Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ab6edabb 1641872462822
Uploaded by
Bakchodi Wala0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views24 pagesOriginal Title
880277c742f248e728967c8724add5baab6edabb-1641872462822
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views24 pagesAb6edabb 1641872462822
Uploaded by
Bakchodi WalaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 24
AEE 302
SYSTEM SIMULATION AND AGRO-ADVISORY
L:2 T:0 P:2 Credits: 3
By
AJIT KUMAR GHOSLYA
Experiment No.-1
To visit Agro-meteorological observatory
Aim: To visit Agro-meteorological observatory
Learning outcome: Enhance the understanding of undergraduate students
regarding measurement of weather elements, their interpretation and role in crop
production. Students will also learn different type of techniques, sensors, skills,
recorders, instruments etc. by standard methods at hours recommended by IMD
and WMO.
Theory/Principles/Background of the topic:
An observatory is a specially designed station or place where the regular
and simultaneous records of the weather data are made by physical
measurements using various techniques, sensors, skills, recorders,
instruments etc. by standard methods at hours recommended by IMD and
WMO. IMD was established during 1875 with its central office at
Pune which takes up this responsibility.
Country is divided into 35 meteorological sub-divisions.
To facilitate the collection of data at one point, five regional centers
were established, which are located in five different places, for
which the headquarters are mentioned against each as detailed below.
North zone — Delhi
East zone — Calcutta
South zone — Chennai
West zone — Bombay
Central zone — Nagpur
Weather affects agriculture at every stage; therefore, knowledge
of crop weather relationship helps in optimizing the agricultural
operations. Since meteorology and climatology are primarily
observational science, adequate care has to be taken for getting
most representative and accurate observations of weather
parameters for their worthwhile application in weather and
climate prediction.
Agro meteorological observatories
Agrometeorological observatories are those stations at which physical elements
of climate and biological, agricultural elements, generally of phonological nature or
both related to agriculture are observed to explore crop environment relationship.
World Meteorological Organization (WMD) has divided agro-met observatories into
four categories-Principal, Ordinary, Auxiliary and Specific purpose agro-met
observatories.
Ancient Method of weather
observation
Until the 18th century, people used sensory observations to
measure the weather data
Wind direction through the movement of leaves
Time of rain through the number of clouds in the sky
Weather instruments :
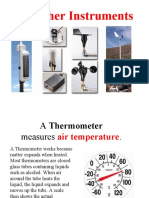
Thermometer
Hygrometer
Barometer
Rain gauge
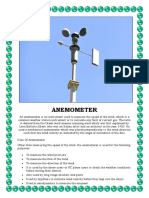
Anemometer
Wind vane
Sunshine recorder
Human eye
Thermometer working principle:
• Made up of Mercury and Alcohol
• Alcohol expand with increasing temp.
• Alcohol contract with falling temp.
• Metal indices shows the max. & min. temp
Barometer measures..?
(a). Wind pressure.
(b). Air flow.
(c). Rainfall.
(d). Atmospheric pressure
Outline of the Procedure:
Things to be observed in lab are
a) Pan Evaporimeter: To measure the evaporation in mm or cm/day.
b)Barometer : It indicates the pressure of atmosphere with respect of time
c) Thermometer : it indicates the air temperature (maximum and minimum
temperature)
d)Wind vane: To know the direction from which wind is blowing
e) Sunshine recorder: To measure the bright sunshine hours/length of the day
f) Rain gauge: To measure rainfall received in a day
g) Anemometer: To measure speed of wind
The Indian Meteorological Organization is situated in..?
(a). Mumbai.
(b). Delhi.
(c). Kolkata.
(d). Pune.
You might also like
- Practical Manual: Jharkhand Rai University Ranchi, JharkhandDocument32 pagesPractical Manual: Jharkhand Rai University Ranchi, JharkhandVishnu SainiNo ratings yet
- 77 Fa 5 C 35 C 4 Agromanual IDocument66 pages77 Fa 5 C 35 C 4 Agromanual IAnonymous BrUMhCjbiBNo ratings yet
- AGR 122 Manual 2018-19Document65 pagesAGR 122 Manual 2018-19BASAVARAJ ARABHANVINo ratings yet
- Weather InstrumentsDocument12 pagesWeather InstrumentsMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Obj. 252u Ray ACARA 1 KLIMATOLOGI Ray Restu FauziDocument24 pagesObj. 252u Ray ACARA 1 KLIMATOLOGI Ray Restu FauziRay Restu FauziNo ratings yet
- What Are The Uses of Meteorological InstrumentsDocument2 pagesWhat Are The Uses of Meteorological InstrumentsCire DuronNo ratings yet
- AGR 102 Introductory Agro-Meteorology - Climate Change (1-1)Document110 pagesAGR 102 Introductory Agro-Meteorology - Climate Change (1-1)Dhanush100% (1)
- Report On The Field Visit To The Philippine AtmosphericDocument3 pagesReport On The Field Visit To The Philippine AtmospherichjgjhgjNo ratings yet
- Geography HYDocument5 pagesGeography HYArpit BarmanNo ratings yet
- Practical Manual ON Agricultural Meteorlogy: Acharya N G Ranga Agricultural University Rajendranagar, Hyderabad - 500 030Document109 pagesPractical Manual ON Agricultural Meteorlogy: Acharya N G Ranga Agricultural University Rajendranagar, Hyderabad - 500 030Souvik Roy ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Report On The Field Visit To The Philippine AtmosphericDocument4 pagesReport On The Field Visit To The Philippine AtmospherichjgjhgjNo ratings yet
- ABEn 145 - Tribunalo - Lab 4Document14 pagesABEn 145 - Tribunalo - Lab 4Jaylou OpondaNo ratings yet
- Visit Report To IMDocument10 pagesVisit Report To IM39 - Deep MandokarNo ratings yet
- Designe and Implementation of Weather Forecasting System in Air Line CompanyDocument53 pagesDesigne and Implementation of Weather Forecasting System in Air Line CompanypromiseNo ratings yet
- Visit Report Meteorological DepartmentDocument16 pagesVisit Report Meteorological DepartmentSarah Suhaini Rahmat100% (1)
- MeteorologicalDocument10 pagesMeteorologicalOgbuehi ObiutoNo ratings yet
- Weather Monitoring SystemDocument67 pagesWeather Monitoring SystemAKOMOLEDE SUNDAY100% (1)
- Report File On Site Visit - Rajeev 4002Document37 pagesReport File On Site Visit - Rajeev 4002rajeev tomarNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of A Computer Based SystemDocument35 pagesDesign and Implementation of A Computer Based Systempromise0% (1)
- AGR205Document108 pagesAGR205Racheal BasseyNo ratings yet
- Presentation Prep: GreetDocument5 pagesPresentation Prep: GreetRushikesh MahajanNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange wi-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesGas Exchange wi-WPS OfficeCandy SantoNo ratings yet
- WEATHER FORECATING, Jatinderpal Singh 13-08-2019Document38 pagesWEATHER FORECATING, Jatinderpal Singh 13-08-2019jatinder100% (1)
- Book Manual 103 BapatlaDocument80 pagesBook Manual 103 BapatlaAjay ReddyNo ratings yet
- 3-CHAPTER 3 - Description of EnvironmentDocument42 pages3-CHAPTER 3 - Description of EnvironmentNishit ChadhaNo ratings yet
- GPSCDocument13 pagesGPSCyashsariya25No ratings yet
- MeteorologyDocument3 pagesMeteorologyGM MostakimNo ratings yet
- EDUM205 - Artifact #3 (POLISHED)Document2 pagesEDUM205 - Artifact #3 (POLISHED)Angel Florence V. VillareNo ratings yet
- Report On The Field Visit To The Philippine AtmosphericDocument3 pagesReport On The Field Visit To The Philippine AtmospherichjgjhgjNo ratings yet
- Weather Instruments, Maps and ChartsDocument2 pagesWeather Instruments, Maps and ChartsRaphael RinhlupuiiNo ratings yet
- Use of Meteorological Instruments - 2Document2 pagesUse of Meteorological Instruments - 2MinatiBindhani100% (1)
- Geography DraftDocument11 pagesGeography Drafts.suchitra1026No ratings yet
- E-Journal in MeteorologyDocument10 pagesE-Journal in MeteorologycuthNo ratings yet
- Weather Tools PPTDocument23 pagesWeather Tools PPTconwenaNo ratings yet
- ABE 31A - Lab Exercise #1 (Agrometeorological Station Site Visit)Document7 pagesABE 31A - Lab Exercise #1 (Agrometeorological Station Site Visit)RAY MARK ABALAYANNo ratings yet
- S1 Geography NotesDocument42 pagesS1 Geography NotesKurtis ChomiNo ratings yet
- INTERNSHIP PresentationDocument13 pagesINTERNSHIP PresentationRushikesh MahajanNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 MeteorologyDocument24 pagesTopic 1 MeteorologySalih TrexieNo ratings yet
- College of Agriculture, Forestry, and Environmental SciencesDocument6 pagesCollege of Agriculture, Forestry, and Environmental SciencesZeus CuiNo ratings yet
- How A Weather Forecast Is MadeDocument2 pagesHow A Weather Forecast Is MadeCy Ber Allen CubonNo ratings yet
- WEATHERFORECASTINGDocument7 pagesWEATHERFORECASTINGMukesh UdathaNo ratings yet
- Weather Forecasting: February 2016Document7 pagesWeather Forecasting: February 2016Dipanwita BasakNo ratings yet
- Weather Instrument PDFDocument7 pagesWeather Instrument PDFjs cyberzoneNo ratings yet
- GHS - Geography - Weather and Climate - WikiEducatorDocument9 pagesGHS - Geography - Weather and Climate - WikiEducatorTamyßieNo ratings yet
- Weather and Weather InstrumentsDocument17 pagesWeather and Weather InstrumentsKyle Cedrick P. PentinioNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Hannah Wynzelle AbanNo ratings yet
- Weather Forecast and InstrumentsDocument9 pagesWeather Forecast and InstrumentsKayPasionNo ratings yet
- AnemometerDocument8 pagesAnemometerEmman PachecoNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Social Studies Week 18 - 2022 - Consolidated WorksheetDocument10 pagesGrade 5 Social Studies Week 18 - 2022 - Consolidated Worksheetshivanah hunteNo ratings yet
- Weather Station Report PDFDocument7 pagesWeather Station Report PDFSunny Sheikh0% (1)
- Rough Draft: Geography ProjectDocument3 pagesRough Draft: Geography ProjectPushpajaNo ratings yet
- Astronomy and MeteorologyDocument24 pagesAstronomy and MeteorologyJeko Betguen PalangiNo ratings yet
- INTERNSHIP PresentationDocument13 pagesINTERNSHIP PresentationRushikesh MahajanNo ratings yet
- Module For Climate Change Chapter 1 - Weather and ClimateDocument12 pagesModule For Climate Change Chapter 1 - Weather and ClimateKurt Morin CantorNo ratings yet
- Form 1 Geography Notes New Curr Online OnlyDocument94 pagesForm 1 Geography Notes New Curr Online OnlyDealNo ratings yet
- Meteorological Instruments: Hamza Mohammad - 2014-Civ-206 - 28-Sep-2016Document7 pagesMeteorological Instruments: Hamza Mohammad - 2014-Civ-206 - 28-Sep-2016mahmoud6y.6al6issawyNo ratings yet
- Agricultural MeteorologyDocument23 pagesAgricultural Meteorologyravidharu6No ratings yet
- Sample Paper IJRPRDocument5 pagesSample Paper IJRPRV D CharanNo ratings yet
- Climate Impacts on Extreme Weather: Current to Future Changes on a Local to Global ScaleFrom EverandClimate Impacts on Extreme Weather: Current to Future Changes on a Local to Global ScaleVictor OngomaNo ratings yet
- Climate Observations: Data Quality Control and Time Series HomogenizationFrom EverandClimate Observations: Data Quality Control and Time Series HomogenizationNo ratings yet
- PerfectionismDocument15 pagesPerfectionismNatacha Cabete100% (1)
- 2016 AL GIT Marking Scheme English Medium PDFDocument24 pages2016 AL GIT Marking Scheme English Medium PDFNathaneal MeththanandaNo ratings yet
- Schoolcity Math q2Document2 pagesSchoolcity Math q2api-297797689No ratings yet
- Elizabeth Malin EDLD 5315 Literature ReviewDocument24 pagesElizabeth Malin EDLD 5315 Literature ReviewebbyfuentesNo ratings yet
- YPD Guide Executive Summary PDFDocument2 pagesYPD Guide Executive Summary PDFAlex FarrowNo ratings yet
- Subject and Predicate Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesSubject and Predicate Lesson Planapi-437536657100% (1)
- TOR EMBeD Summer 2020 InternshipDocument2 pagesTOR EMBeD Summer 2020 InternshipvishakhaNo ratings yet
- Quiles Jonathan Assessment SADDocument3 pagesQuiles Jonathan Assessment SADJonathan Quiles100% (1)
- Minutes SmeaDocument2 pagesMinutes Smearealyn estores67% (6)
- Field Quality Services Engineer in Houston TX Resume Nanut Panpreuk GreenDocument1 pageField Quality Services Engineer in Houston TX Resume Nanut Panpreuk GreenNanutPanpreukGreenNo ratings yet
- Demo K-12 Math Using 4a's Diameter of CircleDocument4 pagesDemo K-12 Math Using 4a's Diameter of CircleMichelle Alejo CortezNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Impairments BrochureDocument2 pagesOrthopedic Impairments Brochureapi-228006451No ratings yet
- 5813 Reported Speech Step by Step Step 6 Reported Statements in The Past With KeyDocument5 pages5813 Reported Speech Step by Step Step 6 Reported Statements in The Past With KeyGabriela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Project 2 ExampleDocument6 pagesProject 2 ExampleShalomNo ratings yet
- João M. Paraskeva, Thad LaVallee (Eds.) - Transformative Researchers and Educators For Democracy - Dartmouth Dialogues-SensePublisDocument264 pagesJoão M. Paraskeva, Thad LaVallee (Eds.) - Transformative Researchers and Educators For Democracy - Dartmouth Dialogues-SensePublisRaphael PellegriniNo ratings yet
- Documentation in Psychiatric NursingDocument15 pagesDocumentation in Psychiatric NursingShiiza Dusong Tombucon-Asis86% (7)
- Game Based Learning FoundationDocument26 pagesGame Based Learning FoundationNessa BleuNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Is WealthDocument100 pagesKnowledge Is WealthmustaqNo ratings yet
- Advisory Assignment Order Junior High SchoolDocument1 pageAdvisory Assignment Order Junior High SchoolJaz and Ysha's ChannelNo ratings yet
- 1UR0 4F Que 20201107Document8 pages1UR0 4F Que 20201107Muhammad SaleemNo ratings yet
- Coaching Islamic Culture 2017chapter1Document8 pagesCoaching Islamic Culture 2017chapter1FilipNo ratings yet
- Perdev 2qDocument1 pagePerdev 2qGrace Mary Tedlos BoocNo ratings yet
- SPH Sabbath and HealthDocument14 pagesSPH Sabbath and HealthFerdy LainsamputtyNo ratings yet
- Agoraphobia 1Document47 pagesAgoraphobia 1We Are HanakoNo ratings yet
- Improve Your Communication Skills: Ghulam Mustafa KhattiDocument21 pagesImprove Your Communication Skills: Ghulam Mustafa KhattiGhulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Comparative-And-Superlative-Survey Activity 6Document2 pagesComparative-And-Superlative-Survey Activity 6Neisa SantamariaNo ratings yet
- Political Science Theory and Practice by Mazhar-Ul-HaqDocument1,028 pagesPolitical Science Theory and Practice by Mazhar-Ul-HaqShahroz AsifNo ratings yet
- Opertti Et Al - Ibe Unesco 2021 Inclusion in EducDocument6 pagesOpertti Et Al - Ibe Unesco 2021 Inclusion in EducSergio RiquelmeNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - Intro To Comp ProgramsDocument11 pagesLab 1 - Intro To Comp Programssyahira NurwanNo ratings yet
- Heather Martin Art Resume 2019Document2 pagesHeather Martin Art Resume 2019api-359491061No ratings yet