Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acoustic Neuroma 2
Acoustic Neuroma 2
Uploaded by
krunal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views14 pagesAcoustic neuroma is a tumor that originates from the vestibular branch of the acoustic nerve. It most commonly affects people between 30-50 years old and presents unilaterally in the majority of cases. Symptoms include progressive hearing loss, tinnitus, unbalance, and compression of nearby nerves causing issues like facial pain or numbness. Diagnosis involves audiometry tests, imaging like CT or MRI to view the tumor size and location, and neurological exams. Treatment options include surgical removal through the middle cranial fossa, translabyrinthine, or retrosigmoid approaches depending on hearing status and tumor size, or non-surgical options like gamma knife radiosurgery or observation.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAcoustic neuroma is a tumor that originates from the vestibular branch of the acoustic nerve. It most commonly affects people between 30-50 years old and presents unilaterally in the majority of cases. Symptoms include progressive hearing loss, tinnitus, unbalance, and compression of nearby nerves causing issues like facial pain or numbness. Diagnosis involves audiometry tests, imaging like CT or MRI to view the tumor size and location, and neurological exams. Treatment options include surgical removal through the middle cranial fossa, translabyrinthine, or retrosigmoid approaches depending on hearing status and tumor size, or non-surgical options like gamma knife radiosurgery or observation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views14 pagesAcoustic Neuroma 2
Acoustic Neuroma 2
Uploaded by
krunalAcoustic neuroma is a tumor that originates from the vestibular branch of the acoustic nerve. It most commonly affects people between 30-50 years old and presents unilaterally in the majority of cases. Symptoms include progressive hearing loss, tinnitus, unbalance, and compression of nearby nerves causing issues like facial pain or numbness. Diagnosis involves audiometry tests, imaging like CT or MRI to view the tumor size and location, and neurological exams. Treatment options include surgical removal through the middle cranial fossa, translabyrinthine, or retrosigmoid approaches depending on hearing status and tumor size, or non-surgical options like gamma knife radiosurgery or observation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
Acoustic Neuroma
NAME: KRUNAL VIMALBHAI RAJPARA
PASSPORT NO.:N2334646
CIU
Background
Originate from vestibular
branch of acoustic nerve
Histological feature:
schwanoma, neuroma,
neurolemmoma
Predilection: 30-50y
Unilateral: majority
Bilateral: Type II acoustic
neuroma
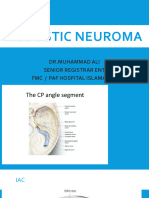
Pathology
Predominate: internal
auditory canal
Extension to CPA
Compression on brainstem
and brain hydrops
Anterior: trigeminal
nerve,
Medial: abducent nerve
Inferior: IX, X, XI, XII
Clinical presentations
Hearing loss and tinnitus
Progressive HL 90%
SDS reduction
10% of patients complain of sudden HL.
Unbalance
Otalgia and compression due to depression of
sensor fiber of facial nerve
Involvement of trigeminal nerve
Compression of cerebellum and brainstem: ataxia,
nystagmus and intracranial hypo-pressure
Work-up
Audiometry
PTA: threshold elevated in high frequency
tone decay test: positive
Speech audiometry
Acoustic impedance
ABR: latency of wave V prolongs, or wave V disappears
Acoustic emission
Work-up
Vestibular function:
Neurologic exam
Image study
CT shows enlargement of
internal auditory canal
MRI
Managements
Surgery
Middle cranionectomy:
useful hearing
Translabyrinectomy:
no useful hearing
Nice exposure of facial nerve
Managements
Retro-sigmoid sinus approach:
Inferior occipital approach:
Big tumor >3cm
Nice exposure tumor
Managements
No surgical intervention
-Knife
observation
THANK YOU
You might also like
- Carlos Herraiz - HYPERACUSISDocument45 pagesCarlos Herraiz - HYPERACUSISavalon_moonNo ratings yet
- Tinnitus 2Document35 pagesTinnitus 2Wael ShamyNo ratings yet
- Rosh NeuroDocument11 pagesRosh NeuroSoni AliNo ratings yet
- Hearing Loss: Mubarak MD Dhawal Mbbs (Iua), Morl (Mak) ENT Lecturer April 2019Document46 pagesHearing Loss: Mubarak MD Dhawal Mbbs (Iua), Morl (Mak) ENT Lecturer April 2019gibreilNo ratings yet
- MeningiomaDocument37 pagesMeningiomaFyodorovich Makarov Nikolai100% (1)
- Vestibular SchwannomasDocument22 pagesVestibular SchwannomasKrisha Anne TaotaoNo ratings yet
- TinnitusDocument26 pagesTinnitusDillan ShettyNo ratings yet
- Respiratory EmergenciesDocument21 pagesRespiratory EmergenciesMohamed Anas SayedNo ratings yet
- Etiology and Diagnosis of Tinnitus - UpToDateDocument18 pagesEtiology and Diagnosis of Tinnitus - UpToDateAdri NolascoNo ratings yet
- Facial Nerve ParalysisDocument73 pagesFacial Nerve ParalysisAys Ghaysa100% (1)
- Tinnitus: Dr. Naveen. G Iind Year Post Graduate Dept. of Ent VMKVMCH, SalemDocument35 pagesTinnitus: Dr. Naveen. G Iind Year Post Graduate Dept. of Ent VMKVMCH, SalemDr. Naveen. GNo ratings yet
- Laryngitis, Laryngeal Paralysis, DDX of Stridor, StertorDocument44 pagesLaryngitis, Laryngeal Paralysis, DDX of Stridor, StertorDurand S. KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Birth TraumaDocument41 pagesBirth TraumaIbrahim Rasim100% (1)
- TinnitusDocument60 pagesTinnitusYowendruJunNo ratings yet
- Acoustic Neuroma: Chunfu Dai M.D & PH.DDocument10 pagesAcoustic Neuroma: Chunfu Dai M.D & PH.DDrravikumar BhandariNo ratings yet
- Tinnitus Grand Rounds: Edward Buckingham, M. D. Jeff Vrabec, M. D., Faculty Sponcer Francis Quinn, M.D., Series EditorDocument61 pagesTinnitus Grand Rounds: Edward Buckingham, M. D. Jeff Vrabec, M. D., Faculty Sponcer Francis Quinn, M.D., Series EditorShauki AliNo ratings yet
- Acoustic Neuroma: Anton B. DarmawanDocument9 pagesAcoustic Neuroma: Anton B. DarmawanHappy MuthiaNo ratings yet
- 9 27 06 Fuller Acoustic Neuroma0Document14 pages9 27 06 Fuller Acoustic Neuroma0frabziNo ratings yet
- Lower Cranial NervesDocument83 pagesLower Cranial NervesVamsi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- 17 Neoplasms of The EarDocument49 pages17 Neoplasms of The Earsunil paiNo ratings yet
- Acoustic NeuromaDocument31 pagesAcoustic NeuromaHreem FarrakhNo ratings yet
- SSNHL SlidesDocument64 pagesSSNHL SlidesRAHMANo ratings yet
- Absite Topics 4-6: Nir HusDocument7 pagesAbsite Topics 4-6: Nir HusIfeanyichukwu OgbonnayaNo ratings yet
- Schwannoma Vestibular TinnitusDocument6 pagesSchwannoma Vestibular TinnitusThomasMáximoMancinelliRinaldoNo ratings yet
- Approach To TinnitusDocument40 pagesApproach To TinnitusAavash PradhanNo ratings yet
- Neuro4Nurses Acustic NeuromaDocument2 pagesNeuro4Nurses Acustic Neuromaputri auliyahNo ratings yet
- 8 Sowmiya EtalDocument4 pages8 Sowmiya EtaleditorijmrhsNo ratings yet
- Imaging of TinnitusDocument8 pagesImaging of TinnitusDianithus169No ratings yet
- Vocal Cord ParalysisDocument74 pagesVocal Cord ParalysisWaqas KhanNo ratings yet
- Auricula 2 PDFDocument27 pagesAuricula 2 PDFCamy Alejandra Gonzales GonzalesNo ratings yet
- System: Chapter 161:tinnitus and Hyperacus SDocument4 pagesSystem: Chapter 161:tinnitus and Hyperacus Sfrita1986No ratings yet
- Acoustic NeuromaDocument4 pagesAcoustic NeuromaEmily AnnNo ratings yet
- Presbycusis 181116131215 PDFDocument66 pagesPresbycusis 181116131215 PDFWael ShamyNo ratings yet
- Nasopharyngeal CarcinomaDocument44 pagesNasopharyngeal CarcinomapopoyingNo ratings yet
- Overview of TinnitusDocument11 pagesOverview of TinnitusJohn JoseNo ratings yet
- Vocal Cord Palsy: An Uncommon Presenting Feature of Myasthenia GravisDocument4 pagesVocal Cord Palsy: An Uncommon Presenting Feature of Myasthenia GravisDivine Jane PurciaNo ratings yet
- Dizziness 3Document37 pagesDizziness 3Anurag SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Penanganan Kegawatdaruratan Pada Trauma Cervicalis: Pembimbing: Dr. Akhyar H. Nasution, SP - An, KAKVDocument67 pagesPenanganan Kegawatdaruratan Pada Trauma Cervicalis: Pembimbing: Dr. Akhyar H. Nasution, SP - An, KAKVAnusha ChandransikaranNo ratings yet
- Brainstem Evoked ResponseDocument57 pagesBrainstem Evoked ResponseGerald PagalingNo ratings yet
- Acoustic NeuromaDocument33 pagesAcoustic NeuromahafizNo ratings yet
- Ocupational Hearing LossDocument38 pagesOcupational Hearing LossNIKOLAOS CHATZAKISNo ratings yet
- Tuli Mendadak (Sudden Deafness)Document26 pagesTuli Mendadak (Sudden Deafness)Marisa FatkiyaNo ratings yet
- Suddensnhl 160220190525Document80 pagesSuddensnhl 160220190525mariahovhannisyanNo ratings yet
- Tinnitus Update 2021Document10 pagesTinnitus Update 2021tumi maryNo ratings yet
- Meniere's DiseaseDocument50 pagesMeniere's DiseaseRaisa CleizeraNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomical Considerations of Isolated Hearing Loss in Thalamic HemorrhageDocument3 pagesNeuroanatomical Considerations of Isolated Hearing Loss in Thalamic HemorrhageBella Cynthia BettabestariNo ratings yet
- Preoperative Management of CP Angle TumorDocument18 pagesPreoperative Management of CP Angle TumorDrSayk YousufNo ratings yet
- Preoperative Management of CP Angle TumorDocument18 pagesPreoperative Management of CP Angle TumorDrSayk YousufNo ratings yet
- SNHL (19 Dec)Document11 pagesSNHL (19 Dec)ismailmazhar9988No ratings yet
- Barotrauma 4Document8 pagesBarotrauma 4nurmawinawanNo ratings yet
- Hertzano 2020Document12 pagesHertzano 2020Moisés AarónNo ratings yet
- Case PresentationDocument26 pagesCase PresentationJason OngNo ratings yet
- 15 Menieres DiseaseDocument72 pages15 Menieres DiseaseDrravikumar BhandariNo ratings yet
- TTH Journal 4 PDFDocument5 pagesTTH Journal 4 PDFRumah Kost Kontrakan AntapaniNo ratings yet
- Ent Emergencies: DR Mohammad Almayouf Associat Consultant ENTDocument27 pagesEnt Emergencies: DR Mohammad Almayouf Associat Consultant ENTMuhammad ANo ratings yet
- Tinnitus: Causes and Clinical Management: Cite This PaperDocument12 pagesTinnitus: Causes and Clinical Management: Cite This PaperMuhammad RumiNo ratings yet
- TRI Tinnitus FlowchartDocument106 pagesTRI Tinnitus FlowchartSidharthMahotraNo ratings yet
- 2 5400160637227631067 PDFDocument7 pages2 5400160637227631067 PDFSiska HarapanNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation AudiologyDocument17 pagesCase Presentation AudiologynuhaNo ratings yet