Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Concepts of National Income
Uploaded by
Haren Shylak0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views22 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views22 pagesThe Concepts of National Income
Uploaded by
Haren ShylakCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 22
Concept of National Income
There are various concepts of National Income.
1.Gross National Product (GNP).
2.Net National Product (NNP)/National Income.
3.Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
4.National Income at Factor Cost.
5. Personal Income.
6. Disposable Personal Income.
1.Gross National Product (GNP)
Definition and Explanation of GNP:
• The concept of Gross National Product (GNP) is
comprehensive. It enables us to measure and
analyze as to how much is the aggregate economic
production of a country in a given period.
• The gross national product of a country (GNP) is
defined as:
• “The total money value of all final goods and
services produced by the residents of a country
in one year period”.
• In the words of W.C. Peterson:
“Gross National Product may be defined as the
current market value of all final goods and
services produced by the economy during an
income period regardless of where the output is
produced”.
Remember the following aspects of GNP:
• GNP is a flow concept: GNP represents a flow. It
is a quantity produced per unit of time. It is the
value of final goods and services produced in a
country during a given time period.
• GNP measures final output: While calculating GNP,
the market value of only final goods and services
produced in a year are added up. Final goods are those
goods that are purchased for final use in the market.
• GNP is the output produced by the citizens of a
country: Gross national product is the final output of
goods and services produced by the citizens and
businesses of a country during a given time period
which is usually a year.
• For example, the economic activity carried out by the
American citizens and businesses outside the country
is counted in GNP. While the income of the residents
who are not USA citizens is subtracted from GNP.
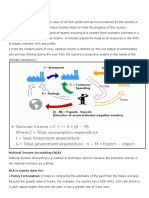
Components of Expenditures in GNP:
• For measuring GNP at market price, the
economists use the Expenditure Approach.
• According to this approach, there are four
categories of expenditures which are added
together to measure Gross National Product
(GNP) at Market Price,
(i) Consumption
(ii) Investment
(iii) Government Expenditure and
(iv) Net exports.
• These four types of expenditures are explained in
brief:
(i) Consumption Expenditure (C): It includes all
personal expenditures incurred by the citizens of a
country on durable and non-durable goods in a period
of one year.
(ii) Investment (I): It is the total expenditure incurred
by firms or households on capital goods.
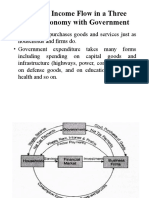
(iii) Govt. expenditures (G): It includes all types of
expenditure incurred by Federal, Provincial, Local
Councils on the purchases of goods and services such
as national defense, law, and order, street lighting, etc.
(iv) Net Exports (X – M): Net exports of goods
and services are the value of exports minus the
value of imports.
• The formula for Gross Profit:
GNP = C + I + G + (X – M)
Where:
C = Consumption, I = Investment,
G = Government Expenditure and X – M = Net
exports.
2. Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
• “Gross domestic product (GDP) is defined as the
total market value at current prices of all final
goods and services produced within a year by the
factors of production located within a country”.
• The labour and the capital of a country working on
its natural resources produce a certain aggregate of
commodities, material, and non-material every year.
• In addition to this, there may be foreign firms
producing goods in the various sectors of the
economy like mining, electricity, manufacturing, etc.
• If we add up the money value of all the final goods
produced both by domestic and foreign-owned
factors annually in the country and valued at market
prices, it will be called gross domestic product
(GDP).
• Gross Domestic Product is the value of aggregate or
total production of goods and services in a country in
one year.
• If we make a detailed list of all such commodities
produced annually or measure the total goods
produced during a year by weight or by volume, it
will not give us any clear and concise impression
about our total national output.
• So, what generally done is that the money value of all final
goods and service produced during a year at current market
prices is added up.
• This total current market value of all final goods and
services produced in an economy in a year period is called
gross domestic product (GDP).
In the words of Campbell:
• “Gross Domestic Product is defined as the total value of all
final goods and services produced in a country in one year”.
According to Shapiro:
• “GDP is defined as a flow variable, measuring the quantity
of final good and services produced” during a year”.
• While calculating the gross domestic product
(GDP), the value of only those goods are added
which have reached their final stage of
production and are available for consumption.
• The primary or intermediate goods are not
counted in GDP.
Distinction Between GDP and GNP:
• The distinguish between Gross Domestic Product
(GDP) and Gross National Product (GNP).
• Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the total
market value of all final goods and services
produced by factors of production within a
nation’s border during a period of one year.
• In other words, GDP is a flow of products
produced within the country by domestically
located resources in a year.
• Gross National Product (GNP) on the other hand, is
the measure of all final goods and services produced
by the citizens within their own country as well as
outside the country during a period of one year.
• In other words, GNP expresses the money value of
the flow of goods and services produced within the
country and the net income received from abroad
during a period of one year.
• Thus when we move from GDP to GNP, we add
factor income receipts from foreigners and
subtract factor income payments to foreigners.
• GDP = GNP – Net Foreign Income From Abroad
3.Net National Product (NNP)/National Income
• Net National Product or National Income at Market
Prices is the net market monetary value of all the final
goods and services produced in a country during a year.
• It is found out by subtracting the amount of
depreciation of the existing capital in a year from the
market value of all final goods and services.
• If we deduct depreciation allowance from gross
national product, we get Net National Product at
current market price.
• NNP at Market Price = GNP at Market Price –
Depreciation
• This fund which is set aside for covering the wear
and tear, deterioration and obsolescence of the
machinery is named as Depreciation Allowance.
• NNP = GNP – Depreciation
4. National Income at Factor Cost
• National Income can be estimated in terms of
either output or total income.
• When national income is measured by adding
together all income payments made to the factors
of production in a year, it is called national income
at factor cost.
• National income thus is the sum total of all income
payments made to the factors of production.
In the words of J. Sloman:
• “National income (Nl) or national income at
factor cost is the aggregate earning of the four
factors of production (land, labour, capital and
organization) which arise from the current
production of goods and services by the
nations’ economy”.
• The main components of national income at
factor cost are as follows:
• The factor incomes are generally divided into four categories:
(i) Compensation to employees – It is the largest component
of national income. It consists of wages and salaries paid by
the firms to the workers for their labour services.
(ii) Interest – Interest is the payment for the use of funds in a
year. The payment is made by private businesses to households
who have lent money to them.
(iii) Rents – Rent is all income earned by individuals for the
use of their real assets such as building, farms etc.
(iv) Profits – Profit is the amount which is left after
compensation to employees, rent, interest has been paid out.
The sum of compensation to employees, interest, rent and
profit is supposed to equal national income at factor cost.
5.Personal Income
• National income is the sum of factor income. In other
words, it is the income which individuals receive for
doing productive work in the form of wages, rent,
interest and profits.
• Personal Income, on the other hand, includes all income
which is actually received by all individuals in a year. It
includes income which is not directly earned but is
received by individuals.
• For example, social security payments, welfare
payments are received by households but these are not
elements of national income because they are transfer
payments.
• In the same way, in national income accounting,
individuals have attributed income which they do
not actually receive.
• For example, undistributed profits, employee’s
contribution to social security corporate income
taxes etc. are elements of national income but are
not received by individuals. Hence they are to be
deducted from national income to estimate the
personal income.
• PI = Nl + Transfer Payments – Corporate
retained earnings, income taxes, social security
taxes.
6. Disposable Personal Income
• Disposable Personal Income is the amount
which is actually at the disposal of
households/persons to spend as they like.
• It is the amount which is left with the
households/persons after paying personal taxes
such as income tax, property tax, national
insurance contributions etc.
• Disposable personal income = Personal Income
– Personal Taxes
DPI = PI – Personal Taxes
• The concept of disposable personal income is
very important for studying the consumption and
saving behaviour of individuals. It is the amount
which households can spend and save.
• Disposable Income = Consumption + Saving
DI = C + S
You might also like
- National Income and Occupational Structure in IndiaDocument45 pagesNational Income and Occupational Structure in IndiaakshatNo ratings yet
- National Income - ConceptsDocument21 pagesNational Income - ConceptsKunal GargNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument29 pagesNational IncomegipaworldNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 NewDocument94 pagesUnit 5 NewrajapatnaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 NewDocument94 pagesUnit 5 NewrajapatnaNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument24 pagesNational IncomePranay Sai Garepally100% (1)
- National Income: Learning ObjectivesDocument19 pagesNational Income: Learning ObjectivesvinuthajoisNo ratings yet
- National Income Accounting: Economics, 7 Edition Boyes and Melvin Houghton Mifflin Company, 2008Document26 pagesNational Income Accounting: Economics, 7 Edition Boyes and Melvin Houghton Mifflin Company, 2008Asad NaseerNo ratings yet
- National Income Explained: GDP, GNP, NNP & Circular FlowDocument27 pagesNational Income Explained: GDP, GNP, NNP & Circular FlowDaniel CookNo ratings yet
- Chap I National IncomeDocument34 pagesChap I National IncomeVAISALY S MBANo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic Analysis For Management 1 - Chapter 3Document21 pagesMacroeconomic Analysis For Management 1 - Chapter 3dawsonNo ratings yet
- Income CalculationDocument15 pagesIncome CalculationranjandkNo ratings yet
- GDP and GNPDocument27 pagesGDP and GNPKeerthikanthGubbalaNo ratings yet
- A275494408 - 22259 - 17 - 2020 - National Income Audio LectureDocument10 pagesA275494408 - 22259 - 17 - 2020 - National Income Audio LectureMehak SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit I: National Income Accounting-Concepts & MeasurementDocument20 pagesUnit I: National Income Accounting-Concepts & MeasurementSudhaSatishNo ratings yet
- GDP and GNP Concepts ExplainedDocument7 pagesGDP and GNP Concepts ExplainedAmjad KhanNo ratings yet
- National Income Concepts & MeasurementDocument30 pagesNational Income Concepts & MeasurementPooza SunuwarNo ratings yet
- Unit-V Managerial EconomicsDocument34 pagesUnit-V Managerial Economicsatulkumar.rise1No ratings yet
- Economics IDocument34 pagesEconomics IKevin kayNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument12 pagesNational IncomeJaskiran KaurNo ratings yet
- National Income in India, Concept and MeasurementDocument87 pagesNational Income in India, Concept and MeasurementPreeti BajajNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument26 pagesNational IncomerajapatnaNo ratings yet
- Concepts and Measurement of National IncomeDocument66 pagesConcepts and Measurement of National IncomesubramanianNo ratings yet
- National Income Analysis: Dr. Gopalakrishna B.VDocument29 pagesNational Income Analysis: Dr. Gopalakrishna B.Vshyam_ceeNo ratings yet
- 1 National IncomeDocument17 pages1 National Incomealekya.nyalapelli03No ratings yet
- NatioDocument16 pagesNatioNisar Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- National Income: - by Shikha SinghDocument40 pagesNational Income: - by Shikha SinghPrashastiNo ratings yet
- Module - 4 National IncomeDocument64 pagesModule - 4 National Incomelakshmi dileepNo ratings yet
- Measuring National Income: GDP, GNP and Other Key ConceptsDocument14 pagesMeasuring National Income: GDP, GNP and Other Key ConceptsDharmapuri Shri lekhaNo ratings yet
- (TOPIC 4) Natl and Intl Accounts (Income, Wealth, and The BoPs)Document80 pages(TOPIC 4) Natl and Intl Accounts (Income, Wealth, and The BoPs)jjho4832No ratings yet
- 1_4994851114739303613Document27 pages1_4994851114739303613Kunal GautamNo ratings yet
- Session 3Document19 pagesSession 3Ramji TripathyNo ratings yet
- Nationalincome 141209072252 Conversion Gate02Document37 pagesNationalincome 141209072252 Conversion Gate02Simmi KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Me Unit-5Document7 pagesMe Unit-5Anuj YadavNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument7 pagesNational IncomeFahadNo ratings yet
- Circular Flow of IncomeDocument66 pagesCircular Flow of IncomeAshish Tewani100% (3)
- Unit IvDocument14 pagesUnit IvsudhanshuNo ratings yet
- Concepts of National IncomeDocument35 pagesConcepts of National IncomeChitraksh MahajanNo ratings yet
- Macro Eco 3Document113 pagesMacro Eco 3br bhandariNo ratings yet
- Measuring National IncomeDocument19 pagesMeasuring National Incomessaeed_4No ratings yet
- Macro Bcom New FinalDocument37 pagesMacro Bcom New FinalUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- The National Income Accounting 1Document15 pagesThe National Income Accounting 1Kyle Kenneth GarciaNo ratings yet
- Lec 9 National IncomeDocument65 pagesLec 9 National IncomeLakhan Subhash TrivediNo ratings yet
- National Income Accounting (NIA)Document8 pagesNational Income Accounting (NIA)Mamta VermaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 National Income AccountingDocument83 pagesUnit 2 National Income Accountingbrianmfula2021100% (1)
- Macroeconomics Mod 1Document18 pagesMacroeconomics Mod 12580 Soumil SinghNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note 1Document10 pagesLecture Note 1mohaimenulakborNo ratings yet
- Measuring National Income Through GDP, GNP & NNPDocument5 pagesMeasuring National Income Through GDP, GNP & NNPAkshit Kumar100% (1)
- National Income: By-Roopak Malik & Raneesh ChoudharyDocument18 pagesNational Income: By-Roopak Malik & Raneesh Choudharyemin4No ratings yet
- UNIT - IV, National Income Accounting: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) All Output Produced Within A NationDocument15 pagesUNIT - IV, National Income Accounting: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) All Output Produced Within A NationanushreeNo ratings yet
- Measurement of National IncomeDocument13 pagesMeasurement of National IncomeSrinivasan KuppusamyNo ratings yet
- CH 2 MacroeconomicsDocument63 pagesCH 2 MacroeconomicsYidid GetachewNo ratings yet
- National Income Analysis Icor and Ilor Kabupaten Situbondo Tahun 2011 A. Definition of National IncomeDocument12 pagesNational Income Analysis Icor and Ilor Kabupaten Situbondo Tahun 2011 A. Definition of National IncomeOkiq ParrotNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument9 pagesNational Incomeshahnawaz malikNo ratings yet
- National Income (Notes) IMBADocument27 pagesNational Income (Notes) IMBASubham .MNo ratings yet
- Measuring the National Income AccountDocument19 pagesMeasuring the National Income AccountAmie Lyyn CabrerosNo ratings yet
- Calculating national income and GDPDocument11 pagesCalculating national income and GDPSujan BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- Summary Of "The Economic System" By Armando Fastman: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESFrom EverandSummary Of "The Economic System" By Armando Fastman: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESNo ratings yet
- Summary of David A. Moss's A Concise Guide to Macroeconomics, Second EditionFrom EverandSummary of David A. Moss's A Concise Guide to Macroeconomics, Second EditionNo ratings yet
- Summary Of "The Economic Aggregates" By Jorge Souto: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESFrom EverandSummary Of "The Economic Aggregates" By Jorge Souto: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESNo ratings yet
- Product Analytics For DummiesDocument21 pagesProduct Analytics For DummiesHaren ShylakNo ratings yet
- Uber Case StudyDocument16 pagesUber Case StudyHaren ShylakNo ratings yet
- Product Assignment - Scheduling Interviews - by Vishal Goyal - Nov, 2023 - MediumDocument12 pagesProduct Assignment - Scheduling Interviews - by Vishal Goyal - Nov, 2023 - MediumHaren ShylakNo ratings yet
- Major Difference Between Micro and Macro EconomicsDocument7 pagesMajor Difference Between Micro and Macro EconomicsHaren ShylakNo ratings yet
- Trip Advisor Case StudyDocument3 pagesTrip Advisor Case StudyHaren ShylakNo ratings yet
- Importance of Macro EconomicsDocument9 pagesImportance of Macro EconomicsHaren ShylakNo ratings yet
- Circular Flow of Income Model in 40 CharactersDocument19 pagesCircular Flow of Income Model in 40 CharactersHaren ShylakNo ratings yet
- GTM Strategy For Nike's NeoStrideDocument3 pagesGTM Strategy For Nike's NeoStrideHaren ShylakNo ratings yet
- Nature and Scope of MacroeconomicsDocument12 pagesNature and Scope of MacroeconomicsHaren Shylak0% (1)
- 19.2 Error - Connection Reset by PeerDocument1 page19.2 Error - Connection Reset by PeerHaren ShylakNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2019-20 ECE1004 ETH VL2019201003919 Reference Material I 04-Sep-2019 CTFT Properties 6Document3 pagesFALLSEM2019-20 ECE1004 ETH VL2019201003919 Reference Material I 04-Sep-2019 CTFT Properties 6Haren ShylakNo ratings yet
- Experiment-1A Nmos I-V Characteristics: REG - NO: 18BEC0711 NAME: Nikhil SubramanianDocument4 pagesExperiment-1A Nmos I-V Characteristics: REG - NO: 18BEC0711 NAME: Nikhil SubramanianHaren ShylakNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2019-20 ECE1004 ETH VL2019201003919 Reference Material I 02-Aug-2019 FourierSeries 4Document20 pagesFALLSEM2019-20 ECE1004 ETH VL2019201003919 Reference Material I 02-Aug-2019 FourierSeries 4Haren ShylakNo ratings yet
- Say's Law of MarketDocument14 pagesSay's Law of MarketHaren ShylakNo ratings yet
- Circular Income Flow in A Three Sector and Four Sector EconomyDocument12 pagesCircular Income Flow in A Three Sector and Four Sector EconomyHaren ShylakNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2019-20 ECE1004 ETH VL2019201003919 Reference Material V 02-Aug-2019 Ref 31Document82 pagesFALLSEM2019-20 ECE1004 ETH VL2019201003919 Reference Material V 02-Aug-2019 Ref 31Haren ShylakNo ratings yet
- Fallsem2019-20 Ece1004 Eth Vl2019201003919 Reference Material IV 02-Aug-2019 Ctfs and CTFT 29Document47 pagesFallsem2019-20 Ece1004 Eth Vl2019201003919 Reference Material IV 02-Aug-2019 Ctfs and CTFT 29Haren ShylakNo ratings yet
- Labtask 2Document3 pagesLabtask 2Haren ShylakNo ratings yet
- Experiment-4 4 Bit Adder/Subtractor: REG - NO: 18BEC0711 NAME: Nikhil SubramanianDocument3 pagesExperiment-4 4 Bit Adder/Subtractor: REG - NO: 18BEC0711 NAME: Nikhil SubramanianHaren ShylakNo ratings yet
- 21 Continuous-Time Second-Order Systems: Solutions To Recommended ProblemsDocument15 pages21 Continuous-Time Second-Order Systems: Solutions To Recommended ProblemsHaren ShylakNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics - I: Dr. Yogesh Kumar ChoukikerDocument8 pagesElectrostatics - I: Dr. Yogesh Kumar ChoukikerHaren ShylakNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics - IX: Dr. Yogesh Kumar ChoukikerDocument4 pagesElectrostatics - IX: Dr. Yogesh Kumar ChoukikerHaren ShylakNo ratings yet
- Task 3 - Cmos Nand and Nor Nikhil Subramanian 18BEC0711Document3 pagesTask 3 - Cmos Nand and Nor Nikhil Subramanian 18BEC0711Haren ShylakNo ratings yet
- Fallsem2019-20 Ece1004 Eth Vl2019201003919 Reference Material IV 14-Aug-2019 Ctfs and CTFT 30Document47 pagesFallsem2019-20 Ece1004 Eth Vl2019201003919 Reference Material IV 14-Aug-2019 Ctfs and CTFT 30Haren ShylakNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2019-20 ECE1003 TH VL2019201000575 Reference Material I 04-Sep-2019 Lecture 16 19 PDFDocument7 pagesFALLSEM2019-20 ECE1003 TH VL2019201000575 Reference Material I 04-Sep-2019 Lecture 16 19 PDFHaren ShylakNo ratings yet
- Ece1003 Electromagnetic-field-Theory TH 2.1 47 Ece1003Document2 pagesEce1003 Electromagnetic-field-Theory TH 2.1 47 Ece1003Utkarsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Irjet V3i5676 PDFDocument5 pagesIrjet V3i5676 PDFHaren ShylakNo ratings yet
- 4-Terminated Lossless Transmission Line-09-Dec-2019Material - I - 09-Dec-2019 - Module - 1-3Document13 pages4-Terminated Lossless Transmission Line-09-Dec-2019Material - I - 09-Dec-2019 - Module - 1-3Haren ShylakNo ratings yet
- Electrodynamics - I: Dr. Yogesh Kumar ChoukikerDocument13 pagesElectrodynamics - I: Dr. Yogesh Kumar ChoukikerHaren ShylakNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics 5th Edition Hubbard Solutions ManualDocument21 pagesMacroeconomics 5th Edition Hubbard Solutions Manualroryhungzad6100% (26)
- An Empirical Analysis of The Effects of Student Work and AcademicDocument15 pagesAn Empirical Analysis of The Effects of Student Work and AcademicCely jisonNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2: National Income Accounting: ContentsDocument89 pagesChapter-2: National Income Accounting: ContentsFaris KhalidNo ratings yet
- Ey Worldwide Personal Tax and Immigration Guide 4 February 2021Document1,751 pagesEy Worldwide Personal Tax and Immigration Guide 4 February 2021Valeria MunteanuNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Macroeconomics Theories and Policies 10th Edition Froyen Test Bank PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Macroeconomics Theories and Policies 10th Edition Froyen Test Bank PDFprunellamarsingillus100% (9)
- Chapter One: 1.1. Background of The StudyDocument28 pagesChapter One: 1.1. Background of The StudyEmebet TesemaNo ratings yet
- National Income ConceptsDocument34 pagesNational Income ConceptsQammer ShahzadNo ratings yet
- MACROECONOMICS HOMEWORK GDPDocument7 pagesMACROECONOMICS HOMEWORK GDPNGÂN ĐẶNG HOÀNGNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic Analysis and Policy: Biswa Swarup MisraDocument40 pagesMacroeconomic Analysis and Policy: Biswa Swarup Misrakanmani FelixNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 2Document7 pagesProblem Set 1 2Ngọc NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Ecu - 08606 Lecture 6Document21 pagesEcu - 08606 Lecture 6DanielNo ratings yet
- Estate, Trust, and Heir Tax CalculationsDocument4 pagesEstate, Trust, and Heir Tax CalculationsJESTONI RAMOSNo ratings yet
- Fiscal Federalism and Power of TaxationDocument37 pagesFiscal Federalism and Power of TaxationWagner Adugna100% (1)
- Ncert Solutions For Class 12 Macroeconomics Chapter 2 National Income AccountingDocument12 pagesNcert Solutions For Class 12 Macroeconomics Chapter 2 National Income AccountingNxirjaonfbsNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet For AP EconomicsDocument3 pagesCheat Sheet For AP EconomicsMingrui QianNo ratings yet
- Module - 4 National IncomeDocument64 pagesModule - 4 National Incomelakshmi dileepNo ratings yet
- Aat 20803 Taxation II Key Highlights in Budget 2023Document10 pagesAat 20803 Taxation II Key Highlights in Budget 2023Ikmal IshamudinyyNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class-12 Economics Important Questions - Macro Economics 02 National Income AccountingDocument10 pagesCBSE Class-12 Economics Important Questions - Macro Economics 02 National Income AccountingSachin DevNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Under Canadian RegulationsDocument10 pagesIncome Tax Under Canadian Regulationshemayal0% (1)
- Practice QuestionsDocument45 pagesPractice QuestionsMẫn Chi Nguyễn PhạmNo ratings yet
- TXPOL 2019 Dec QDocument14 pagesTXPOL 2019 Dec QKAH MENG KAMNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument267 pagesUntitledGaurav KothariNo ratings yet
- Internal Generated Revenue and Economic Development: A Study of Akwa Ibom StateDocument85 pagesInternal Generated Revenue and Economic Development: A Study of Akwa Ibom Statevictor wizvikNo ratings yet
- Taxing Wages BrochureDocument16 pagesTaxing Wages BrochureYgro4wiNNo ratings yet
- Chap 1Document30 pagesChap 1Hong NguyenNo ratings yet
- 0014PIMMBXDXFDocument7 pages0014PIMMBXDXFanasfinkileNo ratings yet
- National Income Calculation MethodsDocument15 pagesNational Income Calculation MethodsRishab Jain 2027203No ratings yet
- National Income Accounting Quiz SolutionsDocument2 pagesNational Income Accounting Quiz SolutionsAngeline Maquiso SumaoyNo ratings yet
- Understanding National Income conceptsDocument33 pagesUnderstanding National Income conceptsSandip GhimireNo ratings yet
- TBS Midterm Exam MACRO 2016Document6 pagesTBS Midterm Exam MACRO 2016OussemaNo ratings yet