Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class 8 21th
Uploaded by
Abdulmonir Mominyar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views9 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views9 pagesClass 8 21th
Uploaded by
Abdulmonir MominyarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
Introduction
The kingdom Plantae constitutes large and varied groups
of organisms. There are more than 300,000 species of
classified plants. Of these, more than 260,000 are seed
plants. But mosses and ferns are also members of the plant
kingdom. Most biologists also consider some green algae
to be plants, although others exclude all algae from the
plant kingdom. The reason for this disagreement stems
from the fact that not all algae but only green algae, the
Chlorophytes and Charophytes, share common
characteristics with land plants.
Characteristics of Plants
Organisms living on land have to solve several challenges in the
terrestrial environment such as:
Desiccation, or drying out, is a constant danger for an organism
exposed to air. Even when parts of a plant are close to a source of
water, other parts are in danger of drying out.
On land, plants need to develop structural support.
The land organisms are also subject to radiation coming from the sun
because air does not filter out ultraviolet rays of sunlight.
The male gametes must reach the female gametes and both gametes
and zygotes must be protected from desiccation.
Not all plants have strategies to cope with all at once. Some
species never move very far from the aquatic environment,
whereas others have structures to conquer the driest
environments on Earth. Plants need temperatures above freezing
while they are actively growing and photosynthesizing. They also
need sunlight, carbon dioxide and water for photosynthesis. Like
most other organisms, plants need oxygen for cellular respiration
and minerals to build proteins and other organic molecules. Most
plants support themselves above the ground with stems in order
to get light, carbon dioxide and oxygen. Most plants also grow
roots down into the soil to absorb water and minerals.
During photosynthesis, plants take in carbon dioxide from
the air and water from the soil. Plant cells with the light
absorbing pigment chlorophyll transform the water and the
carbon dioxide into glucose by using the energy from the
sunlight. Oxygen is produced as a by product. The plant
then releases the oxygen into the air. The chlorophyll, the
light absorbing pigment, which is responsible for giving
the plant its green color, absorbs energy from the sunlight
and make the energy from the sun available for food
production. Unlike prokaryotic organisms, the
chlorophylls are placed in an organelle called chloroplast.
Plants are multicellular eukaryotes: Eukaryotes are
organisms whose cells contain a nucleus and other
membrane-bound organelles. All plants are
multicellular.
Plants need external factors for reproduction: As
non-motile organisms, plants are dependent on
external factors, such as wind, water, or animals, to
complete sexual reproduction and disperse their
genetic presence to distant locations. In the simplest
land plants, sperm cells swim to eggs through water.
Plants are photosynthetic: Plants are primarily photo
autotrophs (autotrophs that use light) except obligate
parasitic plants, they can produce their organic food by
photosynthesis in which oxygen is released as a byproduct.
Most life on Earth depends on photosynthesis.
Plant growth is limitless: Most plants have no defined size
or shape, though some have a well-defined lifespan. They
expand indefinitely, adding new photosynthetic and
absorptive organs throughout their life. Growth in plants
is carried out in specialized tissues called meristems.
Diversity of Plants
An incredible variety of plants populates the terrestrial
landscape. From simple to complex designs, plants may
grow across the forest floor, on rocks, on other plants or
even on animals. While seed plants have adaptations that
allow them to populate even the most arid habitats on
Earth, dependence on water is the major factor that
defines their distribution in all plants. In plant
classification, the formation of seed (and flower) during
reproduction is one of the major characteristics and the
presence of a transport system is the second one.
The physical characteristics are common to all
plants but within the plant kingdom, there are four
fundamentally different types of plants, each of which
has its own unique set of physical features. These are
the non-vascular seedless plants, which include
mosses; the vascular seedless plants, which include
ferns; the gymnosperms, which include coniferous
(cone-bearing) trees; and the angiosperms, a vast
division of flowering plants.
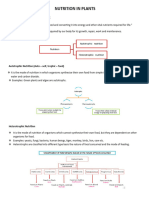
Kingdom Plantae: 1. Seed Plants
2. Seedless plants
1: Seed plants: A. Flowering Seed Plants
Angiosperms (Hide seed), B. Cone-bearing Seed
Plants Gymnosperms
2: Seedless plants: A. Non-Vascular Seedless
Plants B. Vascular Seedless Plants
You might also like
- SBI 3U Final Exam Review Part 2Document4 pagesSBI 3U Final Exam Review Part 2Sama GIlaniNo ratings yet
- 25.1 Early Plant Life: Algae and Evolutionary Paths To PhotosynthesisDocument7 pages25.1 Early Plant Life: Algae and Evolutionary Paths To Photosynthesisklavier10244379No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document5 pagesChapter 3Lebanan Aprille MarieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25. Seedless PlantsDocument76 pagesChapter 25. Seedless PlantsRicardo RicoNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument21 pagesNutrition in PlantsRavinder Sutari100% (1)
- CHAPTER 1 Bhsa InggrisDocument8 pagesCHAPTER 1 Bhsa InggrisNurmalasariNo ratings yet
- CBSE NCERT Class 7 Science Nutrition in PlantsDocument7 pagesCBSE NCERT Class 7 Science Nutrition in PlantsAmos JosephatNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument12 pagesNutrition in Plantsdvrao_chowdaryNo ratings yet
- Resume Plants Structure SRI UTAMI 2084205034 2.2 PbioDocument1 pageResume Plants Structure SRI UTAMI 2084205034 2.2 PbioSri Az-zahraNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Plants Class 7 Science Notes - Chapter 1Document5 pagesNutrition in Plants Class 7 Science Notes - Chapter 1Yash ArdeshnaNo ratings yet
- Rawr ProjectDocument1 pageRawr ProjectCheska Jamilla SantiagoNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument20 pagesDocumentMohammad Daniyal SidiquieNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Plants Class 7 Science NotesDocument4 pagesNutrition in Plants Class 7 Science NotesshravandownloadNo ratings yet
- Bio EssayDocument6 pagesBio EssayPEONo ratings yet
- W7 NotesDocument21 pagesW7 NotesAmy SuarezNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 1 Nutrition in PlantsDocument5 pagesCBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plantsgtbit.cse.aashishNo ratings yet
- Variety of Living OrganismDocument60 pagesVariety of Living OrganismThaw ThawNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School - Bopal, Ahmedabad (2021-22) : Class: VII Subject: Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants Study NotesDocument10 pagesDelhi Public School - Bopal, Ahmedabad (2021-22) : Class: VII Subject: Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants Study Notesbhargav guptaNo ratings yet
- The First Plants Grow on Land: The Golden Serie of History: From the First Life Forms to the Latest Humanoid Robot, #3From EverandThe First Plants Grow on Land: The Golden Serie of History: From the First Life Forms to the Latest Humanoid Robot, #3No ratings yet
- C H A P T e R VA IDocument8 pagesC H A P T e R VA IArnel AdinoNo ratings yet
- Seedless PlantsDocument52 pagesSeedless PlantsEdnin Francisco100% (1)
- 3.unit - I, Subunit-C, Producers, Consumers and Decomposers in An EcosystemDocument2 pages3.unit - I, Subunit-C, Producers, Consumers and Decomposers in An Ecosystemmilf hunterNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Plants or Nutrients in Plants For Class 7 CBSE Science PDFDocument8 pagesNutrition in Plants or Nutrients in Plants For Class 7 CBSE Science PDFAtanu Ghosh100% (1)
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument6 pagesNutrition in PlantsSarada KasyapNo ratings yet
- Principles of Crop ProductionDocument6 pagesPrinciples of Crop ProductionJanice VaflorNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument14 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESIStintin plataNo ratings yet
- Group DiscussionDocument4 pagesGroup DiscussionVijay RohillaNo ratings yet
- Science SCMDocument98 pagesScience SCMKoustavi ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- NCERT-class 7 Science - SummaryDocument181 pagesNCERT-class 7 Science - Summarypawan nishalNo ratings yet
- Class 7 SCIENCE CH 1Document20 pagesClass 7 SCIENCE CH 1Saurabh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Biology Book ReportDocument7 pagesBiology Book ReportDebbyshumNo ratings yet
- The Amazing World of PlantsDocument4 pagesThe Amazing World of PlantsFabrizio MVNo ratings yet
- Extinct of Plants and Animals Species in IndiaDocument1 pageExtinct of Plants and Animals Species in IndiaHarshal PandavNo ratings yet
- Abiotic and Biotic Components Free Essay ExampleDocument5 pagesAbiotic and Biotic Components Free Essay ExampleEnash RidNo ratings yet
- Introduction Class: Plant Morphology, Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument29 pagesIntroduction Class: Plant Morphology, Anatomy and PhysiologykerryNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes SummaryDocument12 pagesBiology Notes Summaryrobin.kipchumbaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 - Abiotic Components of An EcosystemDocument3 pagesLesson 8 - Abiotic Components of An EcosystemAbegail HernandezNo ratings yet
- About Plants For KidsDocument2 pagesAbout Plants For KidsSumaiya FaizalNo ratings yet
- Formative TestDocument2 pagesFormative TestNahya kamilaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Plant?Document35 pagesWhat Is A Plant?Precious UdoadaNo ratings yet
- Biology Photosynthesis How Do Plants Get Their Energy?Document11 pagesBiology Photosynthesis How Do Plants Get Their Energy?rickyNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Fungi and PlantsDocument3 pagesDifference Between Fungi and PlantsAgrimonyNo ratings yet
- Actividad 1 U4Document13 pagesActividad 1 U4Lesem Jahdai Moo PisteNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Submitted To: Dr. JS DEOL Submitted By: Anish Jalota (L-2015-A-1-BTFT) 1 YearDocument19 pagesAssignment: Submitted To: Dr. JS DEOL Submitted By: Anish Jalota (L-2015-A-1-BTFT) 1 YearAnish JalotaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument16 pagesUntitledArnav SNo ratings yet
- Process of Plants/Crops Making Their Food and The Importance To Study The Mechanism For Plant PhysiologistsDocument17 pagesProcess of Plants/Crops Making Their Food and The Importance To Study The Mechanism For Plant PhysiologistsJos siNo ratings yet
- DavongDocument4 pagesDavongArthadian De PeraltaNo ratings yet
- What Is Plant Physiology BOTANYDocument12 pagesWhat Is Plant Physiology BOTANYfatima manzoorNo ratings yet
- Sinh Li Thuc VatDocument83 pagesSinh Li Thuc VatNguyễn HiếuNo ratings yet
- Plaant WorldDocument10 pagesPlaant WorldBallen ZayrNo ratings yet
- AP Biology - Chapter 29 NotesDocument9 pagesAP Biology - Chapter 29 NotesTrinidad AlcalaNo ratings yet
- Study Questions EcologyDocument9 pagesStudy Questions EcologyLaya ShrbagiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Botany: Exploratory Science-Period 6Document6 pagesIntroduction To Botany: Exploratory Science-Period 6erincoleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Plant ProcessesDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Plant ProcessesRajiv SinghNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument4 pagesNutrition in PlantsAaron Dave CanteroNo ratings yet
- Algae JupebDocument6 pagesAlgae JupebDavid AsuquoNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms Get NutritionDocument1 pageHow Do Organisms Get NutritionlucyNo ratings yet
- Camp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.From EverandCamp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.No ratings yet
- Understanding Photosynthesis with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandUnderstanding Photosynthesis with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet