100% found this document useful (2 votes)
3K views44 pagesLiteracy and Numeracy Remediation Strategies
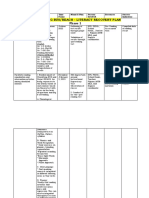
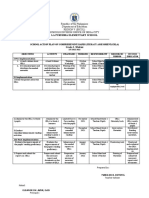
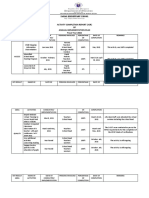
This document discusses remediation and intervention lessons for literacy and numeracy. It defines literacy, numeracy, remediation and intervention. Remediation aims to heal or cure learning difficulties, while intervention seeks to improve a situation. Both programs are designed to close gaps between what learners know and what is expected. The document outlines principles of remediation for reading and math, including differentiated instruction, small group work and building self-esteem. Effective remediation considers learner strengths, uses multiple teaching strategies and representations, and accounts for issues like disabilities, attention, memory and motivation.
Uploaded by
Labelle RamosCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (2 votes)
3K views44 pagesLiteracy and Numeracy Remediation Strategies
This document discusses remediation and intervention lessons for literacy and numeracy. It defines literacy, numeracy, remediation and intervention. Remediation aims to heal or cure learning difficulties, while intervention seeks to improve a situation. Both programs are designed to close gaps between what learners know and what is expected. The document outlines principles of remediation for reading and math, including differentiated instruction, small group work and building self-esteem. Effective remediation considers learner strengths, uses multiple teaching strategies and representations, and accounts for issues like disabilities, attention, memory and motivation.
Uploaded by
Labelle RamosCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd