Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8 - Illustrating A Normal Random
Uploaded by
Clariza Jane Metro0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views47 pages1. A normal random variable represents a set of continuous numerical values that follow a normal distribution.
2. The normal distribution is a probability distribution of continuous random variables that is represented graphically by a normal curve.
3. Key characteristics of the normal curve include being bell-shaped and symmetric, having tails that extend indefinitely in both directions without touching the horizontal axis, and having the mean, median and mode located at the center.
Original Description:
Original Title
8- Illustrating a Normal Random
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. A normal random variable represents a set of continuous numerical values that follow a normal distribution.
2. The normal distribution is a probability distribution of continuous random variables that is represented graphically by a normal curve.
3. Key characteristics of the normal curve include being bell-shaped and symmetric, having tails that extend indefinitely in both directions without touching the horizontal axis, and having the mean, median and mode located at the center.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views47 pages8 - Illustrating A Normal Random
Uploaded by
Clariza Jane Metro1. A normal random variable represents a set of continuous numerical values that follow a normal distribution.
2. The normal distribution is a probability distribution of continuous random variables that is represented graphically by a normal curve.
3. Key characteristics of the normal curve include being bell-shaped and symmetric, having tails that extend indefinitely in both directions without touching the horizontal axis, and having the mean, median and mode located at the center.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 47
Illustrating a Normal
Random Variable and its
Characteristics
Let’s have a review first. Read the following statements carefully
and determine whether it is TRUE or FALSE. Write the word TRUE
if it is correct and FALSE if it is incorrect, then modify the
statement to make it true.
TRUE
________________1. Probability is the value greater than or equal to
zero but less than or equal to one.
FALSE
________________2. Discrete variables are the infinite numerical
values like heights, weights, distance and length
TRUE
________________3. 34% is also equal 0.34.
FALSE
________________4. Mean, mode and standard deviation are the
measures of central tendency.
TRUE
________________5. Mean is equal to the summation of scores
divided by the number of cases.
The following items show four pictures
captured by the author during his travel in
the different places and constructed using
GeoGebra application which represents a
common object. Analyze the group of
pictures carefully then identify the common
object they represent. Write your answer by
filling in the empty boxes below each item.
A hint is also provided for you.
Area
curve
Asymptote
Bell-Shape
Symetric
Normal Probability
Distribution is a
probability distribution of
continuous random
variables.
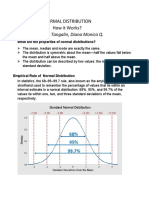
Properties of Normal Curve
The graphical representation of
the normal distribution is
popularly known as
a normal curve. The normal
curve is described clearly by the
following characteristics
1. The normal curve is
bell-shaped.
2. The curve is symmetrical about its
center. This means that, if we draw a
segment from the peak of the curve
down to the horizontal axis, the segment
divides the normal curve into two equal
parts or areas.
3. The mean, median, and mode
coincide at the center. This also
means that in
a normal distribution, or a
distribution described by a
normal curve, the
mean, median, and mode are
equal.
4. The width of the
curve is determined by
the standard deviation
of the
distribution.
5. The tails of the curve are plotted in
both directions and flatten out
indefinitely
along the horizontal axis. The tails are
thus asymptotic to the baseline. A
portion of the graph that is asymptotic
to a reference axis or another graph is
called an asymptote, always
approaching another but never touching
it.
6. The total area under a normal
curve is 1. This means that the
normal curve
represents the probability, or the
proportion, or the percentage
associated with
specific sets of measurement
values.
A normally distributed random variable
with a mean μ = 0 and standard
deviation ơ = 1 is called a standard
normal variable. It is presented using
standard normal distribution where the
center of the curve is zero, which is
mean and added one unit from the
center to the right and subtract one unit
from the center to the left.
c. When the means are different and the
standard deviations are also
different (μ ≠ μ ơ ≠ ơ ), the curves are centered at
1 2; 1 2
different points and
vary in shapes, as shown in figure 6.
EMPIRICAL RULE
The empirical rule is better known as
68% - 95% - 99.70% rule. This rule
states that the data in the distribution
lies within one (1), two (2), and three (3)
of the
standard deviation from the mean are
approximately 68%, 95%, and 99.70%,
respectively.
EMPIRICAL RULE
Since the area of a normal curve is equal to
1 or 100% as stated on its
characteristics, there are only a few data
which is 0.30% falls outside the 3-standard
deviation from the mean. For instance, the
distribution of the grades of the Senior High
School students in Statistics and Probability
for the Third Quarter is shown
below in Figure 7.
68% of data lies within 1 standard
deviation from the mean have a grade of
83 to 91
95% of data lies within 2 standard
deviations from the mean have a grade of
79 to 95
99.70% of data lies within 3 standard
deviations from the mean have a grade of
83 to 9
Illustrative Example 1:
The scores of the Senior High School
students in their Statistics and
Probability quarterly examination are
normally distributed with a mean of 35 and a
standard deviation of 5.
Answer the following questions:
a. What percent of the scores are between 30
to 40?
b. What scores fall within 95% of the
distribution?
Illustrative Example 1:
The scores of the Senior High School
students in their Statistics and
Probability quarterly examination are
normally distributed with a mean of 35 and a
standard deviation of 5.
Answer the following questions:
a. What percent of the scores are between 30
to 40?
b. What scores fall within 95% of the
distribution?
Answer:
a. The scores 30 to 40 falls within the first
standard deviation from the mean.
Therefore, the scores that fall between 30
and 40 is approximately 68% of the
distribution.
b. Since 95% of the distribution lies within 2
standard deviations from the mean, then the
scores corresponding to this area of the
distribution are scores from 25 up to 45.
Illustrative Example 2:
The district nurse of Candelaria East needs
to measure the BMI (Body Mass Index) of the
Alternative Learning System students. She
found out that the heights of male students
are normally distributed with a mean of 160
cm and a standard deviation of 7 cm. Find
the percentage of male
students whose height is within 153 cm to
174 cm.
Solution: The mean of this
problem is 160, it is subtracted
by 7 to the left (e.g. 160
-7 = 153; 153-7 = 146; 146 – 7
= 139) and add 7 to the right.
(e.g. 160 + 7 = 167; 167
+ 7 = 174 + 7 = 181).
As stated in figure 8, 153 cm falls at 1
standard deviation from the mean to
the left and the height of 174 cm falls
at 2 standard deviations from the
mean to the
right. Therefore, it covers the whole
68% and 13.5%. of the distribution
and the sum
of it is 81.5%
ANSWER: 81.5% of the male students
have a height between 153 cm to 174
cm.
168-258
1. A normal random variable
is a set of a numerical value
of continuous random
variables which is normally
distributed.
2. Normal Distribution is a
probability distribution of
continuous random variables.
It also represents the probability,
or the proportion, or the
percentage associated
with specific sets of measurement
values.
3. A normal curve has the following characteristics:
a. It should be bell-shaped and symmetric about its center.
b. Both sides of the tails of a normal curve do not touch the
horizontal axis.
c. In the horizontal axis, use 0 at the center where the mean is
located and
use 1, 2, and 3 to the right and -1, -2 and -3 to the left. But
still,
remember there is an integral part of each number. However, it
is not
limited to the -3 and 3, it is extended indefinitely
d. The distances between numbers in the horizontal line or the
x-axis are
always equal.
4. Empirical rule. This rule states
that the data in the distribution
lies within the 1,
2, and 3 of the standard deviation
of the mean.
5. Sixty-eight percent (68%) of
data lies within 1 standard
deviation from the mean.
6. Ninety-five percent
(95%) of data lies within
the 2-standard
deviation from the
mean.
7. Ninety-nine and seven-
tenths percent (99.70%) of
data lies within the 3-
standard
deviation from the mean.
You might also like
- Module 5Document38 pagesModule 5cuasayprincessnicole4No ratings yet
- Handouts Normal Probability Distribution Is A Probability Distribution of Continuous Random VariablesDocument2 pagesHandouts Normal Probability Distribution Is A Probability Distribution of Continuous Random VariablesJULIUS GONZALESNo ratings yet
- Las Statistics&probability Week4Document27 pagesLas Statistics&probability Week4Jemar AlipioNo ratings yet
- Chapter II Normal DistributionDocument39 pagesChapter II Normal DistributionMaricris Jagto-calixtoNo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument35 pagesNormal DistributionRoselyn VecinalNo ratings yet
- Self-Learning Module For Grade 11: Chapter Ii: Normal DistributionDocument38 pagesSelf-Learning Module For Grade 11: Chapter Ii: Normal DistributionAldrin Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Probab Stat 5 8 1Document29 pagesProbab Stat 5 8 1Roan CaluagNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 Skewness, Kurtosis and MomentsDocument49 pagesCHAPTER 5 Skewness, Kurtosis and MomentsAyushi Jangpangi100% (2)
- CHAPTER 5 Skewness, Kurtosis and MomentsDocument49 pagesCHAPTER 5 Skewness, Kurtosis and MomentsAyushi Jangpangi0% (1)
- Stat LAS 10 PDFDocument6 pagesStat LAS 10 PDFaljun badeNo ratings yet
- StatProb LAS Week2 Normal Distribution PDFDocument9 pagesStatProb LAS Week2 Normal Distribution PDFMark Cidric Roquero IINo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionsDocument27 pagesNormal DistributionsArianne Trish MaggayNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Describing Location in A Distribution: HW: P. 105 (1, 5, 9-15 ODD, 19-23 ODD, 31, 33-38)Document24 pages2.1 Describing Location in A Distribution: HW: P. 105 (1, 5, 9-15 ODD, 19-23 ODD, 31, 33-38)dfgdfgdfgdfNo ratings yet
- Activity 3. Illustrating A Normal Random Variable and Its CharacteristicsDocument22 pagesActivity 3. Illustrating A Normal Random Variable and Its CharacteristicsVillasan ,Lei ashley I.No ratings yet
- Assignment 2 State ArmanDocument9 pagesAssignment 2 State ArmanM.NadeemNo ratings yet
- Empirical RuleDocument25 pagesEmpirical RuleJash Antoneth TimbangNo ratings yet
- Presentation 7 Chap6Document17 pagesPresentation 7 Chap6Kevin NyakundiNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution Tangalin ReportDocument3 pagesNormal Distribution Tangalin ReportVanessa LacbayanNo ratings yet
- What Is ProbabilityDocument8 pagesWhat Is Probabilitykaliman2010No ratings yet
- Think Tank: Normal DistributionDocument19 pagesThink Tank: Normal DistributionNikki AlquinoNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Q3M4Document11 pagesStatistics and Probability Q3M4Anna Marie PelandasNo ratings yet
- Intro To Political Analysis and Research - Measures of Variablity and Normal DistriDocument5 pagesIntro To Political Analysis and Research - Measures of Variablity and Normal Distribyun baek hyunNo ratings yet
- Saint Joseph College Senior High School Department Tunga-Tunga, Maasin City, Southern Leyte 6600 PhilippinesDocument11 pagesSaint Joseph College Senior High School Department Tunga-Tunga, Maasin City, Southern Leyte 6600 PhilippinesJimkenneth RanesNo ratings yet
- Analysis Interpretation and Use of Test DataDocument50 pagesAnalysis Interpretation and Use of Test DataJayson EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal StatistikDocument7 pagesJurnal StatistikAry PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Standard Normal DistributionDocument26 pagesLesson 4 - Standard Normal Distributionktamog16No ratings yet
- Introduction To Descriptive StatisticsDocument73 pagesIntroduction To Descriptive StatisticsVinay DuttaNo ratings yet
- Applied Statistics SummaryDocument9 pagesApplied Statistics SummaryRutger WentzelNo ratings yet
- Module Using The Empirical RuleDocument14 pagesModule Using The Empirical RuleIzyle CabrigaNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency and VariabilityDocument2 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency and VariabilitynesumaNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendecyDocument5 pagesMeasures of Central TendecyLight_of_LifeNo ratings yet
- Applications of Normal DistributionDocument13 pagesApplications of Normal DistributionMohammed Demssie MohammedNo ratings yet
- Compilation of Lessons and ActivitiesDocument37 pagesCompilation of Lessons and ActivitiesMara M. LabanderoNo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument24 pagesNormal DistributionRossel Jane CampilloNo ratings yet
- 14 Normal DistributionDocument37 pages14 Normal DistributionJomar Porteros100% (2)
- Module 10 Introduction To Data and StatisticsDocument63 pagesModule 10 Introduction To Data and StatisticsRainiel Victor M. CrisologoNo ratings yet
- Chapt 10-14 ExamplesDocument11 pagesChapt 10-14 ExamplesViet NguyenNo ratings yet
- Measure of SkewnessDocument13 pagesMeasure of SkewnessDaiChi J3SNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution LESSON 2Document65 pagesNormal Distribution LESSON 2Chuck DaleNo ratings yet
- The Normal CurveDocument29 pagesThe Normal CurveKent gonzagaNo ratings yet
- Dispersion TheoryDocument7 pagesDispersion TheorySIVARANJANI PNo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument25 pagesNormal DistributionPauline Anne LopezNo ratings yet
- Cheb YshevDocument13 pagesCheb Yshevkriss WongNo ratings yet
- UALL 2044 Lecture 13Document34 pagesUALL 2044 Lecture 13PDooruNo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument41 pagesNormal DistributionRenee Jezz Lopez100% (1)
- Standard Deviation and Its ApplicationsDocument8 pagesStandard Deviation and Its Applicationsanon_882394540100% (1)
- Statistics and Probability PDFDocument12 pagesStatistics and Probability PDFCvNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 - Measures of Central Tendency (Part 1)Document20 pagesChapter 03 - Measures of Central Tendency (Part 1)BS Accoutancy St. SimonNo ratings yet
- T DistibutionDocument25 pagesT DistibutionFritz AstilloNo ratings yet
- Business StatisticsDocument7 pagesBusiness StatisticsFresher DatascienceNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Lesson 8Document45 pagesCHAPTER 1 Lesson 8menesesjelloNo ratings yet
- The Normal Distribution: ConceptsDocument17 pagesThe Normal Distribution: ConceptsJay Ian GeronaNo ratings yet
- Week 3 StatProb ModuleDocument37 pagesWeek 3 StatProb Modulealex antipuestoNo ratings yet
- Central Tendency Variation Skewness Individual Performance RelationshipsDocument9 pagesCentral Tendency Variation Skewness Individual Performance RelationshipsWena PurayNo ratings yet
- Class 2 Lab2Document6 pagesClass 2 Lab2GsUpretiNo ratings yet
- Normal Probability Distribution CHARLS PDFDocument21 pagesNormal Probability Distribution CHARLS PDFAnne BergoniaNo ratings yet
- How To Prepare Statistics For SSC CGL Tier II Study Notes in PDFDocument10 pagesHow To Prepare Statistics For SSC CGL Tier II Study Notes in PDFRahul DasNo ratings yet
- Interpreting The Mean and Variance of A Probability DistributionsDocument18 pagesInterpreting The Mean and Variance of A Probability DistributionsClariza Jane MetroNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability: Clariza Jane L. Metro Teacher IiiDocument53 pagesStatistics and Probability: Clariza Jane L. Metro Teacher IiiClariza Jane MetroNo ratings yet
- 5-Illustrating Mean and VarianceDocument34 pages5-Illustrating Mean and VarianceClariza Jane MetroNo ratings yet
- Finding Possible Values of A Random VariableDocument34 pagesFinding Possible Values of A Random VariableClariza Jane MetroNo ratings yet
- Computing Probability Corresponding To A Given Random VariableDocument18 pagesComputing Probability Corresponding To A Given Random VariableClariza Jane MetroNo ratings yet
- Illustrating A Random Variable (Discrete and Continuous)Document47 pagesIllustrating A Random Variable (Discrete and Continuous)Clariza Jane MetroNo ratings yet
- Illustrating Mean, Median, Mode and Variance & Standard Deviation of Discrete Random VariableDocument5 pagesIllustrating Mean, Median, Mode and Variance & Standard Deviation of Discrete Random VariableClariza Jane MetroNo ratings yet
- Week1 StatisticsDocument11 pagesWeek1 StatisticsNancy LantinganNo ratings yet
- ACTUARIES Statistical MethodsDocument21 pagesACTUARIES Statistical Methodsvg284No ratings yet
- Tutsheet 2Document4 pagesTutsheet 2sauraviitd09No ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Counting RulesDocument14 pagesUnit 3 - Counting RulesMatone MafologelaNo ratings yet
- ENGSTAT Lecture 6 Probability PDFDocument152 pagesENGSTAT Lecture 6 Probability PDFNatalie CuNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Tutorial Sheet 3 - 18MAB303T - 22-23 EvenDocument2 pagesUnit 1 - Tutorial Sheet 3 - 18MAB303T - 22-23 EvenJEMINA J (RA2011037010010)No ratings yet
- Al-Khatib's Combinatoric TheoryDocument10 pagesAl-Khatib's Combinatoric Theoryazraq68No ratings yet
- Econometrics Chapter 14, 15 & 16 PPT SlidesDocument113 pagesEconometrics Chapter 14, 15 & 16 PPT SlidesIsabelleDwight100% (2)
- Problems 2021June-StatisticsDocument2 pagesProblems 2021June-StatisticsHoàng AnnhNo ratings yet
- Copia de FUNCRESDocument207 pagesCopia de FUNCRESRichard CampusmanaNo ratings yet
- Queuing Theory LN 4Document102 pagesQueuing Theory LN 4M S PrasadNo ratings yet
- Uncertainties in Extreme Value Modelling of Wave Data in A Climate Change Perspective PDFDocument21 pagesUncertainties in Extreme Value Modelling of Wave Data in A Climate Change Perspective PDFAbd El Alim DahmaniNo ratings yet
- Analysis andDocument206 pagesAnalysis andLindaBravoNo ratings yet
- ch6 PDFDocument47 pagesch6 PDFRizkha HayatiNo ratings yet
- Exploratory Data AnalysisDocument26 pagesExploratory Data AnalysisTrini_thug100% (2)
- Application of Naïve Bayes Classification in Fraud DetectionDocument30 pagesApplication of Naïve Bayes Classification in Fraud Detectionneha doshiNo ratings yet
- Hypergeometric DistributionDocument15 pagesHypergeometric DistributionrollramsNo ratings yet
- Weibull Analysis in ExcelDocument7 pagesWeibull Analysis in ExcelPurwantoroNo ratings yet
- Basics of Statistics - 2Document77 pagesBasics of Statistics - 2Rajat ShettyNo ratings yet
- 18 SolutionsDocument6 pages18 SolutionsChuluunzagd BatbayarNo ratings yet
- Unit Two Problem AssignmentDocument2 pagesUnit Two Problem Assignmentahaque08No ratings yet
- AP Statistics Study GuideDocument12 pagesAP Statistics Study Guidegeoffreygao1100% (1)
- Revision - Bayesian InferenceDocument4 pagesRevision - Bayesian InferenceMevin ConhyeNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Probability: Solutions To Self-Quizzes and Self-TestsDocument7 pagesFundamentals of Probability: Solutions To Self-Quizzes and Self-TestsRaul Santillana QuispeNo ratings yet
- Biostat ManualDocument97 pagesBiostat ManualTwaha R. Kabandika100% (1)
- BALANGUE ALLEN JOHN Lesson 7Document12 pagesBALANGUE ALLEN JOHN Lesson 7James ScoldNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence Assignment 5Document9 pagesArtificial Intelligence Assignment 5natasha ashleeNo ratings yet
- A Novel Markov-Based Temporal-SoC Analysis For Characterizing PEV Charging DemandDocument11 pagesA Novel Markov-Based Temporal-SoC Analysis For Characterizing PEV Charging DemandZedequias AlvesNo ratings yet
- Last Assignment DistributionsDocument3 pagesLast Assignment Distributionsayaan khanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document61 pagesChapter 2Riaz Hussain JunejoNo ratings yet