Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture8-Sturtured Assembly Language Programming
Lecture8-Sturtured Assembly Language Programming
Uploaded by
Universal Hosiery Store Karad0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views14 pagesThis document discusses structured assembly language programming and flowcharts. It explains that structured assembly language programming uses a methodology to develop complicated software with minimal errors. Flowcharts aid in designing programs to solve problems and allow for corrections. Common flowchart symbols include processes, inputs/outputs, decisions, and connectors. The document provides examples of if-then-else, repeat-until, and do-while programming structures.
Original Description:
8085
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses structured assembly language programming and flowcharts. It explains that structured assembly language programming uses a methodology to develop complicated software with minimal errors. Flowcharts aid in designing programs to solve problems and allow for corrections. Common flowchart symbols include processes, inputs/outputs, decisions, and connectors. The document provides examples of if-then-else, repeat-until, and do-while programming structures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views14 pagesLecture8-Sturtured Assembly Language Programming
Lecture8-Sturtured Assembly Language Programming
Uploaded by
Universal Hosiery Store KaradThis document discusses structured assembly language programming and flowcharts. It explains that structured assembly language programming uses a methodology to develop complicated software with minimal errors. Flowcharts aid in designing programs to solve problems and allow for corrections. Common flowchart symbols include processes, inputs/outputs, decisions, and connectors. The document provides examples of if-then-else, repeat-until, and do-while programming structures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
TK2633:
MICROPROCESSOR &
INTERFACING
Structured Assembly
Language Programming
LECTURER: ASS PROF DR MASRI AYOB
Dr. Masri Ayob: TK2633
Structured Assembly Language
Programming
What is structured assembly language
programming ?
It is a programming methodology that
aids in the development of complicated
software with a minimum amount of
error.
Dr. Masri Ayob: TK2633
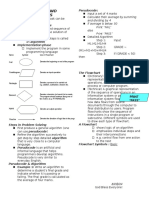
Flow Chart
Flow chart is a flow design structured programme
to solve the problems.
Flow chart also helps to correct and modify
developed software.
There are symbols to use in designing flow chart
to ease programmer. These symbols consists of
following process:
Process, predefined process, input/output, decision,
connector and terminal.
Table shows examples of symbols to use in flow
chart programme.
Dr. Masri Ayob: TK2633
Dr. Masri Ayob: TK2633
Structured Assembly Language
Programming
Process Symbol:
Shows any type of process in a programme.
Predefined process:
Usually contains the name of the subroutine or module.
Input / output symbol:
Whenever data are input to the programme or output
from the programme.
The input / output symbol usually shows the type of
data and the directioin of data flow.
Decision symbol:
Computer systems’s most capability is ability to make
decisions.
The symbol asks question to determine the direction of
programme sequence.
Dr. Masri Ayob: TK2633
Structured Assembly Language
Programming
Connector:
Eliminates crisscrossed connecting lines in
complicated flowcharts.
Ease in understanding the developed
programme.
Terminal Symbol:
Programmes all start somewhere and require
a symbol to show where they start.
Dr. Masri Ayob: TK2633
Flow chart
Flow chart example: mean calculation of a set of numbers
Dr. Masri Ayob: TK2633
If-Then-Else
Dr. Masri Ayob: TK2633
If-Then-Else
The solution.
Dr. Masri Ayob: TK2633
Repeat-Until
Allows process to be executed or repeated until an event
occurs.
Whenever this construct appears, the process first executes a
task and then a test checks for a true or a false condition.
The following figures shows the repeat-until-true and repeat-
until-false.
Dr. Masri Ayob: TK2633
Repeat-Until: Example
Reads the keyboard until a CR (carriage return) is
detected.
Dr. Masri Ayob: TK2633
Do-While
Is comparable to the repeat-until except for one basic
difference.
The do-while construct checks the condition and then, if
required, performs the process and repeats the check.
There are two forms: do-while-false and do-while-true.
Dr. Masri Ayob: TK2633
Do-While
Dr. Masri Ayob: TK2633
Thank you
Q&A
Dr. Masri Ayob: TK2633
You might also like
- Visual FoxproDocument20 pagesVisual Foxprovalentina orejuelaNo ratings yet
- Algorithm Design & Data StructuresDocument85 pagesAlgorithm Design & Data StructuresAbigail MatheNo ratings yet
- Structure of AlgorithmDocument40 pagesStructure of AlgorithmMangaras Yanu FlorestiyantoNo ratings yet
- 01Document5 pages01Ram AnandNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document14 pagesChapter 2Sadish PuriNo ratings yet
- FUNDAMENTALS UNIT 3yDocument21 pagesFUNDAMENTALS UNIT 3ylimbika zangazangaNo ratings yet
- EST102: Programming in C: The World of Problem SolvingDocument18 pagesEST102: Programming in C: The World of Problem SolvingMercy SajiNo ratings yet
- Computer Programming Lab ManualDocument159 pagesComputer Programming Lab ManualMuhammad AttiqueNo ratings yet
- VerificationDocument149 pagesVerificationP Brahma ReddyNo ratings yet
- Writing PsuedoCodeDocument31 pagesWriting PsuedoCodeapi-3814408100% (3)
- Lec.1 Algorithm & Flow ChartDocument17 pagesLec.1 Algorithm & Flow Chartهشام رعد ناجيNo ratings yet
- Algorithmic Problem SolvingDocument20 pagesAlgorithmic Problem SolvingOmegaNo ratings yet
- Flow ChartDocument60 pagesFlow Chartnavjotjyoti50% (2)
- LoopingDocument27 pagesLoopingHoneyNo ratings yet
- C NotesDocument11 pagesC NotesKh JlNo ratings yet
- What Is Computer Science?Document43 pagesWhat Is Computer Science?Franz Ivan De VillaNo ratings yet
- Computer Programming: Algorithms and Control StructuresDocument61 pagesComputer Programming: Algorithms and Control Structureskurddoski28No ratings yet
- Algorithms, Pseudo Code, FlowchartDocument6 pagesAlgorithms, Pseudo Code, Flowchartazuka_devil66674850% (1)
- Pseudo Code Algorithm FlowchartDocument11 pagesPseudo Code Algorithm FlowchartOm Prakash Mahato100% (5)
- (A) Computer Application 40 Marks TheoryDocument8 pages(A) Computer Application 40 Marks TheoryGourav SainiNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Algorithm DesignDocument18 pages2.2 Algorithm DesignElly StephenNo ratings yet
- Class 3 - AlgorithmsDocument12 pagesClass 3 - Algorithmschinmayamalik861No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document32 pagesChapter 2yohans shegawNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Problem Solving StrategiesDocument6 pages1.2 Problem Solving StrategiesKalai SureshNo ratings yet
- ch2 Lec1Document62 pagesch2 Lec1Dagmawe ZewengelNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 NotesDocument5 pagesUnit 2 NotesVishal DeoreNo ratings yet
- PF Lecture2Document51 pagesPF Lecture2Shafaq YousufNo ratings yet
- Black-Box Testing: Test ProceduresDocument15 pagesBlack-Box Testing: Test ProceduresAlishbah Khan NiaziiNo ratings yet
- Types of TestBench and Fork JoinDocument46 pagesTypes of TestBench and Fork JoinEman zakriaNo ratings yet
- Symbols: Flowline ConnectorDocument11 pagesSymbols: Flowline ConnectorJada CameronNo ratings yet
- PCD Lab Manual 2017Document46 pagesPCD Lab Manual 2017Shubhajit MallickNo ratings yet
- Scott Hudson (2014) - Scilab Lectures. Pág. 1-9Document16 pagesScott Hudson (2014) - Scilab Lectures. Pág. 1-9Francisco AristizabalNo ratings yet
- FlowchartDocument7 pagesFlowchartsharmashnNo ratings yet
- What Is A Programming AlgorithmDocument10 pagesWhat Is A Programming AlgorithmWalea Nama DhugaNo ratings yet
- 2 Problem SolvingDocument19 pages2 Problem SolvingNarasimhan TNo ratings yet
- Problem-Solving and Design AS - 1Document97 pagesProblem-Solving and Design AS - 1do0020No ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Algorithm and FlowchartDocument31 pagesTopic 2 - Algorithm and FlowchartPamela EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 Past Paper and Excercise QuestionsDocument10 pagesChapter 02 Past Paper and Excercise Questionssana mahmoodNo ratings yet
- 2 ProblemSolvingDocument40 pages2 ProblemSolvingMadeehah AatifNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving: Algorithms and FlowchartsDocument19 pagesProblem Solving: Algorithms and Flowchartssyed abdullahNo ratings yet
- The Structure of An Awk Program: Pattern (Action) Pattern (Action)Document12 pagesThe Structure of An Awk Program: Pattern (Action) Pattern (Action)Ray ChiranjibiNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note: Week 1Document15 pagesLecture Note: Week 1Devesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- 1 Overview To System DevelopmentDocument7 pages1 Overview To System DevelopmentMay-ann NoricoNo ratings yet
- Problem SolvingDocument90 pagesProblem SolvinghsamailaNo ratings yet
- 1 Algorithm Pseudocode FlowchartDocument32 pages1 Algorithm Pseudocode FlowchartDanielNo ratings yet
- White Box Testing: A Complete Guide With Techniques, ExamplesDocument9 pagesWhite Box Testing: A Complete Guide With Techniques, ExamplesDharaiya Text-tilesNo ratings yet
- Lecture06 Computer Fundamentals and ProgrammingDocument34 pagesLecture06 Computer Fundamentals and ProgrammingXentrix CritzNo ratings yet
- Notes For Computer Science 10th Class BISEDocument18 pagesNotes For Computer Science 10th Class BISEH S Wajid Hussain88% (72)
- Lab 3: Unix and LinuxDocument3 pagesLab 3: Unix and LinuxMichael FiorelliNo ratings yet
- Studocu DAA Unit 1 NotesDocument52 pagesStudocu DAA Unit 1 Notesthefamousbro123No ratings yet
- 3 - Lecture 3Document37 pages3 - Lecture 3Mohammed MelhemNo ratings yet
- CC FinalsDocument14 pagesCC Finalsabdullah kahloonNo ratings yet
- Problem-Solving and Design AS - 1Document96 pagesProblem-Solving and Design AS - 1LisaNo ratings yet
- Algorithms and FlowchartsDocument12 pagesAlgorithms and FlowchartsGeovanni Collantes DumpasanNo ratings yet
- o Levelcomputer Ruknuddin Patels Web PortalDocument29 pageso Levelcomputer Ruknuddin Patels Web Portaltahir.76224No ratings yet
- Performance PDFDocument109 pagesPerformance PDFRafa SoriaNo ratings yet
- Pseudocode NotesDocument4 pagesPseudocode Notestarrant HighNo ratings yet
- Notes For Computer Science 10th Class BISEDocument18 pagesNotes For Computer Science 10th Class BISEsajidazeem2013100% (1)
- Hacks To Crush Plc Program Fast & Efficiently Everytime... : Coding, Simulating & Testing Programmable Logic Controller With ExamplesFrom EverandHacks To Crush Plc Program Fast & Efficiently Everytime... : Coding, Simulating & Testing Programmable Logic Controller With ExamplesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Advanced SAS Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandAdvanced SAS Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNo ratings yet
- Lecture11 Time DelayDocument20 pagesLecture11 Time DelayUniversal Hosiery Store KaradNo ratings yet
- Lecture10-Fixed Point ArithmeticDocument24 pagesLecture10-Fixed Point ArithmeticUniversal Hosiery Store KaradNo ratings yet
- Lecture7 Assembly LanguageDocument36 pagesLecture7 Assembly LanguageUniversal Hosiery Store KaradNo ratings yet
- Lecture9 Programming Techniques Looping CounterDocument18 pagesLecture9 Programming Techniques Looping CounterUniversal Hosiery Store KaradNo ratings yet
- Title of ResearchDocument4 pagesTitle of ResearchMohsin AzeemNo ratings yet
- How To Force A Crash Dump On SPARC T5Document4 pagesHow To Force A Crash Dump On SPARC T5Tolulope AbiodunNo ratings yet
- Software Testing: Katalon StudioDocument15 pagesSoftware Testing: Katalon StudioNguyên HưngNo ratings yet
- Feedback Control SystemDocument32 pagesFeedback Control SystemKelvin KongNo ratings yet
- KUNAL GUPTA 19212220 - How To Move From Paper To Impact in Business Process Management - The Journey of SAP (CIA-1-B)Document3 pagesKUNAL GUPTA 19212220 - How To Move From Paper To Impact in Business Process Management - The Journey of SAP (CIA-1-B)NARANG MAHIR 19215034No ratings yet
- Smart Electrical Technology: Normal (Technical) Examination SyllabusDocument18 pagesSmart Electrical Technology: Normal (Technical) Examination Syllabuskarthik karthikNo ratings yet
- Epicor10 APHierarchy 102200 PDFDocument26 pagesEpicor10 APHierarchy 102200 PDFWarian PTINo ratings yet
- Internal Controls ITGCs Part 1 Introduction To ITGCs HandoutDocument3 pagesInternal Controls ITGCs Part 1 Introduction To ITGCs Handoutcharm.lopezz12No ratings yet
- Lakewood PoliceDept HistoryBook SinglePg WebDocument122 pagesLakewood PoliceDept HistoryBook SinglePg WebNick PaleyNo ratings yet
- 154.45.4021 EN KPLC User Guide V.72-73 R.05Document15 pages154.45.4021 EN KPLC User Guide V.72-73 R.05Mustafa BalNo ratings yet
- Boarding PassDocument1 pageBoarding Passyadagirireddy bolluNo ratings yet
- Brownfield Iot Development: Benefits of The Road Less TravelledDocument21 pagesBrownfield Iot Development: Benefits of The Road Less TravelledAdarsh AjNo ratings yet
- Ug470 7series Config PDFDocument180 pagesUg470 7series Config PDFabc789159No ratings yet
- Work Experience: Kohnadi Construction CompanyDocument3 pagesWork Experience: Kohnadi Construction CompanyEhsan Ullah MurwatNo ratings yet
- What Is Reengineering?: Some Common Descriptions About What ItisandwhatitisnotDocument4 pagesWhat Is Reengineering?: Some Common Descriptions About What ItisandwhatitisnotRohit ShahNo ratings yet
- Sentry Video Quality Monitor Datasheet 10Document8 pagesSentry Video Quality Monitor Datasheet 10Carlos PipiNo ratings yet
- VLF CR-28 - Up To 60 KV: BenefitsDocument4 pagesVLF CR-28 - Up To 60 KV: BenefitslblancoingNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Energy Consumption in Smart Homes Using Machine Learning TechniquesDocument7 pagesOptimizing Energy Consumption in Smart Homes Using Machine Learning TechniquesLakshmana Nainar Sundar S.No ratings yet
- Aztech DSL605EU DatasheetDocument2 pagesAztech DSL605EU DatasheetownlinkscribdNo ratings yet
- Pspice Bjtamp DC SweepDocument3 pagesPspice Bjtamp DC SweepManoj KavediaNo ratings yet
- Sharp Dojo Content GuidelineDocument64 pagesSharp Dojo Content GuidelineCSNo ratings yet
- Yan 2015 PRN DPABIDocument39 pagesYan 2015 PRN DPABIzhuyi biNo ratings yet
- An Introductory Guide To Facebook For Business-2Document61 pagesAn Introductory Guide To Facebook For Business-2fskhsfkhkfshkhfsNo ratings yet
- PDF Kendall Sad9 Im 03 - Compress PDFDocument45 pagesPDF Kendall Sad9 Im 03 - Compress PDFThania FlorantiNo ratings yet
- Write A Routine To Call PRODUCE - DEAL.SLIP As Shown BelowDocument3 pagesWrite A Routine To Call PRODUCE - DEAL.SLIP As Shown BelowGopal ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Office 2003Document10 pagesMicrosoft Office 2003Yu BenNo ratings yet
- Xcode Tutorial For Beginners (Just Updated For Xcode 11)Document77 pagesXcode Tutorial For Beginners (Just Updated For Xcode 11)Carlos ParraNo ratings yet
- 6.888 Advanced Topics in Networking: Lecture 1: IntroductionDocument51 pages6.888 Advanced Topics in Networking: Lecture 1: Introductionsetia wulandariNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Computers of The WorldDocument7 pagesTop 10 Computers of The WorldArham SheikhNo ratings yet