Professional Documents
Culture Documents
National Income - Concepts
Uploaded by
Kunal Garg0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views21 pagesNational Income Concepts Well Explained in this Document
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentNational Income Concepts Well Explained in this Document
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views21 pagesNational Income - Concepts
Uploaded by
Kunal GargNational Income Concepts Well Explained in this Document
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 21
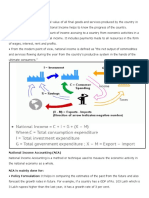
National Income
Introduction
• National income is the total value a country’s final output
of all new goods and services produced in one year.
• National income is the sum total of wages, rent, interest,
and profit earned by the factors of production of a
country in a year. Thus it is the aggregate values of
goods and services rendered during a given period
counted without duplication.
Definition
The labour and capital of a country acting on its natural
resources produce annually a certain net aggregate of
commodities material an immaterial including services of all
kinds- Marshall
National income consists solely of services as received by
ultimate consumers, whether from their material or from their
human environments- Fisher
A national income estimate measures the volume of
commodities and services turned out during a given period
counted without duplication- National Income Committee of
India (1951)
National income is the monetary measure of
•The net value of all products and services
•In an economy during a year
•Counted without duplication
•After allowing for depreciation
•Both in the public and private sector of products and
services
•In consumption and capital goods sector
•The net gains from international transactions.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the total market value of
all final goods and services currently produced within the
domestic territory of a country in a year.
According to Shapiro “GDP is defined as a flow variable,
measuring the quantity of final goods and services
produced during a year.”
Essential features of GDP
GDP is the total market value. It measures the total
market value of output at current market prices.
All goods and services. GDP measures the market
value of all goods (cloth, furniture etc.) and services
(accountant, doctor etc., services) produced in the
economy.
Final goods. GDP includes the value of only final goods.
The value of intermediate goods (yarn for example is
excluded to avoid double counting.
• Currently produced goods. GDP includes only the
value of those goods and services which are currently
produced. For example, a person sells his old house to
another person. The value of the house is not included in
GDP.
• Domestic territory. It includes the value of output of
goods and services produced by all enterprises whether
resident or non-resident located within the domestic
territory of a country.
• Time period. GDP includes the value of all final goods
and services produced in a given period of time which is
usually a year.
• Flow concept. GDP measures the flow of income
produced by all producing enterprises during a year.
Snapshot of GDP of India
Gross National Product (GNP)
The concept of gross national product (GNP) at market
prices is more comprehensive than GDP Gross domestic
product (GDP) is the total value, Measured in current
price, of all final goods and services produced in the
economy during a ‘given period. It includes all factor
incomes of non-residents paid to foreigners.
Gross national product, on the other hand, measures the
total income earned by the permanent residents of a
country in a given time period. GNP includes factor
incomes earned from abroad by the residents of a
country and excludes income that foreigners earn from
here. Thus GNP = GDP + Net factor income earned
from abroad.
Net Domestic Product at Market Price (NDP at MP)
Net domestic product- at market price is the difference
between Net National Product at market price and net
factor income from abroad. Net domestic product at
market price is the difference been GNP at market price
minus depreciation and net factor incomes from abroad.
[Net Domestic Product at Market Price = GNP at MP -
Depreciation - Net factors income form abroad]
Net National Product at Market Price (NNP at
MP)
Net National product measures the net money value of
final goods and services at current prices produced in a
year in a country. It is the gross national product at
market price less depreciation.
[NNP at MP = GNP at MP – Depreciation]
Net Domestic Product at Factor Cost (NDP at
FC)
Net Domestic product of factor cost or domestic income
is the income earned by all the factors of production
within the domestic territory of a country during a year in
the form of wages, interest, profit and rent etc. Thus
NDP at FC is a territorial concept. In other words NDP at
factor cost is equal to NNP at FC less net factor income
from abroad.
[NDP at FC = NNP at FC - Net factor income from
abroad]
Net National Product at Factor Cost (NNP at
FC)
Net national product at factor cost is the aggregate
payments made to the factors of production. NNP at FC
is the total incomes earned by all the factors of
production in the form of wages, profits, rent, interest etc.
plus net factor income from abroad. NNP at FC is the
NDP at FC plus net factor income from abroad. NNP at
FC can also be derived by excluding depreciation from
GNP at FC.
[NNP at FC = NDP at FC + Net Factor Income from
abroad]
Gross Domestic Product at Factor Cost (GDP at FC)
Gross Domestic Product at factor cost refers to the value
of all the final goods and services produced within the
domestic territory of a country. If depreciation or
consumption of fixed capital is added to the net domestic
product at factor cost, it is called Gross domestic Product
at Factor cost.
[GDP at FC = NDP at FC - Depreciation]
Gross National Product at Factor Cost (GNP at
FC)
• Gross national product at factor cost is obtained by
deducting the indirect tax and adding subsidies to GNP
at market price or Gross national Product at factor cost is
obtained by adding net factor incomes from abroad to
the GDP at factor cost.
• [GNP at FC = GNP at MP - Indirect tax + Subsidies]
or, [GNP at FC = GDP at FC + Net Factor Income
from abroad]
Personal Income
Personal Income is the total income received by the
individuals of country from all sources before direct
taxes. Personal income is not the same as National
Income, because personal income includes the transfer
payments where as they are not included in national
income. Personal income includes the wages, salaries,
interest and rent received by the individuals. Personal
income is derived by excluding undistributed corporate
profit taxes etc. from National Income.
[Personal Income = Private Income - Saving of
Private enterprise - Corporate tax]
Disposable Income
Disposable income means the actual income which can
be spent on consumption by individuals and families. It
refers to the purchasing power of the house hold. The
whole of disposable income is not spent on
consumptions; a part of it is paid in the form of direct tax.
Thus disposable income is that part of income, which is
left after the exclusion of direct tax.
[Disposable Income = Personal Income - Direct tax]
Practical Insight
• First Advance Estimates of National Income,
2019-20
• https://pib.gov.in/Pressreleaseshare.aspx?PRI
D=1598643
Importance of National Income
Analysis:
• For the Economy:National income data
are of great importance for the economy
of a country. These days the national
income data are regarded as accounts of
the economy, which are known as social
accounts. These refer to net national
income and net national expenditure,
which ultimately equal each other.
• National Policies: National income data form
the basis of national policies such as employment policy,
because these figures enable us to know the direction in
which the industrial output, investment and savings,
etc. change, and proper measures can be adopted to
bring the economy to the right path.
• Economic Planning:
• In the present age of planning, the national data are of
great importance. For economic planning, it is essential
that the data pertaining to a country’s gross income,
output, saving and consumption from different sources
should be available. Without these, planning is not
possible.
• Economic Models:
• The economists propound short-run as well as long-run
economic models or long-run investment models in
which the national income data are very widely used.
• Research:The national income data are also made use of by
the research scholars of economics. They make use of the
various data of the country’s input, output, income, saving,
consumption, investment, employment, etc., which are
obtained from social accounts.
• Per Capita Income:
• National income data are significant for a country’s per
capita income which reflects the economic welfare of the
country. The higher the per capita income, the higher the
economic welfare of the country.
• Distribution of Income:
• National income statistics enable us to know about the
distribution of income in the country. From the data
pertaining to wages, rent, interest and profits, we learn of
the disparities in the incomes of different sections of the
society. Similarly, the regional distribution of income is
revealed.
You might also like
- Heat and Mass Transfer - E. R. G. Eckert and R. M. Drake PDFDocument46 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer - E. R. G. Eckert and R. M. Drake PDFAnaQatarina50% (4)
- National Income and Occupational Structure in IndiaDocument45 pagesNational Income and Occupational Structure in IndiaakshatNo ratings yet
- The Concepts of National IncomeDocument22 pagesThe Concepts of National IncomeHaren ShylakNo ratings yet
- GDP and GNP Concepts ExplainedDocument7 pagesGDP and GNP Concepts ExplainedAmjad KhanNo ratings yet
- National Income-Concepts and MeasurementsDocument34 pagesNational Income-Concepts and MeasurementsSonali SharmaNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument24 pagesNational IncomePranay Sai Garepally100% (1)
- National Income: - by Shikha SinghDocument40 pagesNational Income: - by Shikha SinghPrashastiNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument23 pagesNational IncomeMohinudeen KhanNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument29 pagesNational IncomegipaworldNo ratings yet
- National Income (Notes) IMBADocument27 pagesNational Income (Notes) IMBASubham .MNo ratings yet
- 1 National IncomeDocument17 pages1 National Incomealekya.nyalapelli03No ratings yet
- UNIT - IV, National Income Accounting: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) All Output Produced Within A NationDocument15 pagesUNIT - IV, National Income Accounting: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) All Output Produced Within A NationanushreeNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic Analysis For Management 1 - Chapter 3Document21 pagesMacroeconomic Analysis For Management 1 - Chapter 3dawsonNo ratings yet
- National Income Concepts & MeasurementDocument30 pagesNational Income Concepts & MeasurementPooza SunuwarNo ratings yet
- National Income in India, Concept and MeasurementDocument87 pagesNational Income in India, Concept and MeasurementPreeti BajajNo ratings yet
- Measuring National IncomeDocument19 pagesMeasuring National Incomessaeed_4No ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument66 pagesEconomicsSangeeta YadavNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument26 pagesNational IncomerajapatnaNo ratings yet
- National Income PDFDocument12 pagesNational Income PDFReshma JainNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument9 pagesNational Incomeshahnawaz malikNo ratings yet
- National Income Accounting: Economics, 7 Edition Boyes and Melvin Houghton Mifflin Company, 2008Document26 pagesNational Income Accounting: Economics, 7 Edition Boyes and Melvin Houghton Mifflin Company, 2008Asad NaseerNo ratings yet
- Inter CA EconomicDocument163 pagesInter CA Economicmoceh87222No ratings yet
- Nationalincome 141209072252 Conversion Gate02Document37 pagesNationalincome 141209072252 Conversion Gate02Simmi KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Gross Domestic Product at Market Price (GDP at MP)Document7 pagesGross Domestic Product at Market Price (GDP at MP)vanvunNo ratings yet
- Macro Eco 3Document113 pagesMacro Eco 3br bhandariNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 NewDocument94 pagesUnit 5 NewrajapatnaNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Mod 1Document18 pagesMacroeconomics Mod 12580 Soumil SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 NewDocument94 pagesUnit 5 NewrajapatnaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Macro EconomicsDocument20 pagesSummary of Macro EconomicsYogesh JhaNo ratings yet
- Concepts of National IncomeDocument35 pagesConcepts of National IncomeChitraksh MahajanNo ratings yet
- Me Unit-5Document7 pagesMe Unit-5Anuj YadavNo ratings yet
- GDP and GNPDocument27 pagesGDP and GNPKeerthikanthGubbalaNo ratings yet
- National Income and Related AggregatesDocument7 pagesNational Income and Related AggregatesAnvi RaiNo ratings yet
- Concepts and Measurement of National IncomeDocument66 pagesConcepts and Measurement of National IncomesubramanianNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument23 pagesNational Incomemagardiwakar11No ratings yet
- Measuring National Income Through GDP, GNP & NNPDocument5 pagesMeasuring National Income Through GDP, GNP & NNPAkshit Kumar100% (1)
- National Income and Related AggregatesDocument18 pagesNational Income and Related AggregatesRishika SinghNo ratings yet
- National Income: Definition, Importance and MeasuresDocument15 pagesNational Income: Definition, Importance and MeasuresDhiraj IppiliNo ratings yet
- Circular Flow of IncomeDocument66 pagesCircular Flow of IncomeAshish Tewani100% (3)
- Module - 4 National IncomeDocument64 pagesModule - 4 National Incomelakshmi dileepNo ratings yet
- Determination of National IncomeDocument3 pagesDetermination of National Incomemanasa_s_ramanNo ratings yet
- National Income Accounting (NIA)Document8 pagesNational Income Accounting (NIA)Mamta VermaNo ratings yet
- The National Income Accounting 1Document15 pagesThe National Income Accounting 1Kyle Kenneth GarciaNo ratings yet
- Unit I: National Income Accounting-Concepts & MeasurementDocument20 pagesUnit I: National Income Accounting-Concepts & MeasurementSudhaSatishNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument7 pagesNational IncomeFahadNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5: Indian Economy - A ProfileDocument30 pagesChapter - 5: Indian Economy - A ProfileDipesh ThakkarNo ratings yet
- National income and aggregate demand concepts explainedDocument22 pagesNational income and aggregate demand concepts explainedHarsh Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Goals, Instruments and National IncomeDocument5 pagesMacroeconomics Goals, Instruments and National IncomeIlma Sadan Guji'iiNo ratings yet
- Macro Economics: National Income Fiscal Policy Monetary Policy Trade CyclesDocument48 pagesMacro Economics: National Income Fiscal Policy Monetary Policy Trade Cyclesusne902No ratings yet
- National Income AnalysisDocument25 pagesNational Income Analysisvaibhav001988No ratings yet
- Lec 9 National IncomeDocument65 pagesLec 9 National IncomeLakhan Subhash TrivediNo ratings yet
- Unit IvDocument14 pagesUnit IvsudhanshuNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument16 pagesNational Incomejyoti pillayNo ratings yet
- NATIONAL INCOMEDocument22 pagesNATIONAL INCOMEHitesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- NatioDocument16 pagesNatioNisar Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit-V Managerial EconomicsDocument34 pagesUnit-V Managerial Economicsatulkumar.rise1No ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument21 pagesNational IncomeMurali Krishna Pavan PappuNo ratings yet
- National Income: Concepts & MeasurementDocument12 pagesNational Income: Concepts & MeasurementRajeshsharmapurangNo ratings yet
- VariantsDocument20 pagesVariantsRobert AyalaNo ratings yet
- Summary Of "The Economic System" By Armando Fastman: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESFrom EverandSummary Of "The Economic System" By Armando Fastman: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESNo ratings yet
- FavicolDocument21 pagesFavicolKunal GargNo ratings yet
- Business CycleDocument12 pagesBusiness CycleKunal GargNo ratings yet
- Measuring National Income - ExamplesDocument17 pagesMeasuring National Income - ExamplesKunal GargNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Macro EconomicsDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Macro EconomicsKunal GargNo ratings yet
- Index NumbersfDocument28 pagesIndex NumbersfKunal GargNo ratings yet
- Dividend Valuation GuideDocument25 pagesDividend Valuation GuideKunal GargNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Cost Of Capital ExplainedDocument17 pagesFinancial Management Cost Of Capital ExplainedKunal GargNo ratings yet
- Cost Ofcapital NumericalsDocument6 pagesCost Ofcapital NumericalsKunal GargNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting Case StudyDocument1 pageCapital Budgeting Case StudyKunal GargNo ratings yet
- Milk ManualsDocument18 pagesMilk ManualsLAKSHYA VERMA0% (1)
- CriticalAppraisalWorksheetTherapy EffectSizeDocument2 pagesCriticalAppraisalWorksheetTherapy EffectSizeFitriArdiningsihNo ratings yet
- MITSUBISHI Elevator PDFDocument12 pagesMITSUBISHI Elevator PDFBirhami AkhirNo ratings yet
- SMPP Gateway Interface Programming GuideDocument21 pagesSMPP Gateway Interface Programming GuideVamsi Krishna TalasilaNo ratings yet
- Student ProfileDocument2 pagesStudent Profileapi-571568290No ratings yet
- Upper-Room UVGI Leaflet G.L.A.Document4 pagesUpper-Room UVGI Leaflet G.L.A.MihaiAnastasiuNo ratings yet
- Learner's Module in Grade 7 Mathematics Pages 1 - 4 Global Mathematics, Page 2 - 18 Synergy For Success in Mathematics, Pages 2 - 13Document12 pagesLearner's Module in Grade 7 Mathematics Pages 1 - 4 Global Mathematics, Page 2 - 18 Synergy For Success in Mathematics, Pages 2 - 13Maricel Tarenio MacalinoNo ratings yet
- Project management software and techniquesDocument2 pagesProject management software and techniquesbinduannNo ratings yet
- Service Manual KTM Adventure 1190Document226 pagesService Manual KTM Adventure 1190Tim BlockxNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Radical Innovation and Significant Relationship of Metromile Car Insurance CompanyDocument10 pagesAssessment of Radical Innovation and Significant Relationship of Metromile Car Insurance CompanyBidisha BhoumickNo ratings yet
- Topics in English SyntaxDocument131 pagesTopics in English SyntaxPro GamerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: 19Th Century Philippines As Rizal'S ContextDocument52 pagesChapter 2: 19Th Century Philippines As Rizal'S ContextJorielyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- Java NoteDocument8 pagesJava NoteTg DgNo ratings yet
- Java Layout ManagersDocument16 pagesJava Layout ManagersVijaya Kumar VadladiNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra and Analytical Geometry: A B C Ab CDDocument3 pagesLinear Algebra and Analytical Geometry: A B C Ab CDTooba AkhtarNo ratings yet
- The Definition of WorkDocument2 pagesThe Definition of WorkCarlton GrantNo ratings yet
- Campus Event ReflectionDocument2 pagesCampus Event ReflectiondntbenfordNo ratings yet
- xg01 Koso Kent Introl PDFDocument22 pagesxg01 Koso Kent Introl PDFhaidinuNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument18 pagesChapter Oneحيدر محمدNo ratings yet
- KETRACO Clarifies Technical Queries for 400kV Transmission ProjectDocument5 pagesKETRACO Clarifies Technical Queries for 400kV Transmission Projectahmadove1No ratings yet
- 6 1 Reducing Rational Expressions To Lowest TermsDocument21 pages6 1 Reducing Rational Expressions To Lowest Termsapi-233527181No ratings yet
- Original Activity 3. Gustavo BurgosDocument3 pagesOriginal Activity 3. Gustavo BurgosVillar BurgosNo ratings yet
- Sonic sdw45Document2 pagesSonic sdw45Alonso InostrozaNo ratings yet
- DDCS Expert User's Manual V1-已压缩Document137 pagesDDCS Expert User's Manual V1-已压缩andréNo ratings yet
- Code: Final Exam in English: Grade 8Document7 pagesCode: Final Exam in English: Grade 8Luka EradzeNo ratings yet
- Dual Band DAB Pocket Radio: User Manual Manuel D'utilisation Manual Del Usuario Benutzerhandbuch GebruikershandleidingDocument21 pagesDual Band DAB Pocket Radio: User Manual Manuel D'utilisation Manual Del Usuario Benutzerhandbuch Gebruikershandleidingminerva_manNo ratings yet
- Characterization of CrudeDocument4 pagesCharacterization of Crudekhushbu hasanNo ratings yet
- Aluminio 2024-T3Document2 pagesAluminio 2024-T3IbsonhNo ratings yet
- Designing An LLC ResonantDocument30 pagesDesigning An LLC Resonant劉品賢No ratings yet