Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Presentation
Uploaded by
fatima zafar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views7 pagesOriginal Title
Presentation (4)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views7 pagesPresentation
Uploaded by
fatima zafarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
Termination
• Once the complete chromosome has been replicated, termination of
DNA replication must occur.
• Although much is known about initiation of replication, less is known
about the termination process.
• Following replication, the resulting complete circular genomes of
prokaryotes are concatenated, meaning that the circular DNA
chromosomes are interlocked and must be separated from each other.
Conti..
• This is accomplished through the activity of bacterial topoisomerase
IV, which introduces double-stranded breaks into DNA molecules,
allowing them to separate from each other; the enzyme then reseals the
circular chromosomes.
• The resolution of concatemers is an issue unique to prokaryotic DNA
replication because of their circular chromosomes
Conti..
• The resolution of concatemers is an issue unique to prokaryotic DNA
replication because of their circular chromosomes.
• Because both bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV are
distinct from their eukaryotic counterparts, these enzymes serve as
targets for a class of antimicrobial drugs called quinolones.
Conclusion
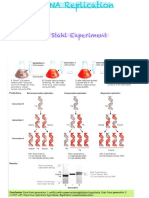
• The DNA replication process is semiconservative, which results in
two DNA molecules, each having one parental strand of DNA and one
newly synthesized strand.
• In bacteria, the initiation of replication occurs at the origin of
replication, where supercoiled DNA is unwound by DNA gyrase,
made single-stranded by helicase, and bound by single-stranded
binding protein to maintain its single-stranded
state. Primase synthesizes a short RNA primer, providing a free 3′-
OH group to which DNA polymerase III can add DNA nucleotides.
Conti..
• During elongation, the leading strand of DNA is synthesized
continuously from a single primer. The lagging strand is synthesized
discontinuously in short Okazaki fragments, each requiring its own
primer. The RNA primers are removed and replaced with DNA
nucleotides by bacterial DNA polymerase I, and DNA ligase seals the
gaps between these fragments.
• Termination of replication in bacteria involves the resolution of
circular DNA concatemers by topoisomerase IV to release the two
copies of the circular chromosome
Conti..
• The linear nature of eukaryotic chromosomes
necessitates telomeres to protect genes near the end of the
chromosomes. Telomerase extends telomeres, preventing their
degradation, in some cell types.
• Rolling circle replication is a type of rapid unidirectional DNA
synthesis of a circular DNA molecule used for the replication of some
plasmids.
You might also like
- DNA ReplicationDocument48 pagesDNA ReplicationAamir MumtazNo ratings yet
- Semi-Conservative DNA ReplicationDocument12 pagesSemi-Conservative DNA ReplicationDibyakNo ratings yet
- Bacterial GeneticsDocument38 pagesBacterial Geneticsfatima zafarNo ratings yet
- Assignment General MicrobiologyDocument4 pagesAssignment General Microbiology05 Jawad ZahoorNo ratings yet
- MB 2Document76 pagesMB 2ahkrabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document67 pagesChapter 5علوم طبية AUG 2020No ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument25 pagesDNA ReplicationPhilani KheswaNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 PDFDocument16 pagesUnit 9 PDFcarlette11No ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument43 pagesDNA ReplicationBilal SajidNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid-Based Cellular ActivitiesDocument30 pagesNucleic Acid-Based Cellular ActivitiesTom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Ten Biosynthesis of Nucleic Acids: Replication: Mary K. Campbell Shawn O. FarrellDocument26 pagesChapter Ten Biosynthesis of Nucleic Acids: Replication: Mary K. Campbell Shawn O. FarrellnidsNo ratings yet
- Learning Unit 3 - PART 2 - DNA ReplicationDocument43 pagesLearning Unit 3 - PART 2 - DNA ReplicationSphesihle ThekoNo ratings yet
- 10 Biosynthesis of Nucleic AcidsDocument26 pages10 Biosynthesis of Nucleic AcidsDayne Ocampo-Soliman100% (1)
- DNA Replication in ProkaryotesDocument24 pagesDNA Replication in ProkaryotesAlbert Jade Pontimayor Legaria100% (1)
- GROUP1-DNA Replication in ProkaryotesDocument24 pagesGROUP1-DNA Replication in ProkaryotesAlbert Jade Pontimayor Legaria100% (1)
- 6 - DNA ReplicationDocument63 pages6 - DNA ReplicationEmad SabbaghNo ratings yet
- 6 DNA ReplicationDocument13 pages6 DNA ReplicationVenkat RaniNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Metabolism TAUDocument38 pagesNucleic Acid Metabolism TAUFaatimah EssaNo ratings yet
- Mira Molecular Biology Part1Document63 pagesMira Molecular Biology Part1Ranim MiraNo ratings yet
- BCH 401 Note 1 - KWASUDocument35 pagesBCH 401 Note 1 - KWASUidriscognitoleadsNo ratings yet
- 2022-04-17 L4 - DNA ReplicationDocument46 pages2022-04-17 L4 - DNA ReplicationTamara ElyasNo ratings yet
- Presentation on-WPS Office DNADocument16 pagesPresentation on-WPS Office DNANaznin ShahriaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Topic 7 BiologyDocument16 pagesUnit 4 Topic 7 BiologySana SyedNo ratings yet
- Please Switch Off Your MobilesDocument35 pagesPlease Switch Off Your MobilesSadia MushtaqNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument19 pagesDNA ReplicationAkss ShauryaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Dna ReplicationDocument53 pagesProkaryotic Dna ReplicationRININo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.2 DNA Replication (Autosaved)Document36 pagesChapter 1.2 DNA Replication (Autosaved)abdullaNo ratings yet
- Lecture-15, DNA Replication-II (New)Document37 pagesLecture-15, DNA Replication-II (New)Vayshnave MuniandyNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication-Sem 2 20222023-UKMFolio-Part 3Document40 pagesDNA Replication-Sem 2 20222023-UKMFolio-Part 3Keesal SundraNo ratings yet
- Molecular BiologyDocument34 pagesMolecular BiologyMega XtericsNo ratings yet
- DNADocument13 pagesDNAjeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- Dna Code of LifeDocument9 pagesDna Code of Lifendlovusenamile401No ratings yet
- DNA Replication Mod IIDocument61 pagesDNA Replication Mod IIAmit KaushikNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic ReplicationDocument45 pagesEukaryotic Replicationeali63807No ratings yet
- Basics of Molecular BiologyDocument69 pagesBasics of Molecular BiologypathinfoNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument16 pagesDNA ReplicationStephen Moore100% (1)
- New Microsoft Office PowerPoint PresentationDocument27 pagesNew Microsoft Office PowerPoint Presentationarunpandey1686No ratings yet
- Lecture No. 10 Cell & Mol Bio DNADocument30 pagesLecture No. 10 Cell & Mol Bio DNAUshna Asif BSCHE-ENo ratings yet
- Transcription ProcessDocument85 pagesTranscription Processshruti shahNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression: Vikrant Joshi F.Y. Biotechnology 6519 Khalsa College AmritsarDocument31 pagesGene Expression: Vikrant Joshi F.Y. Biotechnology 6519 Khalsa College Amritsarvikrant4018No ratings yet
- Dna Organization 2014Document51 pagesDna Organization 2014Christine Karen BumanlagNo ratings yet
- Bacterial GeneticsDocument29 pagesBacterial GeneticsBiruk WondimuNo ratings yet
- Inhibition of DNA Replication and TranscriptionDocument111 pagesInhibition of DNA Replication and TranscriptionPranav Kumar PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Bacterial GeneticsDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Bacterial GeneticseyoelNo ratings yet
- Bic 159: Biochemistry Week 2 Lecture: Dr. Jody Ann JohnsonDocument46 pagesBic 159: Biochemistry Week 2 Lecture: Dr. Jody Ann JohnsonJana-Tae KerrNo ratings yet
- DNA in Brief PDFDocument5 pagesDNA in Brief PDFayushfmNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication, Repair, and RecombinationDocument92 pagesDNA Replication, Repair, and RecombinationJagdesh SajnaniNo ratings yet
- Double-Helical Model Structure Based On Rosalind Franklin's X-Ray Crystallography, The DNA MoleculeDocument9 pagesDouble-Helical Model Structure Based On Rosalind Franklin's X-Ray Crystallography, The DNA MoleculeTherese Jan MangussadNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument24 pagesDNA ReplicationAkhtar MuneerNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument47 pagesDNA ReplicationYSOBELLATHERESE BILOLONo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 BiologyDocument40 pagesChapter 3 BiologyAnam FNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument19 pagesDNA ReplicationLouis HilarioNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument47 pagesDNA ReplicationastrogeniusthreeNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication IIDocument9 pagesDNA Replication IIKhushnood FatimaNo ratings yet
- Chromosome Organization: AkamandalDocument24 pagesChromosome Organization: AkamandalnaomiNo ratings yet
- Different TranscriptionDocument3 pagesDifferent TranscriptionAznoer RanNo ratings yet
- Replication of DNADocument2 pagesReplication of DNAzibnehuqNo ratings yet
- ReplicationDocument39 pagesReplicationhjklknnm jhoiolkNo ratings yet
- Dna and RnaDocument36 pagesDna and RnaMoona MalikNo ratings yet
- H. Pylori PrimersDocument3 pagesH. Pylori Primersasaleh74No ratings yet
- DNA Damage Repair MechanismsDocument40 pagesDNA Damage Repair MechanismspriannaNo ratings yet
- Nucleotides NsDocument118 pagesNucleotides NsRishi ButolaNo ratings yet
- FISH Analysis of Chromosomes and DNA RecombinationDocument32 pagesFISH Analysis of Chromosomes and DNA RecombinationAzry MustapaNo ratings yet
- Human CellDocument22 pagesHuman Cellsen_subhasis_58No ratings yet
- Acc Makalah Semhas AltalarikDocument10 pagesAcc Makalah Semhas AltalarikIgede Arya WedaNo ratings yet
- 1kb Plus LadderDocument4 pages1kb Plus LadderPedro SoaresNo ratings yet
- Genomic Technologies in Clinical Diagnostics - Glossary: Term Alignment AlleleDocument7 pagesGenomic Technologies in Clinical Diagnostics - Glossary: Term Alignment AlleleChloé PleiterNo ratings yet
- DNA DR In-Class ActivitiesDocument15 pagesDNA DR In-Class ActivitiesCéline Engels100% (1)
- Test Bank For Biology Concepts and Investigations 4th Edition Marielle Hoefnagels 2Document17 pagesTest Bank For Biology Concepts and Investigations 4th Edition Marielle Hoefnagels 2AmberClineagwbd100% (36)
- Biology Lesson 1.1Document16 pagesBiology Lesson 1.1Crystal Joy BondadNo ratings yet
- Modeling Recombinant DNA Technology: Background MaterialsDocument6 pagesModeling Recombinant DNA Technology: Background MaterialsChintya AurelyaaNo ratings yet
- RNA and Protein Synthesis QuizDocument6 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis QuizJeremy Guggenheim100% (2)
- Dna SequencingDocument26 pagesDna SequencingIqra FarrukhNo ratings yet
- 01 Fastdigest Conventional Restriction EnzymesDocument234 pages01 Fastdigest Conventional Restriction EnzymesEd PedrazaNo ratings yet
- Touchdown PCR PDFDocument6 pagesTouchdown PCR PDFMatheusRsaNo ratings yet
- Dna Ligase, Terminal Transferase, Adapter and LinkerDocument80 pagesDna Ligase, Terminal Transferase, Adapter and LinkerSujit ShandilyaNo ratings yet
- Rolling Circle PDFDocument20 pagesRolling Circle PDFسٓنج ايكٓNo ratings yet
- Neuclic Acid and Protein SynthesisDocument21 pagesNeuclic Acid and Protein SynthesisPradyut BiswasNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Different Melting Temperature CalculationDocument12 pagesComparison of Different Melting Temperature CalculationOsama AlrawabNo ratings yet
- Dna ReplicationDocument9 pagesDna ReplicationJason Raquin RoqueNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Dna Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesWorksheet - Dna Protein Synthesisapi-270403367100% (1)
- Central DogmaDocument35 pagesCentral Dogmatariqul13017No ratings yet
- Cot CurveDocument16 pagesCot CurveVidyasagar Deshpande100% (1)
- Gene Sequencing Methods (Word Document)Document14 pagesGene Sequencing Methods (Word Document)pavaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Gene Expression From Gene To ProteinDocument18 pagesChapter 17 Gene Expression From Gene To Protein蔡旻珊100% (1)
- By DR Ananya MandalDocument4 pagesBy DR Ananya MandalhasimNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 Nucleic Acids IBDP HL NotesDocument27 pagesTopic 7 Nucleic Acids IBDP HL NotesKathryn BrandwoodNo ratings yet
- MCAT Topic Focus Biology Electrophoresis and Blotting FSQ DrillDocument1 pageMCAT Topic Focus Biology Electrophoresis and Blotting FSQ DrillAnjalie GulatiNo ratings yet