018 "Plate Tectonics" ObjectivessamNo ratings yet
- SciencemidtermDocument9 pagesSciencemidtermapi-281100019No ratings yet
- Topic 1 Plate TectonicsDocument76 pagesTopic 1 Plate TectonicsYogiNo ratings yet
- Yangon Technological University Earthquake PresentationDocument97 pagesYangon Technological University Earthquake PresentationCho WaiNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument15 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate Tectonicsۦۦ JayceeNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics: Plate Tectonics (From The Late Latin: Tectonicus, From TheDocument30 pagesPlate Tectonics: Plate Tectonics (From The Late Latin: Tectonicus, From ThemcmusbixNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics: Earth's Plates and Continental DriftDocument31 pagesPlate Tectonics: Earth's Plates and Continental DriftTeena SeiclamNo ratings yet
- Geology Module 1Document33 pagesGeology Module 1Olga Soephia SantosNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument57 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicshatdoghatdogNo ratings yet
- Impact of Geographical Phenomena - Form 6Document139 pagesImpact of Geographical Phenomena - Form 6Conrod Wayne Smith100% (1)
- Module O3 Tektonika: Gerak Dan Sifat Interaksi Lempeng LitosferikDocument26 pagesModule O3 Tektonika: Gerak Dan Sifat Interaksi Lempeng LitosferikRidho MuhariNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument47 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsShakerMahmoodNo ratings yet
- Tectonics and BasinsDocument43 pagesTectonics and Basinsalbert mwairwaNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument31 pagesPlate TectonicsRyan HoganNo ratings yet
- Overview On Petroleum Geoscience: Understanding Earth Lecture #1 Askury Abd KadirDocument68 pagesOverview On Petroleum Geoscience: Understanding Earth Lecture #1 Askury Abd KadirAban RobertNo ratings yet
- CE16 Earthquake Engineering LP1 1Document23 pagesCE16 Earthquake Engineering LP1 1rosary originalNo ratings yet
- Geo RevisionDocument4 pagesGeo RevisionFarfi UddinNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics NotesDocument20 pagesPlate Tectonics NotesRaj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics: Environmental ManagementDocument6 pagesPlate Tectonics: Environmental Managementvero1curziNo ratings yet
- EARTHQUAKEDocument4 pagesEARTHQUAKEkennsindayenNo ratings yet
- Elements SeismologyDocument18 pagesElements SeismologyReniel SalesNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument19 pagesPlate TectonicsBurhan NurudinNo ratings yet
- Forces That Affect Changes On The Earth's Surface: Earthquake and Volcanic EruptionsDocument21 pagesForces That Affect Changes On The Earth's Surface: Earthquake and Volcanic EruptionsJeric AporboNo ratings yet
- Cursive Words ADocument21 pagesCursive Words AImee TibleNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02 - The Earth - Plate Tectonics and Continental DriftDocument2 pagesLecture 02 - The Earth - Plate Tectonics and Continental DriftZohaib IqbalNo ratings yet
- Why Do Tectonic Plates Crash and Slip? Geology Book for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandWhy Do Tectonic Plates Crash and Slip? Geology Book for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet