Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Classifying and Accomodating Specific Areas of Knowledge
Classifying and Accomodating Specific Areas of Knowledge
Uploaded by
ANJU SB0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views20 pagesOriginal Title
2. Classifying and Accomodating Specific Areas of Knowledge
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views20 pagesClassifying and Accomodating Specific Areas of Knowledge
Classifying and Accomodating Specific Areas of Knowledge
Uploaded by
ANJU SBCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 20
Classifying and Accommodating
Specific Areas of Knowledge
Introduction
School curriculum usually consists of subject
contents drawn from the core disciplines like
languages, social science, science, mathematics
etc.
Knowledge also important such as Art and craft
education, work education, life skill education,
value education, sports and physical education
cannot be incorporated in school education as
separate subjects as they are not treated as
disciplines like languages, social science and
mathematics.
Core Disciplinary Areas of Knowledge
Our school curriculum usually includes
the core subjects of study i.e. Languages,
social science, science and mathematics
Core subjects of study at different stages
of school education
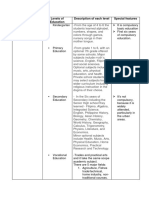
Stages of School Education Subject Areas Presented in School
curriculum
Elementary Lower Primary Languages Mother Tongue, Regional
(I-VIII) (I-V) Languages, Hindi, English
Social Science Includes the theme/topic of
both science and social
science
Science Environmental Studies(EVS)
Mathematics Independent subject of study
Upper Primary Languages Mother Tongue, Regional
(VI-VIII) Languages, Hindi, English
Mathematics Independent subject of study
Science Study of physical science and
natural science under science
Social science Study of History, Plitical
science and Geography under
Social Science
Core subjects of study at different
Stages of School Education Subject Areas Presented in School curricu
stages of school education
Secondary Languages Mother Tongue, Regional
(IX-X) Languages, Hindi, English
Social Science History, Political Scienc
Geography under the subjec
social Science
Science Environmental Studies(EVS
Mathematics Independent subject of study
Stages Streams Languages Studies as Compulsory
Subjects
Senior Arts and History, Different branches of arts and
Secondary Humanities Geography, humanities stream treated as
Economics elective areas of study
Political science,
Sociology,
Psychology,
Languages etc.
Science Physics, Different branches of science
Chemistry, stream, treated as elective
Mathematics, areas of study
Botany, Zoology
etc.
Commerce Accounting Different branches of
Business, studies, commerce stream, treated as
Marketing, elective areas of study.
Finance,
Insurance etc. Subject Areas presented in
school curriculum
Core Subjects in School Curriculum
i. Language:
Socio-cultural perspectives can be found
in language learning.
Different languages and cultures are
existed in India for centuries.
The three language and two language
formula is an attempt to address the
challenges and opportunities of the
linguistic situation in India
Aim is to promote multilingualism and
national harmony.
Guide line s to achieve this
o Language teaching needs to be
multilingual
o Home language should be the medium of
learning in schools
ii. Social Science
The different core components of social
behaviour of human life are economic
behaviour, political behaviour, cultural
behaviour, tradition, customs and social
institutions, religion, faiths and ethics, value
pattern followed in society.
Social values like democracy, socialism,
secularism, liberty, equality, justice, individual
right, freedom, gender equalities are the
outcomes of modern social system.
iii. Humanities
Includes the full range of human thought
and creativity including history, literature,
language, religion, philosophy, music theatre
and all of the performing sorts and visual
arts.
Critical thinking, Team work,
Communication, Empirical and quantitative
reasoning, personal and social responsibility
are the skills strengthened through a
humanities education.
iv. science
the rapid growth of science and technology in
the last hundred years has created of growth of
knowledge.
NCF 2005 states that good science education is
true to the child, true to life and true to science.
Science education should prepare students to
live in the world of increasing interdependence.
v. Mathematics
Maths education serves the reproduction of
society, and the formation of pupils awareness
and ideologies.
Mathematics is a life skill which is required for
any profession at all points of time
Specific Non-Core Areas of Knowledge
in the Curriculum
i. Arts and Craft
the arts and crafts present a unique problem for
epistemology .
The sense of creativity, appreciation, skills,
aesthetic and value based learning opportunities
are possible through art and craft education.
ii. Work Education
Work is an integral part of every individuals
life.
Included in the school curriculum as an
opportunity for learning for the children and
for the preparation for their further work.
Inclusion of SUPW(Socially Useful and
Productive Work)in school curriculum
makes the children appreciate the worth of
social life.
iii. Peace Education
Growth of violence, intolerance, fanaticism,
conflicts and disobedience are the constants
threats to our society
Need to train children and the young adults to
practice to tolerance and peace at home, school
and society
Inculcate the values, human rights, justice,
tolerance, social responsibility, attitude and
skills required for living in harmony with
oneself and others.
v. Life Skill education
Life skills means developing self esteem,
building empathy towards others and different
cultures etc. improving critical and creative
thinking and making them better at problem
solving with a balance approach towards
decision making.
vi. Health and Physical education
NCF (2005) recommends health and physical
education at all levels of school education.
Health and physical education, yoga, health and
physical education need to be part of core
curriculum.
vii. Value Education
The aim of education should reflect a
commitment to democracy and the values of
equality, justice, freedom, secularism, respect of
human dignity and human rights.
CBSE and State Board have tried to incorporate
personal and social values.
You might also like
- Daily Lesson Log Grade 11 UCSPDocument29 pagesDaily Lesson Log Grade 11 UCSPDonald Montano Dela Torre100% (14)
- Signs And Symbols In Education: Educational SemioticsFrom EverandSigns And Symbols In Education: Educational SemioticsNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Language FeaturesDocument49 pagesGrade 11 Language FeaturesJulian VenNo ratings yet
- Professor Grammar's Rule Book PDFDocument66 pagesProfessor Grammar's Rule Book PDFdianita192100% (6)
- Personal and Impersonal Passive ConstructionsDocument3 pagesPersonal and Impersonal Passive ConstructionsKenul heydarova100% (1)
- Adjective-Clauses With ExerciseDocument2 pagesAdjective-Clauses With ExerciseMuhammad muslehNo ratings yet
- Subject Areas For ISE III Oral Exam/ Written Exam Written ExamDocument2 pagesSubject Areas For ISE III Oral Exam/ Written Exam Written ExamAnabel Blasco Martín100% (1)
- Discourse On The MoveDocument304 pagesDiscourse On The MoveChoi PhilipNo ratings yet
- Sobi R (Understanding Disciplines and Subjects)Document10 pagesSobi R (Understanding Disciplines and Subjects)Sobi SobiNo ratings yet
- Analysis of School Curriculum at Different StagesDocument3 pagesAnalysis of School Curriculum at Different Stageschiranjibi behera83% (12)
- 509 Solved Assignment-1Document11 pages509 Solved Assignment-1dakch49No ratings yet
- Curriculum - SrSec - 2024 25 5 6Document2 pagesCurriculum - SrSec - 2024 25 5 6Hitesh SemwalNo ratings yet
- Makabayan ReviewerDocument3 pagesMakabayan ReviewerAbet BarileNo ratings yet
- Academic Courses Offered in 2023 24Document2 pagesAcademic Courses Offered in 2023 24Jiya GuptaNo ratings yet
- (English) Framework: K To 12 Basic Education Curriculum GuideDocument7 pages(English) Framework: K To 12 Basic Education Curriculum GuideKenji ToleroNo ratings yet
- Kothari - CommissionDocument17 pagesKothari - CommissionjagannathbbnNo ratings yet
- Foundation of Social Studies SSM1 M3Document19 pagesFoundation of Social Studies SSM1 M3HAZEL JANE ABAPONo ratings yet
- Pca 8vo Anual InglesDocument24 pagesPca 8vo Anual Inglesjose cepedaNo ratings yet
- Noveno Planificación Curricular Anual InglesDocument32 pagesNoveno Planificación Curricular Anual InglesDilany HenaoNo ratings yet
- Screen PDFDocument20 pagesScreen PDFRovic James A. DuyanNo ratings yet
- Decimo Planificación Curricular Anual Ingles TiniDocument35 pagesDecimo Planificación Curricular Anual Ingles Tinijose cepedaNo ratings yet
- Curriculu M Guide: Here Is Where Your Presentation BeginsDocument22 pagesCurriculu M Guide: Here Is Where Your Presentation BeginsLycea ValdezNo ratings yet
- Teaching English in Peruvian Schools MINEDUDocument23 pagesTeaching English in Peruvian Schools MINEDUEduardo MoyaNo ratings yet
- Science and HumanitiesDocument54 pagesScience and HumanitieselosekialdeaNo ratings yet
- Swedish Educational SysytemDocument12 pagesSwedish Educational SysytemRaiza FamucolNo ratings yet
- Vertical Alignment of The Lesson Across Grade LevelDocument2 pagesVertical Alignment of The Lesson Across Grade LevelDharVin DeVeraNo ratings yet
- IGCSEDocument3 pagesIGCSENehal IsmailNo ratings yet
- HESS (K To 12)Document31 pagesHESS (K To 12)Litera CircleNo ratings yet
- Computer Science F3 - 4 - 5 - Dec 2014Document40 pagesComputer Science F3 - 4 - 5 - Dec 2014Ronic DakNo ratings yet
- SSC ReviewerDocument18 pagesSSC ReviewerAngelei FriasNo ratings yet
- What Is Social Studies?Document2 pagesWhat Is Social Studies?Makoy AguilaNo ratings yet
- 2021 - 2022 Grade 9 Course Information: Grade 9 Typical Schedule Graduation RequirementsDocument8 pages2021 - 2022 Grade 9 Course Information: Grade 9 Typical Schedule Graduation RequirementsNikie Ela CapilitanNo ratings yet
- Compiled Express BookletDocument20 pagesCompiled Express BookletAbhinav KannanNo ratings yet
- Curriculum 300Document6 pagesCurriculum 300milibroNo ratings yet
- Foundation of Social Studies 1Document144 pagesFoundation of Social Studies 1kenthennek25No ratings yet
- What Is K To 12 ProgramDocument13 pagesWhat Is K To 12 ProgramacelNo ratings yet
- Jeza B. Magalang - DISS DLP 2nd Week 1Document2 pagesJeza B. Magalang - DISS DLP 2nd Week 1Jeza MagalangNo ratings yet
- Social Science Sem 1Document123 pagesSocial Science Sem 1faizu vlogNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Secondary Grade TeacherDocument26 pagesSyllabus For Secondary Grade TeacherHari Babu SriramNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Course InformationDocument8 pagesGrade 9 Course InformationMazeNo ratings yet
- EducationDocument11 pagesEducationParañal Elieza BagaweNo ratings yet
- Couse GuideDocument7 pagesCouse GuideVũ ChiNo ratings yet
- Objectives of CurriculumDocument6 pagesObjectives of CurriculumUzma SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Introduction and Concept FrameworkDocument18 pagesChapter-1 Introduction and Concept FrameworkSelva KumarNo ratings yet
- EGE 107 - LA - Study Guide - Unit 1.1Document36 pagesEGE 107 - LA - Study Guide - Unit 1.1its yannahhNo ratings yet
- SHS ChecklistDocument16 pagesSHS ChecklistDaisy YaboNo ratings yet
- Content-Based Instruction (CBI) CurriculumDocument18 pagesContent-Based Instruction (CBI) CurriculumNivethika GandhimathiNo ratings yet
- SeniorHighSchool CalendarDocument55 pagesSeniorHighSchool CalendarNoliver GarciaNo ratings yet
- Meaning and Definition of Social ScienceDocument5 pagesMeaning and Definition of Social ScienceROSEMARY K P100% (1)
- TSC PPTPDocument38 pagesTSC PPTPJoshua CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Basic Education Act of 2013Document6 pagesEnhanced Basic Education Act of 2013Anthony FortalizaNo ratings yet
- Learning Plan 1-3Document13 pagesLearning Plan 1-3Lenard BelanoNo ratings yet
- Paper II CtetDocument6 pagesPaper II CtetJyoti MishraNo ratings yet
- Educ 106 Peter John TevesDocument4 pagesEduc 106 Peter John TevesPeter John TevesNo ratings yet
- Karakteristik Ilmu Pengetahuan Sosial: Kajian Dari Sudut Pandang Filsafat PendidikanDocument6 pagesKarakteristik Ilmu Pengetahuan Sosial: Kajian Dari Sudut Pandang Filsafat PendidikanDien MoudienNo ratings yet
- Activity TimeDocument28 pagesActivity TimeALYSSA DAVIDNo ratings yet
- Exposé D'anglais EslieDocument7 pagesExposé D'anglais Eslielouisdjorogo0No ratings yet
- Textbooks Analysis: Analyzing English As A Foreign Language (Efl) Textbooks From The Perspective of Indonesian Culture Devy Angga GunantarDocument10 pagesTextbooks Analysis: Analyzing English As A Foreign Language (Efl) Textbooks From The Perspective of Indonesian Culture Devy Angga GunantarDefita AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- 75547-Điều văn bản-181209-1-10-20230117Document17 pages75547-Điều văn bản-181209-1-10-20230117Dung trươngNo ratings yet
- Buatesbeverly Ann I Beed II Activity 4 Educ 30023Document4 pagesBuatesbeverly Ann I Beed II Activity 4 Educ 30023Khia Eroles100% (1)
- University of Antique College of Teacher Education Graduate Studies Sibalom, AntiqueDocument11 pagesUniversity of Antique College of Teacher Education Graduate Studies Sibalom, AntiqueRobbie Liza Caytiles100% (1)
- Brief Introduction To Applied LinguisticsDocument2 pagesBrief Introduction To Applied LinguisticsVie BelleNo ratings yet
- CPE108 Lesson 14 TaskDocument3 pagesCPE108 Lesson 14 TaskBai Reman Ebad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Pedagogical Sciences: The Teaching of Language and Literature, Education, Values, Patrimony and Applied ITFrom EverandPedagogical Sciences: The Teaching of Language and Literature, Education, Values, Patrimony and Applied ITNo ratings yet
- Curriculum and Its Importance in Learner-Centred ApproachDocument9 pagesCurriculum and Its Importance in Learner-Centred ApproachAruna JerryNo ratings yet
- Need of Reframing School SubjectsDocument13 pagesNeed of Reframing School SubjectsAruna JerryNo ratings yet
- 5.school Sub Jects and Social JusticeDocument17 pages5.school Sub Jects and Social JusticeAruna JerryNo ratings yet
- Educational AdministrationDocument22 pagesEducational AdministrationAruna JerryNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 07-Jul-2023Document20 pagesAdobe Scan 07-Jul-2023Aruna JerryNo ratings yet
- 12 Verb Tenses Structure (Compatibility Mode)Document21 pages12 Verb Tenses Structure (Compatibility Mode)Briggette QuijijeNo ratings yet
- Federico Giusfredi - Syntax of The Luwian LanguageDocument229 pagesFederico Giusfredi - Syntax of The Luwian LanguageLucySky7No ratings yet
- That That: Adjective + Clause (Tính Từ + Mệnh ĐỀ)Document5 pagesThat That: Adjective + Clause (Tính Từ + Mệnh ĐỀ)vohoangphuNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2019-10-16 at 4.55.12 PM PDFDocument1 pageScreenshot 2019-10-16 at 4.55.12 PM PDFAlmaanNo ratings yet
- English Grammar. Noun Clauses.Document8 pagesEnglish Grammar. Noun Clauses.Bruno GiulianoNo ratings yet
- Future SimpleDocument1 pageFuture Simpleiulia567No ratings yet
- Effective English Learning-SpeakingDocument20 pagesEffective English Learning-SpeakingConstanza Macarena Mira NozigliaNo ratings yet
- 01 Perez GomezDocument6 pages01 Perez GomezCristina BuzatuNo ratings yet
- Heilbron Sistema Mundial de La TraducciónDocument7 pagesHeilbron Sistema Mundial de La Traducciónagf75No ratings yet
- Summit 2Document167 pagesSummit 2mahdia100% (1)
- 5 Razred TestDocument5 pages5 Razred TestIva ČekoNo ratings yet
- Answering Questions in Complete SentencesDocument4 pagesAnswering Questions in Complete SentencesJuan MNo ratings yet
- ED 107 162 Author Morphology. Pub Date Aug 69 Note Austin Edrs Price MF-$O.76 DescriptorsDocument75 pagesED 107 162 Author Morphology. Pub Date Aug 69 Note Austin Edrs Price MF-$O.76 DescriptorsTalha KhanNo ratings yet
- Bai Tap Because Because of Lop 9 Co Dap AnDocument4 pagesBai Tap Because Because of Lop 9 Co Dap AnTrang TrầnNo ratings yet
- 8 Parts of SpeechDocument5 pages8 Parts of SpeechleijuliaNo ratings yet
- AI Generated BookDocument9 pagesAI Generated BookSameer KhanNo ratings yet
- CoevaluationDocument1 pageCoevaluationAngie RomeroNo ratings yet
- Sat Reading Question TypesDocument6 pagesSat Reading Question TypesJasmin AjoNo ratings yet
- Course Anthology Phonetics PDFDocument81 pagesCourse Anthology Phonetics PDFMax Arias SeguraNo ratings yet
- Activity 5Document13 pagesActivity 5Auderest BogotaNo ratings yet
- Super Teacher Worksheets Word SearchDocument3 pagesSuper Teacher Worksheets Word SearchKrisha Mae TakiangNo ratings yet
- Noam ChomskyDocument35 pagesNoam Chomskyfspdd89% (19)
- Porter Institute For Poetics and Semiotics: Duke University PressDocument24 pagesPorter Institute For Poetics and Semiotics: Duke University PresssspiltenNo ratings yet
- ConceptDocument54 pagesConceptAnida Nurafifah100% (1)
- ECI 511 Lesson Plan - Integrating Technology Tools in English/Language ArtsDocument3 pagesECI 511 Lesson Plan - Integrating Technology Tools in English/Language ArtsAnonymous N5M1eg38No ratings yet