Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PDF Comparison of Freud Erikson Piaget Kohlberg Theories Developmental Phenomena
Uploaded by
Johanine VillasantiagoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PDF Comparison of Freud Erikson Piaget Kohlberg Theories Developmental Phenomena
Uploaded by
Johanine VillasantiagoCopyright:
Available Formats
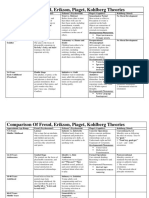
Comparison Of Freud, Erikson, Piaget, Kohlberg Theories
Approximate Age Range Freud (Psychosexual) Erikson* (Psychosocial) Piaget (Cognitive) Kohlberg (Moral)
Birth to 2 years Oral Stage Trust vs. Mistrust Sensorimotor Period No Moral Development
infancy The mouth, tongue, and Babies learn either to trust Most action is reflexive.
gums are the focus of that others will care for Perception of events is
pleasurable sensations in their basic needs, including centered on the body.
tbn j mj y‛ s jh`y, ml ` nourishment, warmth, Objects are extensions of
feeding is the most cleanliness, and physical self. Acknowledges the
stimulating activity. contact, or to lack external environment.
confidence in the care of @nvnihpe nl tmi
others. Vbnl he nl m:
•
Object
permanence
l ½-3 Years Anal Stage Autonomy vs. Shame and No Moral Development
Toddler The anus is the focus of Doubt Stranger anxiety
•
pleasurable sensations in Children learn either to be Preoperational
tbn j mj y‛ s jh`y, ml ` self-sufficient in many (Preconceptual)
thiint Self-centered. Asks many
training is the most activities, including environment.
questions. Language
Explores
important activity. toileting, feeding, walking, development rapid. the
exploring, and talking or the Associates words with
doubt their own abilities. objects. (symbols)
@nvnihpe nl t mi
Vbnl h e nl m:
•
Pretend play
•
Egocentrism
•
Language
3-6 Years Phallic Stage Initiative vs. Guilt development Preconventional
Early Childhood Preoperational
(Preschool) Tmhoestpihmalplourst,aonrt Cmhainlydraednuwlta-lnikt (Intuitive)
oMoMr obradli,tybaisead monat
Egocentricthinking
pbeondiys,piasrth, e etoaucntidveitriteask,e diminishes. Includes others atesr yosftegmooodf
and pleasure is derived from sometimes overstepping the in environment. Enjoys punishments.
genital stimulation. Boys limits set by parents and repeating words, may count 1.Punishment and
are proud of their penis, and feeling guilty. to 10. Words express obedience orientation.
girls wonder why they thoughts. 2.Instrumental relativist
@nvnihpe nl t mi orientation
don t have one. (Oedipal
‛
Vbnl h e nl m:
Conflict) •
Further Language
Development
Comparison Of Freud, Erikson, Piaget, Kohlberg Theories
Approximate Age Range Freud (Psychosexual) Erikson* (Psychosocial) Piaget (Cognitive) Kohlberg (Moral)
7-l l Years Latency Industry vs. Inferiority Concrete Operations Conventional Level
Middle Childhood Not a stage but an interlude, Children busily learn to be Solves concrete problems. Morality seen as following
when sexual needs are quiet competent and productive Begins to understand the rules of society. Tries to
and children put psychic in mastering new skills, or relationships such as size. j n ’ ahh`.―
energy into conventional feel inferior an unable to do Understands right and left. 1. ’ Ahh` jhy, ahh` airi.―
activities like schoolwork anything well. Cognizant of viewpoints. 2. Law - and - order
and sports. @nvnihpe nl t mi orientation.
Vbnl h e nl m:
•
Conservation
•
Mathematical
l 2 - l 8 Years Genital Stage Identity vs. Role Transformation Postconventional
Adolescence The genitals are the focus of Confusion Formal Operations Morality consists of
pleasurable sensations, and Adolescents try Uses rational thinking. standards beyond specific
the young person seeks to figure Reasoning is deductive and group or authority figure.
hut ’ Q bh me futuristic.
Developmental Phenomena:
sexuall satitmisufalacttiioonn eK8― Pbny
a sntdabclairsehesreixduenalt,
•
Abstract logic 1o1.riTenh teastioocnia. l
•
Potential for mature contract
ainnd heterosexual itpieosliotircarle, reasoning
relationships. 2. The universal ethical
confused about what roles principle orientation.
l 8 - 40 Years Freud believed that the Intimacy
to play. vs. Isolation
Adulthood genital stage lasts Young adults seek
throughout adulthood. He companionship and love
also said that the goal of a with another person or
bnmitby iicn is ’ th ihvn become isolated from others
ml ` th whrd wnii.― by fearing refection or
disappointment.
40-65 Years Generativity vs.
Middle Years Stagnation
Middle-aged adults
contribute to the next
generation by performing
meaningful work, creative
activities, and/or raising a
family, or become stagnant
and inactive.
Comparison Of Freud, Erikson, Piaget, Kohlberg Theories
Approximate Age Range Freud (Psychosexual) Erikson* (Psychosocial) Piaget (Cognitive) Kohlberg (Moral)
65 - Years Integrity vs. Despair
Late Adulthood Older adults try to make
sense out of their lives,
whether seeing life as a
meaningful whole or
despairing at goals never
reached and questions never
answered.
*Although Erikson describes two extreme resolutions to each crisis, he recognizes that there is a wide range of outcomes between these extremes
and that most people arrive at some middle course.
Criticisms Of Freud, Erikson, Piaget, Kohlberg Theories
Freud (Psychosexual) Erikson* (Psychosocial) Piaget (Cognitive) Kohlberg (Moral)
Focus on sex Sequence Research methods SampIe
Believed to place too much Do people have to pass Observed his own children Kohlberg formed his theory based
emphasis on sexuality. through one stage to get to and small samples of children solely on male participants.
SampIe the next? from well-educated, CriticaI question: Reasoning or
Developed theories from on SampIe successful parents. action?
case studies based on the Theory developed based on FormaI Operations Where is someone who reasons
recollection of adult patients study of males. Assumption that all children one way, but acts another?
Gender bias Vague move into this stage, Gender bias
Overall theory is biased Erikson did not seek to was environment may play a role Carol Gilligan argued that this
toward males. Karen Horney not explicit about what Underestimated abiIities theory was based on justice,
proposed womb envy as a influences an individual to Egocentrism diminishes and which favors males. Gilligan
response to Freud’s penis develop in certain ways or theory of mind may develop proposed a theory based on
envy theory. how the outcome of each earlier than proposed. The the
PhaIIic stage psychosocial stage later same may be true for other ethics of care.
This stage in particular, influences personality abilities. CuIturaI bias
including Oedipal and Elektra Non-industrial countries may not
Complexes, is considered reach levels 5 and 6; some moral
deeply flawed. concerns for other cultures are
not represented in Kohlberg’s
westernized sample.
You might also like
- Comparison Of Major Theories Of Child DevelopmentDocument3 pagesComparison Of Major Theories Of Child DevelopmentNorashia MacabandingNo ratings yet
- Transactional AnalysisDocument21 pagesTransactional AnalysisLakshya SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Freud, Erikson, Piaget and Kohlberg's theories of developmentDocument8 pagesFreud, Erikson, Piaget and Kohlberg's theories of developmentRic Russel PamaNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development StagesDocument13 pagesGrowth and Development Stagesمحمد عبدالوهاب ابراهيم الطباطبائيNo ratings yet
- L1 THEORIES: BEHAVIOURIST, INNATIST, INTERACTIONISTDocument23 pagesL1 THEORIES: BEHAVIOURIST, INNATIST, INTERACTIONISTAmna AlbraikyNo ratings yet
- Transactional Analysis: - A Model For Explaining Why and HowDocument33 pagesTransactional Analysis: - A Model For Explaining Why and HowAjith ThacholiNo ratings yet
- Child PsycDocument26 pagesChild PsycHrishida PNo ratings yet
- Infancy and ToddlerhoodDocument29 pagesInfancy and ToddlerhoodDOMINGO, Lealyn Q.No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Developmental - PsychologyDocument65 pagesChapter 5 Developmental - PsychologyPhil JacksonNo ratings yet
- Understanding Preschool Child DevelopmentDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Preschool Child DevelopmentGlenn DanoNo ratings yet
- Approach to Pediatric Assessment Across Developmental StagesDocument2 pagesApproach to Pediatric Assessment Across Developmental StagesShane ShaneNo ratings yet
- Transactional AnalysisDocument33 pagesTransactional AnalysisAnoop C Choolayil100% (1)
- GE 1 MODULE 1Document13 pagesGE 1 MODULE 1Jenica Riah DalenNo ratings yet
- Building Baby's Intelligence: Why Infant Stimulation Is So ImportantDocument2 pagesBuilding Baby's Intelligence: Why Infant Stimulation Is So Importantantalmarialuana_6775No ratings yet
- HLC 1.4preschool Devt - MalinitDocument5 pagesHLC 1.4preschool Devt - Malinitlovelots1234No ratings yet
- Grade 2 Home LinksDocument11 pagesGrade 2 Home Linksapi-360345401No ratings yet
- Developmental Theories andDocument54 pagesDevelopmental Theories andJissa YbañezNo ratings yet
- Human Behavior 5 2016Document12 pagesHuman Behavior 5 2016Aazmeer RahmanNo ratings yet
- 1010 Infants Cognitive Development GuideDocument14 pages1010 Infants Cognitive Development GuideAdriana OnofreiNo ratings yet
- Child and Adolescent DevelopmentDocument20 pagesChild and Adolescent Developmentnhicabonit7No ratings yet
- Beyond Med MGMT UCSD FellowsDocument91 pagesBeyond Med MGMT UCSD FellowscirclestretchNo ratings yet
- Comparison Theories PDFDocument3 pagesComparison Theories PDFエド パジャロンNo ratings yet
- Approaches to CounsellingDocument40 pagesApproaches to CounsellingakhiltonyNo ratings yet
- Understanding Behavior Through Transactional Analysis (TADocument14 pagesUnderstanding Behavior Through Transactional Analysis (TASneha SahaNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Learning Through Meta-CognitionDocument337 pagesFacilitating Learning Through Meta-CognitionMichelle ArregLado VistalNo ratings yet
- Us - Psychological Self (Freud)Document43 pagesUs - Psychological Self (Freud)MAGLAMBAYAN, Yvette A.No ratings yet
- Theories of Learner Development in PsychologyDocument17 pagesTheories of Learner Development in PsychologyYolly M MarinayNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development: Society (The Superego)Document11 pagesGrowth and Development: Society (The Superego)Diana CalderonNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development Across the Lifespan: A Guide to Key Concepts and TheoriesDocument9 pagesGrowth and Development Across the Lifespan: A Guide to Key Concepts and TheoriesNicole Audrey JoaquinNo ratings yet
- The Therapeutic Use of Self-ParentsDocument17 pagesThe Therapeutic Use of Self-ParentssepthyaniNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Dev PsyDocument45 pagesUnit IV Dev PsyAnanya JainNo ratings yet
- Stages of Child Development and The Importance of PlayDocument12 pagesStages of Child Development and The Importance of Playlwood06100% (5)
- Psychosexual Theory - Abms 1Document22 pagesPsychosexual Theory - Abms 1barbiehans14No ratings yet
- Developmental Milestones for Newborns and InfantsDocument2 pagesDevelopmental Milestones for Newborns and InfantsJunior SordNo ratings yet
- Babies From Birth To 12 Months:: Becoming Aware of The World Around ThemDocument34 pagesBabies From Birth To 12 Months:: Becoming Aware of The World Around ThemcaeracNo ratings yet
- Developmental PsychologyDocument23 pagesDevelopmental PsychologyememememeNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Child Aged 6 - Copy 2 1Document23 pagesCase Study of Child Aged 6 - Copy 2 1api-582534005No ratings yet
- Teaching Young Children with Autism Spectrum DisorderFrom EverandTeaching Young Children with Autism Spectrum DisorderRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Defining The Young ChildDocument44 pagesDefining The Young ChildMARY JOY DELAROSANo ratings yet
- Aby's: First WishDocument8 pagesAby's: First Wishapi-3704064No ratings yet
- Apss298 l2 Dev Psy 2022 HT STDDocument45 pagesApss298 l2 Dev Psy 2022 HT STDvictor lawNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Developing The Whole PersonDocument59 pagesModule 2 Developing The Whole PersonJoemar MaganteNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 Communicating WITH CHILDRENDocument57 pagesNCM 107 Communicating WITH CHILDRENAnna SantosNo ratings yet
- E-CASE PORTFOLIO - Sasutana Ann Gabrielle L.-1D3Document14 pagesE-CASE PORTFOLIO - Sasutana Ann Gabrielle L.-1D3Marianne EchaviaNo ratings yet
- Transactional AnalysisDocument32 pagesTransactional AnalysisAjith KedarNo ratings yet
- Child Development Abilities - DocDocument2 pagesChild Development Abilities - DocBhanusha MattadeenNo ratings yet
- Developmental TheoriesDocument41 pagesDevelopmental TheoriesConradRaeyRojoNo ratings yet
- Personality and Emotions: Organizational BehaviorDocument28 pagesPersonality and Emotions: Organizational BehaviorshubhamNo ratings yet
- Child PsychologyDocument55 pagesChild PsychologySanchya VibhutiNo ratings yet
- Transactional AnalysisDocument31 pagesTransactional AnalysisHasan SaudNo ratings yet
- FREUDDocument3 pagesFREUDRanpaiku FujiwaraNo ratings yet
- Child Psychology PedodonticsDocument44 pagesChild Psychology Pedodonticsswechchha gupta100% (1)
- Uts Chapter 4Document8 pagesUts Chapter 4Airish Jane MauricioNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS Growth Stages Infant School Age 02Document1 pageNursing CS Growth Stages Infant School Age 02Ciara GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Mindset MattersDocument5 pagesMindset MattersManisha MishraNo ratings yet
- Biological Physiological Development LearnerDocument22 pagesBiological Physiological Development LearnerMary Ann AmparoNo ratings yet
- General Concepts & Historical Developments in Science, Technology, and SocietyDocument43 pagesGeneral Concepts & Historical Developments in Science, Technology, and SocietyMax TooperNo ratings yet
- Language, Memory, and Cognition in Infancy and Early ChildhoodFrom EverandLanguage, Memory, and Cognition in Infancy and Early ChildhoodNo ratings yet
- Parenting Toddlers Years Survival Guide for First-Time Dads: Navigating the Turbulent Toddler Terrain: A First-Time Dad's Survival GuideFrom EverandParenting Toddlers Years Survival Guide for First-Time Dads: Navigating the Turbulent Toddler Terrain: A First-Time Dad's Survival GuideNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument5 pagesResearchJohanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- Review of Related StudiesDocument11 pagesReview of Related StudiesJohanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument1 pageAnatomy and PhysiologyJohanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- PDF Freudian Stages of Psychosexual Development - CompressDocument17 pagesPDF Freudian Stages of Psychosexual Development - CompressJohanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- PDF Lecture Chapter 2 - CompressDocument13 pagesPDF Lecture Chapter 2 - CompressJohanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- PDF 20221001 184546 0000Document13 pagesPDF 20221001 184546 000006Xll IPS 1 Ana MustikaNo ratings yet
- StuffDocument409 pagesStuffAnonymous wQpdpN5J94% (18)
- ACTIVITYDocument2 pagesACTIVITYJohanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- Beige and Grey Vintage Illustrative Archeology History Report Project PresentationDocument13 pagesBeige and Grey Vintage Illustrative Archeology History Report Project PresentationJohanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- Nursing care for pregnancy's psychological and physiological changesDocument180 pagesNursing care for pregnancy's psychological and physiological changesJohanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- Revised Physical Fitness TestDocument18 pagesRevised Physical Fitness TestJohanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- File 7Document23 pagesFile 7Johanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- Gerontological Nursing ConceptsDocument211 pagesGerontological Nursing ConceptsJohanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- PDF Comparison of Freud Erikson Piaget Kohlberg Theories Developmental Phenomena - CompressDocument3 pagesPDF Comparison of Freud Erikson Piaget Kohlberg Theories Developmental Phenomena - CompressJohanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- Start Your Good Plan Right Now With This October CalendarDocument10 pagesStart Your Good Plan Right Now With This October CalendarJohanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- File 5Document43 pagesFile 5Johanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- File 6Document39 pagesFile 6Johanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- File 8Document33 pagesFile 8Johanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- File 1Document20 pagesFile 1Johanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- File 3Document12 pagesFile 3Johanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- 3Document9 pages3Johanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- File 9Document43 pagesFile 9Johanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- Intraoperative Nursing Care EssentialsDocument10 pagesIntraoperative Nursing Care EssentialsJohanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- File 2Document24 pagesFile 2Johanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- 5Document8 pages5Johanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- And Management Office (MDRRMO) Officer of Labo, and Lastly Are The ProspectiveDocument3 pagesAnd Management Office (MDRRMO) Officer of Labo, and Lastly Are The ProspectiveJohanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- Maligaya Falls as Major Tourist Spot Boosts Submakin LivelihoodDocument8 pagesMaligaya Falls as Major Tourist Spot Boosts Submakin LivelihoodJoan DianaNo ratings yet
- Impacts of Promoting Maligaya Falls as a Tourist DestinationDocument5 pagesImpacts of Promoting Maligaya Falls as a Tourist DestinationJohanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- hs200 - 04 0904b Term SyllabusDocument13 pageshs200 - 04 0904b Term Syllabuscindyfuller68No ratings yet
- Cultural DiplomacyDocument414 pagesCultural DiplomacyAdrian Kranjčević100% (2)
- List of Educational Institutions Which Have Sanskrit Phrases As Their Mottos PDFDocument5 pagesList of Educational Institutions Which Have Sanskrit Phrases As Their Mottos PDFAvinash WandreNo ratings yet
- Prize Giving and Speech Day at Precious Blood Secondary School On The 17TH of July 2015Document7 pagesPrize Giving and Speech Day at Precious Blood Secondary School On The 17TH of July 2015Patience100% (1)
- CounselingDocument23 pagesCounselingrashmi patooNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics and Art May1976Document36 pagesComputer Graphics and Art May1976Virginia Lazaro VillaNo ratings yet
- Spectral Methods For Differential ProblemsDocument167 pagesSpectral Methods For Differential ProblemsSurender ReddyNo ratings yet
- Syntax AnalysisDocument27 pagesSyntax Analysisgargsajal9No ratings yet
- Dont Be Left BehindDocument66 pagesDont Be Left BehindkameronkellyNo ratings yet
- K To 12 Mechanical Drafting Teacher's GuideDocument16 pagesK To 12 Mechanical Drafting Teacher's GuideHari Ng Sablay100% (11)
- Moller, L - Pseudoscience or ProtoscienceDocument3 pagesMoller, L - Pseudoscience or Protosciencedominscience1No ratings yet
- Audiences and all that jazzDocument2 pagesAudiences and all that jazzAriana SălăjanNo ratings yet
- ICT Form 5 Chapter 1Document34 pagesICT Form 5 Chapter 1Benammi Al-KhawarizmiNo ratings yet
- General Rules and Guidelines To DebatingDocument30 pagesGeneral Rules and Guidelines To DebatingArindam GhoshNo ratings yet
- The Code of The Extraordinary MindDocument1 pageThe Code of The Extraordinary MindAvi K. Shrivastava100% (1)
- Summer Holiday Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesSummer Holiday Lesson PlanDragana MilosevicNo ratings yet
- Understanding Memes as Responses to ExigenceDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Memes as Responses to ExigenceKenya TaylorNo ratings yet
- Female Stereotypes in Literature (With A Focus On Latin American Writers)Document20 pagesFemale Stereotypes in Literature (With A Focus On Latin American Writers)Violeta ComanNo ratings yet
- Satanic SymbolsDocument123 pagesSatanic SymbolsPoorna Kalandhar67% (9)
- Architecture Thesis Acknowledgement SampleDocument5 pagesArchitecture Thesis Acknowledgement Samplegof1mytamev2100% (1)
- Qazi Assignment Jun 20Document8 pagesQazi Assignment Jun 20kamal62747No ratings yet
- PA v. Cosby - Commonwealth's Motion To Introduce Evidence of Prior Bad Acts of The Defendant 09-06-16 OCRDocument68 pagesPA v. Cosby - Commonwealth's Motion To Introduce Evidence of Prior Bad Acts of The Defendant 09-06-16 OCRLaw&CrimeNo ratings yet
- Policy Paper On Barangay LegislationDocument24 pagesPolicy Paper On Barangay LegislationCorazon Adora SorianoNo ratings yet
- Call Center StudyDocument189 pagesCall Center StudyAmit Rakshe100% (1)
- DeliveryOpenSourceModelBasedBayesian Gunning 030203Document46 pagesDeliveryOpenSourceModelBasedBayesian Gunning 030203Thomas RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Develop Communicative Competence Written SkillsDocument46 pagesDevelop Communicative Competence Written SkillsFabri Pérez FernándezNo ratings yet
- Design Lecturer StudyDocument34 pagesDesign Lecturer StudyNoraidah MusanifNo ratings yet
- Human Humascope Plus - User ManualDocument16 pagesHuman Humascope Plus - User ManualEnrique DuarteNo ratings yet
- GlobalisationDocument11 pagesGlobalisationMaftei ClaudiaNo ratings yet
- El Lexicón Generativo James PustejovskyDocument34 pagesEl Lexicón Generativo James PustejovskyJoel Arturo Pedraza NicolasNo ratings yet