Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biogeographic Zones
Uploaded by
Anand BedgujarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biogeographic Zones
Uploaded by
Anand BedgujarCopyright:
Available Formats
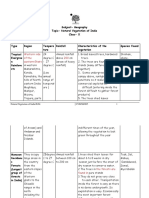
BIOGEOGRAPHIC ZONES OF
INDIA
THE HIMALAYAS
The Himalayas consist of the youngest and loftiest mountain chains in the
world. The Himalayas have attained a unique personality owing to their
high altitude, steep gradient and rich temperate flora.Oak, chestnut,
TRANS-HIMALAYAN REGON
The Himalayan ranges immediately north of the Great
Himalayan range are called the Trans- Himalayas. The Trans-
conifer, ash, pine, deodar are abundant in Himalayas. Chief species Himalayan region with its sparse vegetation h as the richest
include wild sheep, mountain goats, ibex, shrew, and tapir. THE GANGETIC PLAIN wild sheep and goat community in the world.The faunal
In the North is the Gangetic plain extending up to groups best represented here are wild sheep and goats (chief
the Himalayan foothills. This is the largest unit of
ancestral stock), ibex, snow leopard, marbled cat, marmots
THE THAR DESERT the Great Plain of India. The aggradational Great
and black-necked crane.
Plains cover about 72.4mha area with the Ganga
This region consists of parts of Rajasthan, Kutch, Delhi and parts of and the Brahmaputra. The trees belonging to
Gujarat. The climate is characterised by very hot and dry summer and these forests are teak, sal, shisham, mahua
etc.The fauna includes elephants, black buck,
cold winter. Rainfall is less than 70 cm. The plants are mostly gazelle, rhinoceros, Bengal fl orican, crocodile,
xerophytic. Babul, Kikar, wild palm grows in areas of moderate rainfall. freshwater turtle .
Indian Bustard, a highly endangered bird is found here. Camels, wild
asses, foxes, and snakes are found in hot and arid parts of the desert. NORTH-EAST
North-east India is one of the richest flora regions in
SEMI ARID the country. It has several species of orchids,
Adjoining the desert are the semi-arid areas, a transitional bamboos, ferns and other plants. Here the wild
zone between the desert and the denser forests of the relatives of cultivated plants such as banana, mango,
Western Ghats. The natural vegetation is thorn forest. This citrus and pepper can be grown.Mammalian fauna
region is characterized by discontinuous vegetation cover with includes 390 species of which 63% are found in
open areas of bare soil and soil-water deficit throughout the Assam. The area is rich in smaller carnivores. The
year country's highest population of elephants are found
here.
THE COASTS
India has a coastline extending over 7,516. 4 km.It has
WESTERN GHATS sandy beaches,mangroves,mud flats,coral reefs and
The mountains along the west coast of peninsular India are the Western DECCAN PENINSULA marine angiosperm pastures which make them the
Ghats. The mountains rise to average altitudes between 900 and 1500 m It is India's largest Bio-geographical wealth and health zones of India.The backwaters are the
above sea level Western Ghats are amongst the 25 biodiversity hot-spots region. The highlands of the plateau characteristic features of this coast.
recognized globally.Significant secies endemic to this region include Nilgiri are covered with diff erent types of
langur,lion tailed Macaque,malabar grey Hornbill.The Travancore tortoise and forests.The Deccan plateau includes the
Cane turtle are endangered taxa restricted to tis area. region lying south of the
Satpura range.it extends up to th e
ISLANDS
The Two groups of islands, i.e., the Arabian Sea islands and Bay
Add a little bit of body text
southern tip of peninsular
Islands. In India endemic island biodivesity is found only
India.Fauna like tiger, sloth bear, wild here.The Andaman water monitor, giant robber crab, 4 species of
boar, sambar and chital are found turtles, wild boar, Andaman day gecko and the harmless
throughout the zone along with wild Andaman water snake are found only in these islands. Coral
buff aloes. reefs are stretched over in the Andamans and Nicobar.
You might also like
- Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Class 9Document5 pagesNatural Vegetation and Wildlife Class 9Aarshi SareenNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - BiodiversityDocument64 pagesUnit 4 - BiodiversitysparshikaaNo ratings yet
- Biogeographical Classification of IndiaDocument4 pagesBiogeographical Classification of IndiaApoorva ElizaNo ratings yet
- Holiday Homework: Made By: Prasun JainDocument39 pagesHoliday Homework: Made By: Prasun JainSajal JainNo ratings yet
- Thar Desert Information Sheet 3Document2 pagesThar Desert Information Sheet 3SpablaNo ratings yet
- Geography Handout 10Document25 pagesGeography Handout 10Gagandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Terrestrial Biome: Biomes Geographical Location and Climatic Conditions Specific Plant Species Specific Animal SpeciesDocument20 pagesTerrestrial Biome: Biomes Geographical Location and Climatic Conditions Specific Plant Species Specific Animal SpeciesDayana ChelebievaNo ratings yet
- (I) Tropical Evergreen Forests (Ii) Tropical Deciduous Forests (Iii) Tropical Thorn Forests and Scrubs (Iv) Montane Forests (V) Mangrove ForestsDocument7 pages(I) Tropical Evergreen Forests (Ii) Tropical Deciduous Forests (Iii) Tropical Thorn Forests and Scrubs (Iv) Montane Forests (V) Mangrove ForestsVenkat CvnrNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument7 pagesEcosystemMuhammad HabibNo ratings yet
- Grade4 EA Term-3 Folder Final DraftDocument57 pagesGrade4 EA Term-3 Folder Final DraftJyotsna MathurNo ratings yet
- Natural Vegetation, Different Types of Forests of IndiaDocument3 pagesNatural Vegetation, Different Types of Forests of Indiakatrina167No ratings yet
- Critically Endangered SpeciesDocument5 pagesCritically Endangered SpeciesTushar KhatriNo ratings yet
- Biogeographical LassificationDocument31 pagesBiogeographical LassificationErfana Yasmin100% (1)
- Biodiversity and ConservationDocument26 pagesBiodiversity and Conservationprasada hj prasada hjNo ratings yet
- Subject-Geography Topic - Natural Vegetation of India Class - XDocument5 pagesSubject-Geography Topic - Natural Vegetation of India Class - Xpiyush bishtNo ratings yet
- Atural Egetation AND IldlifeDocument9 pagesAtural Egetation AND IldlifeLULIKA VINCENT JACKSONNo ratings yet
- 380 Natural Vegetation Indiashastra PDFDocument2 pages380 Natural Vegetation Indiashastra PDFKarambir Singh DhayalNo ratings yet
- Types of Forest - Western Ghats (Nilgiris)Document8 pagesTypes of Forest - Western Ghats (Nilgiris)Hues of SundropNo ratings yet
- Wa0134.Document33 pagesWa0134.Daliya HericNo ratings yet
- Natural VegetationDocument21 pagesNatural Vegetationcatajol904No ratings yet
- Endangered Mammals of BangladeshDocument5 pagesEndangered Mammals of BangladeshShamim HasanNo ratings yet
- Natural Vegetation and WildlifeDocument6 pagesNatural Vegetation and WildlifeKodanda RamanNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument20 pagesPresentationManoj ModiNo ratings yet
- Wild Life - RemovedDocument7 pagesWild Life - RemovedVenkat CvnrNo ratings yet
- Biology Art IntegrationDocument11 pagesBiology Art IntegrationYASHWIN RAMESHNo ratings yet
- CH 5 FL GeoDocument1 pageCH 5 FL GeoBijay Ketan MiahraNo ratings yet
- Moist Alpine ScrubDocument1 pageMoist Alpine Scrubrashibaisoya.123No ratings yet
- Natural Vegetation and Wildlife One ShortDocument16 pagesNatural Vegetation and Wildlife One Shortvyasmahesh330No ratings yet
- Atural Egetation: Ypes OF OrestsDocument11 pagesAtural Egetation: Ypes OF OrestsChithra ThambyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - (Philoid-IN)Document11 pagesChapter 5 - (Philoid-IN)Nilesh NagarNo ratings yet
- Montane Wet Temperate ForestDocument1 pageMontane Wet Temperate Forestrashibaisoya.123No ratings yet
- Phytogeography of IndiaDocument44 pagesPhytogeography of IndiaAnupama Praveen100% (1)
- Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources-CompressedDocument34 pagesNatural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources-Compressedcome2sandhyaNo ratings yet
- Science - Flora & Fauna - PahalDocument14 pagesScience - Flora & Fauna - PahalNidhi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Natural Vegetation and WildlifeDocument7 pagesNatural Vegetation and Wildlifeanushkagarg1609No ratings yet
- Species and Protected Areas - Revision SheetDocument13 pagesSpecies and Protected Areas - Revision SheetABHIDEV J KNo ratings yet
- Atural Egetation: Ypes OF OrestsDocument11 pagesAtural Egetation: Ypes OF OrestsDibyo ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Natural Vege Eng 73Document4 pagesNatural Vege Eng 73mahimalakhore77No ratings yet
- Ncert-Science and Social Science (9TH Class)Document11 pagesNcert-Science and Social Science (9TH Class)akulasowjanya574No ratings yet
- SCIENCE Study Guide: Georgia Milestones: HABITATS Standard: S3L1Document4 pagesSCIENCE Study Guide: Georgia Milestones: HABITATS Standard: S3L1api-327816044No ratings yet
- Natasha Mukhtar 16241514-018 Mam Kiran Aftab Bs-VII ZoologyDocument29 pagesNatasha Mukhtar 16241514-018 Mam Kiran Aftab Bs-VII Zoologynatasha mukhtarNo ratings yet
- Kegy105 PDFDocument11 pagesKegy105 PDFAlisha ChopraNo ratings yet
- Notes of CH 5 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife ClaDocument15 pagesNotes of CH 5 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife ClaGurman SinghNo ratings yet
- BY Sheza Rizeen Kudachikar 4 C' 1 Greenfield Public SchoolDocument4 pagesBY Sheza Rizeen Kudachikar 4 C' 1 Greenfield Public SchoolAijaz ZendeNo ratings yet
- E.V.S Unit 4 Biodiversity and ConservationDocument11 pagesE.V.S Unit 4 Biodiversity and ConservationSHIREEN TEKADENo ratings yet
- Biodiversity For Notes IMPORTANTDocument7 pagesBiodiversity For Notes IMPORTANTjoyNo ratings yet
- Geography and Ecology: Sasan Gir, Sasan, JunagadhDocument46 pagesGeography and Ecology: Sasan Gir, Sasan, JunagadhlalaNo ratings yet
- Natural Vegetation and WildlifeDocument8 pagesNatural Vegetation and Wildlifevinay19891989No ratings yet
- Natural Veg NotesDocument4 pagesNatural Veg NotesGaurav ManglaNo ratings yet
- Flora and Fauna of Jammu and Kashmir: Related TopicsDocument3 pagesFlora and Fauna of Jammu and Kashmir: Related TopicsAxcNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument2 pagesAssignmentJuhi NeogiNo ratings yet
- Cardamom Africa ResearchDocument7 pagesCardamom Africa Researchgobu09No ratings yet
- Geo RevisionDocument7 pagesGeo RevisionNITU TAPARIANo ratings yet
- Geography and Major Biomes of IndiaDocument8 pagesGeography and Major Biomes of IndiavikasNo ratings yet
- Rbse - Geography PDFDocument10 pagesRbse - Geography PDFNeelesh BenaraNo ratings yet
- Biome Characteristics Countries Temperature and Precipitation Species PresentDocument12 pagesBiome Characteristics Countries Temperature and Precipitation Species PresentBismarck John SalazarNo ratings yet
- English ProjectDocument3 pagesEnglish ProjectJaycee JayceeNo ratings yet
- Gexography NotesDocument8 pagesGexography NotesKaran SinghNo ratings yet
- Types of Forests of India 38Document5 pagesTypes of Forests of India 38athira vijayanNo ratings yet
- OPSS 415 Feb90Document7 pagesOPSS 415 Feb90Muhammad UmarNo ratings yet
- Emma The Easter BunnyDocument9 pagesEmma The Easter BunnymagdaNo ratings yet
- Notice: Constable (Driver) - Male in Delhi Police Examination, 2022Document50 pagesNotice: Constable (Driver) - Male in Delhi Police Examination, 2022intzar aliNo ratings yet
- BSBHRM405 Support Recruitment, Selection and Induction of Staff KM2Document17 pagesBSBHRM405 Support Recruitment, Selection and Induction of Staff KM2cplerkNo ratings yet
- FCAPSDocument5 pagesFCAPSPablo ParreñoNo ratings yet
- Best Interior Architects in Kolkata PDF DownloadDocument1 pageBest Interior Architects in Kolkata PDF DownloadArsh KrishNo ratings yet
- Sheet PilesDocument5 pagesSheet PilesolcayuzNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment: Sudha Goel, Ph.D. Department of Civil Engineering, IIT KharagpurDocument33 pagesWastewater Treatment: Sudha Goel, Ph.D. Department of Civil Engineering, IIT KharagpurSubhajit BagNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Case of ScoliosisDocument54 pagesApproach To A Case of ScoliosisJocuri KosoNo ratings yet
- Pea RubricDocument4 pagesPea Rubricapi-297637167No ratings yet
- Ikramul (Electrical)Document3 pagesIkramul (Electrical)Ikramu HaqueNo ratings yet
- Positive Accounting TheoryDocument47 pagesPositive Accounting TheoryAshraf Uz ZamanNo ratings yet
- Cryptography Practical 1Document41 pagesCryptography Practical 1Harsha GangwaniNo ratings yet
- CPGDocument9 pagesCPGEra ParkNo ratings yet
- PSIG EscalatorDocument31 pagesPSIG EscalatorNaseer KhanNo ratings yet
- Brahm Dutt v. UoiDocument3 pagesBrahm Dutt v. Uoiswati mohapatraNo ratings yet
- Psychology Research Literature Review ExampleDocument5 pagesPsychology Research Literature Review Exampleafdtsebxc100% (1)
- 1INDEA2022001Document90 pages1INDEA2022001Renata SilvaNo ratings yet
- E Tech SLHT QTR 2 Week 1Document11 pagesE Tech SLHT QTR 2 Week 1Vie Boldios Roche100% (1)
- Feng Shui GeneralDocument36 pagesFeng Shui GeneralPia SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Queen of Hearts Rules - FinalDocument3 pagesQueen of Hearts Rules - FinalAudrey ErwinNo ratings yet
- Financial Performance Report General Tyres and Rubber Company-FinalDocument29 pagesFinancial Performance Report General Tyres and Rubber Company-FinalKabeer QureshiNo ratings yet
- TOURISM AND HOSPITALITY ORGANIZATIONS Di Pa TapooosDocument97 pagesTOURISM AND HOSPITALITY ORGANIZATIONS Di Pa TapooosDianne EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Book Review On PandeymoniumDocument2 pagesBook Review On PandeymoniumJanhavi ThakkerNo ratings yet
- Precertification Worksheet: LEED v4.1 BD+C - PrecertificationDocument62 pagesPrecertification Worksheet: LEED v4.1 BD+C - PrecertificationLipi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Food Combining PDFDocument16 pagesFood Combining PDFJudas FK TadeoNo ratings yet
- Cover Letter For Lettings Negotiator JobDocument9 pagesCover Letter For Lettings Negotiator Jobsun1g0gujyp2100% (1)
- Specification - Pump StationDocument59 pagesSpecification - Pump StationchialunNo ratings yet
- A Practical Guide To Transfer Pricing Policy Design and ImplementationDocument11 pagesA Practical Guide To Transfer Pricing Policy Design and ImplementationQiujun LiNo ratings yet
- Taxation: Presented By: Gaurav Yadav Rishabh Sharma Sandeep SinghDocument32 pagesTaxation: Presented By: Gaurav Yadav Rishabh Sharma Sandeep SinghjurdaNo ratings yet