Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dna Stages
Uploaded by
Hafi Malik0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views12 pagesChromatin is the combination of DNA, RNA, and proteins that make up chromosomes in eukaryotic cell nuclei. The structure of chromatin changes during the cell cycle and cell division. There are three stages of chromatin organization: nucleosomes formed by DNA wrapping around histone proteins, multiple histones wrapping into a 30nm fiber, and higher-level packaging of the fiber into metaphase chromosomes. Methods used to analyze chromatin structure and protein interactions include chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing, DNA footprinting, and micrococcal nuclease sequencing. The main functions of chromatin are preventing DNA damage, tightly packing DNA, controlling DNA replication and gene expression, and supporting the DNA during cell division.
Original Description:
DNA
Original Title
DNA STAGES
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentChromatin is the combination of DNA, RNA, and proteins that make up chromosomes in eukaryotic cell nuclei. The structure of chromatin changes during the cell cycle and cell division. There are three stages of chromatin organization: nucleosomes formed by DNA wrapping around histone proteins, multiple histones wrapping into a 30nm fiber, and higher-level packaging of the fiber into metaphase chromosomes. Methods used to analyze chromatin structure and protein interactions include chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing, DNA footprinting, and micrococcal nuclease sequencing. The main functions of chromatin are preventing DNA damage, tightly packing DNA, controlling DNA replication and gene expression, and supporting the DNA during cell division.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views12 pagesDna Stages
Uploaded by
Hafi MalikChromatin is the combination of DNA, RNA, and proteins that make up chromosomes in eukaryotic cell nuclei. The structure of chromatin changes during the cell cycle and cell division. There are three stages of chromatin organization: nucleosomes formed by DNA wrapping around histone proteins, multiple histones wrapping into a 30nm fiber, and higher-level packaging of the fiber into metaphase chromosomes. Methods used to analyze chromatin structure and protein interactions include chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing, DNA footprinting, and micrococcal nuclease sequencing. The main functions of chromatin are preventing DNA damage, tightly packing DNA, controlling DNA replication and gene expression, and supporting the DNA during cell division.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
University of Okara
Assignment : cell biology
Topic: chromatin material
Submitted by : Iqra liaqat
Submitted to : sir Ali umar
Chromatin
material
– Chromatin is a genetic
material or a macromolecule
comprising of DNA, RNA,
and associated proteins,
which constitute
chromosomes in the nucleus
of an eukaryotic cell.
Structure of
chromatin
– The structure of chromatin is
governed by a number of
factors. The complete
structure mainly depends on
the phases of the cell cycle.
They undergo various
structural changes during cell
division
– The structure of
chromosomes is clearly
visible under a light
microscope during
metaphase, which changes
their shape while the DNA is
duplicated and divided into
two cells.
Stages in
chromatin
group
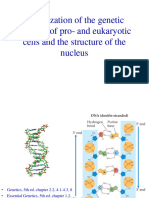
– There are 3 stages in chromatin group:
– Nucleosomes are formed by the wrapping of
DNA around the histone proteins
– Multiple histones wrap into a 30 nm fibre
consisting of the nucleosome.
– Higher-level DNA packaging of the 30 nm
fibre into the metaphase chromosome.
Methods used to
analysis chromatin
– There are several methods to analysis chromatin
which are:
– Chromatin Immunoprecepitation
Sequencing
– A process mainly used for analyzing the
interactions of the protein with DNA.
– The binding sites of DNA
combined proteins are identified by the
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation and
parallel DNA sequencing.
DNA
footprinting
– A technique mainly used for
identifying the DNA-binding
protein:
Micrococcal Nuclease
Sequencing
– A method mainly used for
studying about the
nucleosomes by digesting
chromatins. This sequence
mainly uses micrococcal
nuclease enzyme for
identifying the position of the
nucleosome throughout the
genome.
Functions of
chromatin
– This chromatin is located
within the cell nucleus. The
main functions of this genetic
material include:
– Preventing DNA damage.
– Tightly packing of the DNA
to fit into the cell
Functions
– Control the DNA replication and
gene expression.
– Support the DNA molecule to
permit the process of cell cycle –
meiosis and mitosis.
You might also like
- 03 NucleusDocument11 pages03 NucleusRadon WilsonNo ratings yet
- Gene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyFrom EverandGene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Unit 3. The NucleusDocument130 pagesUnit 3. The NucleusArio AhmadieNo ratings yet
- FOI 6 (I) DNA Organisation, Replication & RepairDocument81 pagesFOI 6 (I) DNA Organisation, Replication & RepairSohail RanaNo ratings yet
- 6 Cytology Nucleus 1Document35 pages6 Cytology Nucleus 1SamNo ratings yet
- 2 NucleusDocument19 pages2 NucleusYuu Ayu'k LifestarNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology I: Dr. Roquyya GulDocument13 pagesMolecular Biology I: Dr. Roquyya GulayeshaNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Unit 3Document27 pagesBiology Notes Unit 3Ralph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Genome Expression: Alick MwambunguDocument72 pagesGenome Expression: Alick Mwambungumwambungup100% (1)
- Materi Minggu 6Document44 pagesMateri Minggu 6HafizahNo ratings yet
- Basic Techniques To Manipulate Genetic MaterialDocument7 pagesBasic Techniques To Manipulate Genetic MaterialRogelio Arellano LawayanNo ratings yet
- Genetics Seminars 1-3Document289 pagesGenetics Seminars 1-3Мөнхгэрэл ГанбатNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Dna, Gene ChromosomeDocument31 pagesRelationship Between Dna, Gene ChromosomemaimonsabiNo ratings yet
- GenomesDocument36 pagesGenomesMariakayNo ratings yet
- Neuclic Acid and Protein SynthesisDocument21 pagesNeuclic Acid and Protein SynthesisPradyut BiswasNo ratings yet
- Foundations in Microbiology: TalaroDocument68 pagesFoundations in Microbiology: Talaromertx013No ratings yet
- q3l3 - 3ndquarter Science 10Document12 pagesq3l3 - 3ndquarter Science 10Billy Jasper DomingoNo ratings yet
- Bio ToulouseDocument15 pagesBio ToulouseMohamed AlaeddinNo ratings yet
- Chromatin Structure and Histones Code - CCBDocument44 pagesChromatin Structure and Histones Code - CCBhafssa BachirNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Cell Biology: Chapter 7: The Nucleus and DNA ReplicationDocument28 pagesFundamentals of Cell Biology: Chapter 7: The Nucleus and DNA ReplicationPlinio GuzmanNo ratings yet
- The Nucleus: Genome (Genetic Information) in Eukaryotic Cells, So It Is ResponsibleDocument9 pagesThe Nucleus: Genome (Genetic Information) in Eukaryotic Cells, So It Is ResponsibleAbbas TalibNo ratings yet
- NucleusDocument56 pagesNucleussreekarwNo ratings yet
- III. Chapter 3 (Nucleus)Document5 pagesIII. Chapter 3 (Nucleus)rosalesjirehrNo ratings yet
- TransesDocument3 pagesTransesits mitziNo ratings yet
- BBMS1001 NotesDocument41 pagesBBMS1001 NotesHelen WanNo ratings yet
- Nucleus: The Nucleus Occurs Only in EukaryotesDocument5 pagesNucleus: The Nucleus Occurs Only in Eukaryotesapi-3706483No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Cell Bio NotesDocument18 pagesChapter 5 Cell Bio NotesJenny100% (1)
- MB 2Document76 pagesMB 2ahkrabNo ratings yet
- Bio ModelDocument12 pagesBio ModelDouuNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Topic 7 BiologyDocument16 pagesUnit 4 Topic 7 BiologySana SyedNo ratings yet
- 2 Genetics Lecture - DNA PackagingDocument45 pages2 Genetics Lecture - DNA PackagingAMIRA HELAYELNo ratings yet
- Chromosome Organization: AkamandalDocument24 pagesChromosome Organization: AkamandalnaomiNo ratings yet
- Mammalian Artificial ChromosomesDocument5 pagesMammalian Artificial ChromosomesKanzaNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument25 pagesCellsAshwika RajanNo ratings yet
- Animal Cells IDocument3 pagesAnimal Cells Irandomscribduser2012No ratings yet
- The Eukaryotic Cell's Genetic Instruction Are Haused in The Nucleus and Carried Out by The RibosomesDocument3 pagesThe Eukaryotic Cell's Genetic Instruction Are Haused in The Nucleus and Carried Out by The Ribosomesvin caNo ratings yet
- Chromosomes, Genes and DNA: Biology-Grade 11 Mrs. Aarti NairDocument38 pagesChromosomes, Genes and DNA: Biology-Grade 11 Mrs. Aarti NairRafiqul IslamNo ratings yet
- NucleusDocument10 pagesNucleusPinak ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document94 pagesWeek 4wieka mawieNo ratings yet
- 3 1-HistoDocument7 pages3 1-HistoLouise Nicole CastroNo ratings yet
- Histo Book (1-3)Document5 pagesHisto Book (1-3)Gwen YosheenNo ratings yet
- Nucleus: Sudhanshu Shekhar, M.Tech BiotechDocument22 pagesNucleus: Sudhanshu Shekhar, M.Tech BiotechSudhanshu ShekharNo ratings yet
- ٣٢٥ Molecular Biology Sabah Linjawi ١Document15 pages٣٢٥ Molecular Biology Sabah Linjawi ١Zainab RaikNo ratings yet
- Xii Semana - El Nucleo InterfasicoDocument67 pagesXii Semana - El Nucleo Interfasicofiorella pahuachonNo ratings yet
- Inti Sel Dan Ribosom - Bagus PriambodoDocument61 pagesInti Sel Dan Ribosom - Bagus PriambodoAHMAD IQBALNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 - CellDocument9 pagesWorksheet 1 - CellDiva putri DamayantiNo ratings yet
- What Is Genome ?Document9 pagesWhat Is Genome ?Bhumi Gameti100% (1)
- Transcriptomics: Shivangi Asthana B.Sc. BiotechDocument22 pagesTranscriptomics: Shivangi Asthana B.Sc. Biotechsachin kumarNo ratings yet
- GN0303 Notes - Unit1-Part1Document20 pagesGN0303 Notes - Unit1-Part1Abhi KannanNo ratings yet
- CHP 10 (Bio)Document10 pagesCHP 10 (Bio)Serena BautistaNo ratings yet
- Chromatin, Chromosomes, and The Cell Nucleus pp.105-110 122Document11 pagesChromatin, Chromosomes, and The Cell Nucleus pp.105-110 122Zainab Jamal SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- 02 Lecture Presentation (Bio20-1, Mapua Institute of Technology)Document47 pages02 Lecture Presentation (Bio20-1, Mapua Institute of Technology)Christelle ZuluetaNo ratings yet
- 121 Lecture Section 2Document134 pages121 Lecture Section 2FENo ratings yet
- Kanzul Cell & Molecular BiologyDocument12 pagesKanzul Cell & Molecular BiologyMuhammad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Curs 4 - Structura NucleuluiDocument33 pagesCurs 4 - Structura NucleuluiBodeaGabrielaNo ratings yet
- Transmission GeneticsDocument7 pagesTransmission GeneticsAnas KhanNo ratings yet
- TM-04 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Chromosome Structure (Genap 2016-2017)Document32 pagesTM-04 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Chromosome Structure (Genap 2016-2017)Fiy Jannatin AliyahNo ratings yet
- Genetics: The Genetic MaterialDocument25 pagesGenetics: The Genetic Materialعمار مصعب عادلNo ratings yet
- Genetics - Chapter 2 - Mitosis and Meiosis-Cellular ReproductionDocument37 pagesGenetics - Chapter 2 - Mitosis and Meiosis-Cellular ReproductionDuy AnhNo ratings yet