0% found this document useful (0 votes)
239 views17 pagesHeart Block
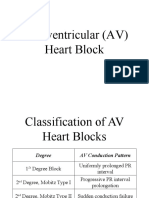
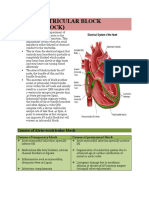
This document summarizes different types of heart block based on ECG findings. It describes first degree AV block where the PR interval is prolonged but every P wave is followed by a QRS complex. It then describes three types of second degree heart block: Mobitz type 1 where the PR interval gradually prolongs before a blocked P wave; Mobitz type 2 where the PR interval remains fixed; and advanced or high grade block where 2 or more P waves are not conducted. Complete heart block is described as a failure of P waves to conduct resulting in dissociation of P waves and QRS complexes.
Uploaded by
litan dasCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
239 views17 pagesHeart Block
This document summarizes different types of heart block based on ECG findings. It describes first degree AV block where the PR interval is prolonged but every P wave is followed by a QRS complex. It then describes three types of second degree heart block: Mobitz type 1 where the PR interval gradually prolongs before a blocked P wave; Mobitz type 2 where the PR interval remains fixed; and advanced or high grade block where 2 or more P waves are not conducted. Complete heart block is described as a failure of P waves to conduct resulting in dissociation of P waves and QRS complexes.
Uploaded by
litan dasCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd