Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FM Bones
Uploaded by
sneha0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views12 pagesBone consists of a mineral phase and an organic matrix containing bone cells. Bones receive blood supply through nutrient arteries and penetrating periosteal vessels. Bone formation, or ossification, is the process where connective tissue differentiates and calcium is deposited. There are three main types of joints: cartilage joints with fibrocartilage, fibrous joints between bones, and synovial joints like knees and hips. X-rays, discovered by Wilhelm Rontgen in 1895, are used to image bones in different views and produce reports detailing findings and recommendations. Provisional diagnoses are given along with differential diagnoses when certainty is low.
Original Description:
Original Title
fm Bones
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBone consists of a mineral phase and an organic matrix containing bone cells. Bones receive blood supply through nutrient arteries and penetrating periosteal vessels. Bone formation, or ossification, is the process where connective tissue differentiates and calcium is deposited. There are three main types of joints: cartilage joints with fibrocartilage, fibrous joints between bones, and synovial joints like knees and hips. X-rays, discovered by Wilhelm Rontgen in 1895, are used to image bones in different views and produce reports detailing findings and recommendations. Provisional diagnoses are given along with differential diagnoses when certainty is low.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views12 pagesFM Bones
Uploaded by
snehaBone consists of a mineral phase and an organic matrix containing bone cells. Bones receive blood supply through nutrient arteries and penetrating periosteal vessels. Bone formation, or ossification, is the process where connective tissue differentiates and calcium is deposited. There are three main types of joints: cartilage joints with fibrocartilage, fibrous joints between bones, and synovial joints like knees and hips. X-rays, discovered by Wilhelm Rontgen in 1895, are used to image bones in different views and produce reports detailing findings and recommendations. Provisional diagnoses are given along with differential diagnoses when certainty is low.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
Bones
Bone consists of solid mineral phase, an organic matrix of
osteoid and bone cells- osteocyte, osteoblasts and
osteoclasts.
BLOOD SUPPLY:
1. nutrient artery accounting for the richly vascularized
medulla.
2. penetrating periosteal vessel
Bone formation ( ossification)
Ossification defined as process of connective tissues
differentiation.
Calcification is the term applied to the deposition of calcium
in tissue.
Metastatic calcification occurs when calcium is removed from
the bone for e.g hyperparathyroidism.
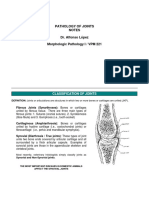
Joints
Cartilage joints: is usually of fibrocartilage type. For e.g
symphysis pubis, .intervertebral disk and sternoclavicular
joints.
Fibrous joints: found in sutures, btw radius and ulna or tibia
and fibula.
Synovial joints: joints are fingers, toes and knee, hip and
sacroiliac joint.
X-ray: (Wilhelm konrad rontgen
1895)
Views: anterior-posterior view , posterior-anterior view
&Lateral view.
REPORTS:
Name of doctor:
His qualification
Complete add with telephone numbers
Patient name age and sex with date
Details of bones:
Details of Cartilage:
Details of Soft tissue:
RECOMMENDATION:
Describe every positive findings:
Describe negative findings also which help in reaching a
diagnosis:
If patient is to be examined further give instruction:
Provisional diagnosis:
If you are very sure of diagnosis clearly mention it and ask I
to correlate clinically.
If you not sure give provisional diagnosis and write
differential diagnosis giving 3- more probabilities looking like.
THE END
You might also like
- m5 Skeletal SystemDocument33 pagesm5 Skeletal Systemapi-464344582No ratings yet
- Orthopedic NursingDocument21 pagesOrthopedic NursingCris Constantino San JuanNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Anatomy and Physiology 5Document36 pagesMusculoskeletal Anatomy and Physiology 5Dennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RMNo ratings yet
- Histology of BoneDocument20 pagesHistology of Boneyudha anantha khaerul putraNo ratings yet
- Exam A-3Document11 pagesExam A-3yapues87No ratings yet
- Orthopedic NursingDocument9 pagesOrthopedic Nursingsilimaanghang100% (3)
- Power Point Presentation SKELETAL SYSTEMDocument75 pagesPower Point Presentation SKELETAL SYSTEMaprillianlozanoNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument9 pagesFunctions of The Musculoskeletal SystemLinda XueNo ratings yet
- Bone HistologyDocument50 pagesBone HistologyMajd HusseinNo ratings yet
- Organic Matrix: 1. According To Shape and SizeDocument9 pagesOrganic Matrix: 1. According To Shape and SizePrashant PandeyNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthrosis / Osteoarthritis: Entitlement Eligibility GuidelinesDocument26 pagesOsteoarthrosis / Osteoarthritis: Entitlement Eligibility GuidelinesNinaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Bone (Assignment)Document7 pagesBiochemistry of Bone (Assignment)haseeb ShafaatNo ratings yet
- DUSTIN NUESTRO Skeletal System Lab. WorksheetDocument10 pagesDUSTIN NUESTRO Skeletal System Lab. WorksheetDustin NuestroNo ratings yet
- Histology 4 Cartilage and BoneDocument61 pagesHistology 4 Cartilage and BoneAbdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- Bone Patology PDFDocument12 pagesBone Patology PDFLuis Humberto Padilla VazquezNo ratings yet
- BonesDocument4 pagesBonesSushmitha GandhiNo ratings yet
- Histology of Bone: Presented By: Tinaye Blessing Nyamuda IDocument12 pagesHistology of Bone: Presented By: Tinaye Blessing Nyamuda Imr_cool3858No ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis LaikaDocument4 pagesOsteomyelitis LaikaAl Lai KaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument104 pagesSkeletal Systemsyafi zulNo ratings yet
- Avn On ScriptDocument13 pagesAvn On Scriptclaire.deveraNo ratings yet
- 2 Bone MetabolicDocument30 pages2 Bone MetabolicMona Rucita L. ANo ratings yet
- Chap9 JointsDocument21 pagesChap9 JointstoofangekajloolzxcvbnmNo ratings yet
- Bones and Joints: Bone Is A Specialised Connective Tissue Which HasDocument34 pagesBones and Joints: Bone Is A Specialised Connective Tissue Which HasvaishnaviNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System - JaniDocument20 pagesSkeletal System - Janijanijannahh17No ratings yet
- Skeletal System LectureDocument87 pagesSkeletal System LectureHannah Faye PacomaNo ratings yet
- Joints: Capt Poonam Singh PG ResidentDocument43 pagesJoints: Capt Poonam Singh PG ResidentSadiq Wadood SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Paget's Disease: Support. Bones Provide A Framework For The Attachment of Muscles andDocument11 pagesPaget's Disease: Support. Bones Provide A Framework For The Attachment of Muscles andAndrew MckinleyNo ratings yet
- Pathology of JointsDocument13 pagesPathology of JointswobblegobbleNo ratings yet
- Presentation OrthoDocument51 pagesPresentation OrthoPrateek ShivamNo ratings yet
- K00429 - 20180831105725 - Skeletal SystemDocument3 pagesK00429 - 20180831105725 - Skeletal Systemroesil juniNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal and Articular SystemDocument8 pagesThe Skeletal and Articular SystemAgatha joy MadrazoNo ratings yet
- What Is OsteologyDocument5 pagesWhat Is Osteology69722No ratings yet
- Anaphy Exercise 5 - SKELETAL AND ARTICULAR SYSTEMDocument12 pagesAnaphy Exercise 5 - SKELETAL AND ARTICULAR SYSTEMKenzoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Cartilage and BoneDocument5 pagesChapter 6 Cartilage and BoneSuperjunior8No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Basics of OrthopaedicsDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Basics of OrthopaedicsMD cubeNo ratings yet
- Bone & Jt. HoDocument10 pagesBone & Jt. Hojessa mae dugayNo ratings yet
- Orthopaedic SlidesDocument163 pagesOrthopaedic SlidesVivian ChepkemeiNo ratings yet
- Alveolar Bone in HealthDocument43 pagesAlveolar Bone in HealthAdit VekariaNo ratings yet
- 骨科部實習生核心課程 (20160909)Document32 pages骨科部實習生核心課程 (20160909)ChenNo ratings yet
- Cartilagebonembbsi 120126081822 Phpapp01Document28 pagesCartilagebonembbsi 120126081822 Phpapp01Muhammad AwaisNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System PhysiologyDocument17 pagesSkeletal System PhysiologyAmalia NahdaNo ratings yet
- Histology of Bone FormationDocument28 pagesHistology of Bone FormationNwaoha Chibuzor AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument31 pagesStructure and Function of The Musculoskeletal SystemSaminathan KayarohanamNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal System Notes Removed Removed-1-FrDocument23 pagesMusculoskeletal System Notes Removed Removed-1-FrSage AtimNo ratings yet
- BONE (Histology)Document65 pagesBONE (Histology)fhfebriiNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument88 pagesThe Skeletal SystemjpotiNo ratings yet
- Alveolar BoneDocument42 pagesAlveolar BonedrabhijeetsheteNo ratings yet
- Bones and Soft Tissue - Clinical GateDocument10 pagesBones and Soft Tissue - Clinical GateAkira MasumiNo ratings yet
- 2 Skeletal System HandoutDocument8 pages2 Skeletal System Handoutapi-302873465No ratings yet
- Topic 6 Skeletal SystemDocument8 pagesTopic 6 Skeletal SystemMary Ann Morillo TenederoNo ratings yet
- Week 12 Article 1 BrickleyDocument16 pagesWeek 12 Article 1 BrickleyJean-Claude TissierNo ratings yet
- BoneDocument33 pagesBoneNihal BilalNo ratings yet
- Lecture: Histology of Cartilage and BoneDocument49 pagesLecture: Histology of Cartilage and BonevictorNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology and Disease For The Health Professions 3rd Edition Booth Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesAnatomy Physiology and Disease For The Health Professions 3rd Edition Booth Solutions Manual 1stevenbrownxockdjatwe100% (18)
- Anatomy Physiology and Disease For The Health Professions 3Rd Edition Booth Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesAnatomy Physiology and Disease For The Health Professions 3Rd Edition Booth Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFcatherine.hanson719100% (17)
- Ch6Bone StudentDocument67 pagesCh6Bone Studentbhattiareeba13No ratings yet
- Alveolar BoneDocument81 pagesAlveolar BoneLavanya KalapalaNo ratings yet
- Bone 2Document4 pagesBone 2Elyka Alivan Valdez PolonioNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Bones (Salman)Document29 pagesAnatomy of Bones (Salman)Radu StoenescuNo ratings yet
- Advanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionFrom EverandAdvanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation Pleural EffusionDocument50 pagesCase Presentation Pleural EffusionsnehaNo ratings yet
- Paraplegia 070522Document25 pagesParaplegia 070522snehaNo ratings yet
- Goo Case PresentationDocument23 pagesGoo Case PresentationsnehaNo ratings yet
- Submandibular SwellingDocument19 pagesSubmandibular SwellingsnehaNo ratings yet
- Subitcha T S - Case of Thyroid SwellingDocument26 pagesSubitcha T S - Case of Thyroid SwellingsnehaNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nerve Injuries: Sneha Lakshmi Roll No 78Document9 pagesPeripheral Nerve Injuries: Sneha Lakshmi Roll No 78sneha100% (1)