Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Programmable Array Logic
Uploaded by
Shaurya0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views10 pagesProgrammable Array Logic (PAL) is a programmable logic device with a programmable AND array and fixed OR array. It is easier to use than a Programmable Logic Array but less flexible because only the AND array is programmable. PAL consists of a small Programmable Read Only Memory and additional output logic to implement desired logic functions with limited components. PAL has programmable AND gates followed by fixed OR gates, allowing simpler programming than PLA which has programmable AND and OR gates. PAL provides advantages of low cost, high efficiency, security, reliability and flexibility compared to other programmable logic devices.
Original Description:
Original Title
Programmable Array Logic PPT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentProgrammable Array Logic (PAL) is a programmable logic device with a programmable AND array and fixed OR array. It is easier to use than a Programmable Logic Array but less flexible because only the AND array is programmable. PAL consists of a small Programmable Read Only Memory and additional output logic to implement desired logic functions with limited components. PAL has programmable AND gates followed by fixed OR gates, allowing simpler programming than PLA which has programmable AND and OR gates. PAL provides advantages of low cost, high efficiency, security, reliability and flexibility compared to other programmable logic devices.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views10 pagesProgrammable Array Logic
Uploaded by
ShauryaProgrammable Array Logic (PAL) is a programmable logic device with a programmable AND array and fixed OR array. It is easier to use than a Programmable Logic Array but less flexible because only the AND array is programmable. PAL consists of a small Programmable Read Only Memory and additional output logic to implement desired logic functions with limited components. PAL has programmable AND gates followed by fixed OR gates, allowing simpler programming than PLA which has programmable AND and OR gates. PAL provides advantages of low cost, high efficiency, security, reliability and flexibility compared to other programmable logic devices.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
Programmable By Shaurya Bahl
Array Logic (21CSU189)
Contents
• Definition of Programmable Array Logic
(PAL)
• Block Diagram of PAL
• Circuit Diagram of PAL
• Comparison with other Programmable
Logic Devices
• Example of PAL
• Advantages of PAL
• Programmable Array Logic (PAL) is a
commonly Used programmable logic device
(PLD). It has programmable AND array and
fixed OR array.
Definition of • It is easier to use but not flexible as
compared to Programmable Logic Array
Programmable (PLA) because only the AND array is
programmable.
Array Logic • The Limitation of PAL is number of AND
gates.
(PAL) • PAL consists of small Programmable Read
Only Memory (PROM) and additional
output logic used to implement a particular
desired logic function with limited
components.
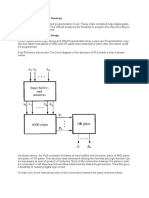
Block Diagram of
Programmable
Array Logic
Circuit Diagram
of Programmable
Array Logic
Comparison • Main Difference between PLA, PAL and
ROM is their basic structure.
with other • In PLA, Programmable AND gate is followed
by programmable OR gate.
Programmable • In PAL, programmable AND gate is followed
by fixed OR gate.
Logic Devices • In ROM, fixed AND gate is followed by
programmable OR gate array.
Example of PAL (1 of 2)
• Example 1: Implement the Boolean functions
F1= A’BC’D + A’BCD’ + ABC’D and F2= A’BC’ +
A’BC + AB’C + ABC’ with PAL device.
• Solution: The given Boolean expressions can
be simplified to get a reduced equation:
Example of PAL (2 of 2)
• The simplified expression can be
realized using PAL. The given function
has four inputs and two outputs.
• It has five product terms. Each
Product term is obtained by placing
the fuse link to the corresponding
input line.
Advantages of PAL
• Highly Efficient
• Low Production cost as compared to PLA
• Highly secure
• High Reliability
• Low power required for working
• More flexible to design
Thank You
You might also like
- Lec 12 - Chap 10-PLDsDocument22 pagesLec 12 - Chap 10-PLDsAliRazaNo ratings yet
- VashisthZatakia DLD 09Document4 pagesVashisthZatakia DLD 09Vashisth ZatakiaNo ratings yet
- Pal & PlaDocument4 pagesPal & PlaĹalam ŠainaťhNo ratings yet
- Programmable Logic Devices (PLD)Document33 pagesProgrammable Logic Devices (PLD)Rishikesh BhavsarNo ratings yet
- Pla Pal RomDocument33 pagesPla Pal Romvpj_jamesNo ratings yet
- PLD PLA PAL Programmable Logic Devices ExplainedDocument3 pagesPLD PLA PAL Programmable Logic Devices ExplainedDarshan Iyer NNo ratings yet
- Programmable Logic Devices (PLDs): Types, Programming & ComparisonDocument32 pagesProgrammable Logic Devices (PLDs): Types, Programming & ComparisonChristian LunaNo ratings yet
- DC - Unit VI - ASVDocument52 pagesDC - Unit VI - ASVAnup S. Vibhute DITNo ratings yet
- PLD'sDocument81 pagesPLD'sMICECE100% (1)
- Programmable Logic DevicesDocument12 pagesProgrammable Logic Devicesrobinpt100% (1)
- Programmable Logic Devices: Edit By: Zulhelman, ST. MTDocument47 pagesProgrammable Logic Devices: Edit By: Zulhelman, ST. MTShafira LuthfiyahNo ratings yet
- Wa0003Document30 pagesWa0003Akash Kumar PatelNo ratings yet
- VHDL Class Note2017CLASS2Document30 pagesVHDL Class Note2017CLASS2Leena VsNo ratings yet
- Programmable Logic Devices 2, TutorialDocument10 pagesProgrammable Logic Devices 2, Tutorialindresh.verma100% (1)
- Pal and PlaDocument10 pagesPal and PlaRahul Kumar67% (6)
- 4 Computer ArchitectureDocument30 pages4 Computer ArchitectureARAFAT GaamanNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Programmable Devices: PLA, PAL, CPLD & FPGADocument25 pagesIntroduction to Programmable Devices: PLA, PAL, CPLD & FPGAPrashant SarrafNo ratings yet
- Programmable Logic Design Grzegorz Budzy Ń L Ecture 1Document43 pagesProgrammable Logic Design Grzegorz Budzy Ń L Ecture 1LOUIS SEVERINO ROMANONo ratings yet
- Assignment - Muhammad Ali Asad - 014Document39 pagesAssignment - Muhammad Ali Asad - 014mumtazNo ratings yet
- Ee128 Lecture9Document22 pagesEe128 Lecture9KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- FPGA and PLD SurveyDocument29 pagesFPGA and PLD SurveykavitaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document4 pagesUnit 1muskan vermaNo ratings yet
- Programmable Logic ArrayDocument2 pagesProgrammable Logic Arraymaresh436No ratings yet
- Unit - 1 System Design Using Plds Programmable Logic DevicesDocument21 pagesUnit - 1 System Design Using Plds Programmable Logic DevicesPalaniVelRajanNo ratings yet
- SPLDS-PPT 1Document88 pagesSPLDS-PPT 1ramakrishnaNo ratings yet
- 21bce2845 VL2022230104423 Da02Document7 pages21bce2845 VL2022230104423 Da02Sidharth GhaiNo ratings yet
- Programmable Logic ArrayDocument18 pagesProgrammable Logic ArrayLê Văn LợiNo ratings yet
- Intro PLDsDocument24 pagesIntro PLDsElice FerNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 02 - Programmable Logic DeviceDocument25 pagesChapter - 02 - Programmable Logic DeviceThanh Diện NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Combinational Logic DesignDocument17 pagesChapter 3 - Combinational Logic DesignMuhammad AzeemNo ratings yet
- VLSI Design and Modeling System Chapter on Basic VLSI Design Styles and Programmable LogicDocument34 pagesVLSI Design and Modeling System Chapter on Basic VLSI Design Styles and Programmable LogicKhairul IslamNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document59 pagesUnit 5Niharika KorukondaNo ratings yet
- Course Slides 2018Document484 pagesCourse Slides 2018venkatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Programmable Logic DevicesDocument63 pagesChapter 4: Programmable Logic DevicesKasi ChinnaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Programmable Logic DevicesDocument92 pagesIntroduction to Programmable Logic DevicesRamakrishna MarkondaNo ratings yet
- Pals - Investigation Slides (Team Rickygirls)Document10 pagesPals - Investigation Slides (Team Rickygirls)Adrian Andres Santiago MaciasNo ratings yet
- Programmable Logic Devices ReportDocument7 pagesProgrammable Logic Devices ReportRoemil CabalNo ratings yet
- 15 ProgLogicDocument18 pages15 ProgLogicVijaya KumarNo ratings yet
- Programmable Arrays of Logic Gates: PALs and PLAsDocument10 pagesProgrammable Arrays of Logic Gates: PALs and PLAsjeddo2005No ratings yet
- Programmable Array LogicDocument1 pageProgrammable Array Logicnazibhd786No ratings yet
- Lecture1 PLDsDocument41 pagesLecture1 PLDsMoayid AldeebNo ratings yet
- FPGA Architecture and ImplementationDocument59 pagesFPGA Architecture and ImplementationManas BhattNo ratings yet
- Digital ElectronicsDocument16 pagesDigital ElectronicsB LAKSHMI PRIYANo ratings yet
- Programmable Logic Devices ExplainedDocument5 pagesProgrammable Logic Devices ExplainedIshmael ZibaniNo ratings yet
- PLDDocument5 pagesPLDPanchal Abhishek JagdishchandraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Programmable Logic Devices and Fpgas: - by Sparsh Sharma 11815030 Ec-2Document20 pagesIntroduction To Programmable Logic Devices and Fpgas: - by Sparsh Sharma 11815030 Ec-2Sparsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Name: Mohamad Faiz Omar Bin Mahmud - Id: 2009286466Document16 pagesName: Mohamad Faiz Omar Bin Mahmud - Id: 2009286466fal_qadiriNo ratings yet
- PLD Lecture OverviewDocument33 pagesPLD Lecture OverviewKrishna SrivathsaNo ratings yet
- Programmable Logic Arrays (PLA) ExplainedDocument5 pagesProgrammable Logic Arrays (PLA) ExplainedSitotaw NigussieNo ratings yet
- DSD PresentationDocument16 pagesDSD PresentationMeezan ChandNo ratings yet
- Documentation Standards: - Block Diagrams - Schematic Diagrams - Timing Diagrams - Circuit DescriptionsDocument29 pagesDocumentation Standards: - Block Diagrams - Schematic Diagrams - Timing Diagrams - Circuit DescriptionsYunus TorunNo ratings yet
- CPLD and FpgaDocument28 pagesCPLD and FpgaUday KumarNo ratings yet
- Programmable Logic Devices (PLD) and ASICs ExplainedDocument36 pagesProgrammable Logic Devices (PLD) and ASICs ExplainedLemi RajesaNo ratings yet
- Unit 7Document54 pagesUnit 7Pavankumar GorpuniNo ratings yet
- Architecture of FPGAs and CPLDS: A TutorialDocument41 pagesArchitecture of FPGAs and CPLDS: A Tutorialgongster100% (5)
- PLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.From EverandPLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.No ratings yet
- Advanced Oracle PL/SQL Developer's Guide - Second EditionFrom EverandAdvanced Oracle PL/SQL Developer's Guide - Second EditionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Pollution Status of Ambuja Cement LTD by Shaurya BahlDocument5 pagesPollution Status of Ambuja Cement LTD by Shaurya BahlShauryaNo ratings yet
- Green Hydrogen Potential in India's Clean Energy TransitionDocument2 pagesGreen Hydrogen Potential in India's Clean Energy TransitionShauryaNo ratings yet
- The LuckDocument1 pageThe LuckShauryaNo ratings yet
- Cinema Ticket BookingDocument10 pagesCinema Ticket BookingShauryaNo ratings yet
- Vision of Sustainable City - IndoreDocument7 pagesVision of Sustainable City - IndoreShauryaNo ratings yet
- Follow Your Passion by Shaurya21csu189 1Document9 pagesFollow Your Passion by Shaurya21csu189 1ShauryaNo ratings yet
- Follow Your Passion by Shaurya21csu189 1Document9 pagesFollow Your Passion by Shaurya21csu189 1ShauryaNo ratings yet
- Indore (Sas)Document7 pagesIndore (Sas)ShauryaNo ratings yet