0% found this document useful (0 votes)
85 views25 pagesLearning Targets for Assessment Methods
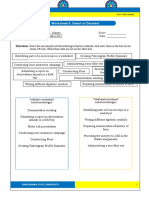
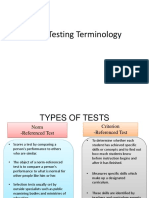
The document discusses learning targets and Bloom's taxonomy of educational objectives. It covers the three domains of learning: cognitive, affective, and psychomotor. For each domain, it lists the different levels or types of learning objectives from simplest to most complex. Examples are provided to illustrate each level. The purpose is to help match appropriate learning targets to alternative forms of assessment.
Uploaded by
Janine AbrinaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
85 views25 pagesLearning Targets for Assessment Methods
The document discusses learning targets and Bloom's taxonomy of educational objectives. It covers the three domains of learning: cognitive, affective, and psychomotor. For each domain, it lists the different levels or types of learning objectives from simplest to most complex. Examples are provided to illustrate each level. The purpose is to help match appropriate learning targets to alternative forms of assessment.
Uploaded by
Janine AbrinaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd