Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3 Electric and Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles-1
3 Electric and Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles-1
Uploaded by
samuel Gyimah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views26 pagesElectric vehicles 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentElectric vehicles 2
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views26 pages3 Electric and Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles-1
3 Electric and Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles-1
Uploaded by
samuel GyimahElectric vehicles 2
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 26
Automotive Technology: Principles,
Diagnosis, and Service
Sixth Edition
Chapter 93
Electric and Plug-In Hybrid Electric
Vehicles
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Learning Objectives
93.1 Identify a plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHE V) and
explain how the high-voltage battery is recharged.
93.2 Discuss the battery capacity and range correlation of an
E V.
93.3 Describe the levels of chargers used to charge a PHE V
or an E V.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (1 of 3)
• Principles
– A plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHE V) is a vehicle
that is designed to be plugged into an electrical outlet
at night to charge the batteries.
• Identifying a PHE V
– Different badges (usually stating that it is a PHE V)
– An electrical connection door and a door for fuel for the
IC E
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (2 of 3)
• PHE V Battery Capacity
– Battery capacity is measured in kilowatt-hours,
abbreviated kWh.
– The higher the kWh rating of the battery, the more
electrical energy it can store and the greater the
distance it can travel before recharging.
• PHE V Examples
– Toyota Prius has a 1.3 kWh battery pack.
– A plug-in Prius has a 4.4 kWh battery.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (3 of 3)
• Charging a PHE V
– The I C E is used to keep the battery charged enough to
propel the vehicle, but it does not fully recharge the
battery pack.
– To fully charge the high-voltage battery pack in a PHE
V requires that it be plugged into either a 120-volt or a
240-volt outlet.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Figure 93.1 (a) About the only way to
tell a plug-in prius from a regular
prius is from the badge on the sides
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Figure 93.1 (b) By the charge port
door on the passenger side at the
rear
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Figure 93.2 A Chevrolet volt extended-range
electric vehicle (ERE V), also called a plug-in
hybrid electric vehicle (PHE V), being
charged at a row of charging stations at the
Corvette assembly plant in Bowling Green, K
Y
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Figure 93.3 (a) Charging stations that are
equipped with SA E standard J1772 chargers are
often found at large companies, colleges,
universities, and shopping malls in many parts
of the country
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Figure 93.3 (b) A typical SA E J1772 charging station that
is in a designated electric vehicle parking location,
which is often in a premiere location to encourage use
of electric and plug-in electric vehicles
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Question 1: ?
What is the difference between a HE V and a PHE V?
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Answer 1
The PHE V is plugged into the grid to charge the battery.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Electric Vehicles (1 of 3)
• Principles
– An electric vehicle (E V) uses a high-voltage battery
pack to supply electrical energy to an electric motor(s)
to propel the vehicle under all driving conditions.
• Cold Weather Concerns
– Cold weather is a major disadvantage to the use of
E Vs because it reduces the battery efficiency. Power is
also consumed to heat the passenger compartment
and the battery.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Electric Vehicles (2 of 3)
• Hot Weather Concerns
– Batteries do not function well at high temperatures,
and, therefore, some type of battery cooling must be
added to the vehicle to allow for maximum battery
performance.
• Range
– The range of an E V depends on many factors,
including:
o Vehicle weight, battery energy storage capacity,
outside temperature, terrain, and use of electrical
devices
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Question 2: ?
What factors effect the range of an electric vehicle?
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Answer 2
Vehicle weight, battery energy storage capacity, outside
temperature, terrain, and use of electrical devices.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Electric Vehicle Charging
• SA E Standard Charger Plug
– Most EV s and PHEV s, such as the Chevrolet Volt and
Toyota Prius, use a standard charger plug. The
standard charger plug meets the specification as
designated by SA E standard J1772 (updated in 2009).
• Charging Levels
– Level 1—Level 1 uses 110- to 120-volt standard
electric outlet (20-amp circuit).
– Level 2—Level 2 chargers use 220–240 volts to charge
the vehicle.
– Level 3—Level 3 charging stations use 440 volts and
can charge most electric vehicles to 80% charge in
less than 30 minutes.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Figure 93.4 The SA E J1772 plug is used
on most electric and plug-in hybrid
electric vehicles and is designed to work
with level 1 (110–120 volt) and level 2
(220–240 volt) charging
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Figure 93.5 (a) A Chevrolet volt being
charged using the supplied 110-volt
charger
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Figure 93.5 (b) Always lay out the entire length of the
charging cord before plugging the vehicle into the
outlet. E cord is not kept straight, the current flow can
not only create a coil, but the flow of current can
overheat the wires and, in some cases, can actually
cause the insulation to melt
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Figure 93.6 A Nissan leaf plugged
into a charging station at a college
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Figure 93.7 (a) An SA E combo plug that includes
the J-1776 design at the top for level 1 and level 2
charging, with the added two large terminals that
are used to charge using high-voltage DC
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Figure 93.7 (b) A Chevrolet bolt electrical
charging terminal. The orange plastic tab
can be pivoted to cover the level 3
terminals if a level 1 or 2 is being used
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Figure 93.8 A Nissan leaf electric
vehicle charging ports located at the
front of the vehicle under a hinged
door for easy access
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Question 3: ?
What are the differences between level 1, level 2, and level 3
chargers?
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Answer 3
The voltage level and the amount of time it takes to charge
the battery.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
You might also like
- C0904 091814 PDFDocument54 pagesC0904 091814 PDFBuddy JohnsonNo ratings yet
- EVlink Electric Vehicle Charging SolutionsDocument60 pagesEVlink Electric Vehicle Charging SolutionsMario StrašniNo ratings yet
- Installation of Electric Vehicle Supply Equipement - Guidance DocumentDocument32 pagesInstallation of Electric Vehicle Supply Equipement - Guidance DocumentThermoAmbient Jacob60% (5)
- Planning For EV Charging Infrastructure A Toolkit June 2013Document38 pagesPlanning For EV Charging Infrastructure A Toolkit June 2013Melecio Jesus Leano Jr.No ratings yet
- EV Charging Station DesignDocument5 pagesEV Charging Station DesignetnantoNo ratings yet
- Electric Vehicle On-Board Chargers and Charging StationsDocument11 pagesElectric Vehicle On-Board Chargers and Charging StationsShiva AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Site Design For EV Charging StationsDocument35 pagesSite Design For EV Charging Stationsoksprakash1988100% (1)
- Charging of EVs: Slow Vs FastDocument25 pagesCharging of EVs: Slow Vs FastRavi Kashyap50% (2)
- Paper Presentation On E - VehicleDocument20 pagesPaper Presentation On E - VehicleAmaye Gatalawar80% (5)
- BSB Circular 11of 2011Document4 pagesBSB Circular 11of 2011sakura1930No ratings yet
- Ev Charging TechnlogiesDocument43 pagesEv Charging TechnlogiesAtheli Vijay Chandra100% (1)
- Basic OF HEV & EVDocument24 pagesBasic OF HEV & EVMayukh MajumderNo ratings yet
- Types of Electric VehiclesDocument17 pagesTypes of Electric VehiclesjokerNo ratings yet
- Electric VehiclesDocument31 pagesElectric Vehiclesmiaomiao yangNo ratings yet
- Industrial Electronics For Electric Transportation: Current State-of-the-Art and Future ChallengesDocument12 pagesIndustrial Electronics For Electric Transportation: Current State-of-the-Art and Future ChallengesAbhijeet KumarNo ratings yet
- SM Module III - Vehicle SystemsDocument10 pagesSM Module III - Vehicle SystemsPedroNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal-AdmDocument20 pagesProject Proposal-Admsofiyyahaliyah14No ratings yet
- Design and Simulation of A Fast Charging Station For PHEV/EV BatteriesDocument6 pagesDesign and Simulation of A Fast Charging Station For PHEV/EV Batteriesprabhu rachutiNo ratings yet
- Modelling of Hybrid Electric Vehicle Charger and Study The Simulation ResultsDocument6 pagesModelling of Hybrid Electric Vehicle Charger and Study The Simulation ResultsNarendra YadavNo ratings yet
- Alternative Fuels Data Center - Developing Infrastructure To Charge Electric VehiclesDocument4 pagesAlternative Fuels Data Center - Developing Infrastructure To Charge Electric VehiclesAugustine OkaforNo ratings yet
- Enabling EV Charging in CondominiumsDocument24 pagesEnabling EV Charging in Condominiumsdaniel SegallNo ratings yet
- Levels of Charging - EVTownDocument1 pageLevels of Charging - EVTownsakho nihaNo ratings yet
- Trends in Electric Vehicle Ev Charging and Key Technology Developments IJERTV9IS090042Document5 pagesTrends in Electric Vehicle Ev Charging and Key Technology Developments IJERTV9IS090042Navpreet HansNo ratings yet
- Iss 1.3 Aug 2019 EVSE Protocol Controller (EPC) Manual - Viridian EV 1Document17 pagesIss 1.3 Aug 2019 EVSE Protocol Controller (EPC) Manual - Viridian EV 1Martin HuckoNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 41 - 43 - UploadDocument54 pagesLecture - 41 - 43 - UploadSurajit SahaNo ratings yet
- Research Report On Electric CarsDocument25 pagesResearch Report On Electric Carssyeda ume rubabNo ratings yet
- Problems For Electric Vehicle Adoption in India and Recommendations To Boost Electric Vehicle Adoption in IndiaDocument5 pagesProblems For Electric Vehicle Adoption in India and Recommendations To Boost Electric Vehicle Adoption in Indiathumula.rameshNo ratings yet
- 4.battery Chargers in Electric VehiclesDocument3 pages4.battery Chargers in Electric VehiclesEssa SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- 2 Hybrid High Voltage BatteriesDocument55 pages2 Hybrid High Voltage Batteriessamuel GyimahNo ratings yet
- Improved Power Quality On-Board Integrated Charger With Reduced Switching StressDocument11 pagesImproved Power Quality On-Board Integrated Charger With Reduced Switching Stressamala081998No ratings yet
- Development of Fast Charging Station ForDocument7 pagesDevelopment of Fast Charging Station ForDhayanandhNo ratings yet
- EV and EV Charging Station Trends For 2019 and Beyond: 44 IIEE Annual National ConventionDocument29 pagesEV and EV Charging Station Trends For 2019 and Beyond: 44 IIEE Annual National ConventionMiguel CuisiaNo ratings yet
- Executive SummaryDocument28 pagesExecutive SummaryRAJSHEKAR SNo ratings yet
- Fast Charging Station: Pure Electric VehiclesDocument25 pagesFast Charging Station: Pure Electric VehiclesDîñ Êsh Chä ÛhâñNo ratings yet
- A Study On Power Distribution For Electric Vehicles Using Wireless Power TransmissionDocument11 pagesA Study On Power Distribution For Electric Vehicles Using Wireless Power TransmissionbrightlinNo ratings yet
- HOMEWORK 2. EV ChargerdocxDocument1 pageHOMEWORK 2. EV Chargerdocx88kevalpatelNo ratings yet
- Bidirectional Isolated DC-DC Converter For Hybrid Electric Vehicle ChargingDocument9 pagesBidirectional Isolated DC-DC Converter For Hybrid Electric Vehicle ChargingIJSREDNo ratings yet
- Topic:: Improving Efficiency of Battery Charging and Its DischargingDocument15 pagesTopic:: Improving Efficiency of Battery Charging and Its DischargingKushagra VermaNo ratings yet
- Ev Charging StationDocument30 pagesEv Charging StationMayur LadwaNo ratings yet
- Day 1 EV Battery Management - Module 1Document43 pagesDay 1 EV Battery Management - Module 1Para CommandoNo ratings yet
- Energy Storage System Using Battery and Ultracapacitor On Mobile Charging Station For Electric VehicleDocument9 pagesEnergy Storage System Using Battery and Ultracapacitor On Mobile Charging Station For Electric VehiclemduartepriNo ratings yet
- G2V and V2G Electric Vehicle Charger For Smart Grids: Ricardo G. Gago Sónia F. Pinto José F. SilvaDocument6 pagesG2V and V2G Electric Vehicle Charger For Smart Grids: Ricardo G. Gago Sónia F. Pinto José F. Silvapratap68No ratings yet
- SomervilleGuide EVChargingathomeDocument21 pagesSomervilleGuide EVChargingathomeTony JamesNo ratings yet
- Design of 2kW DC Charger For Two Wheelers: D. M. Chandwadkar, Azmina Gayasuddin Maniyar, S. P. UgaleDocument4 pagesDesign of 2kW DC Charger For Two Wheelers: D. M. Chandwadkar, Azmina Gayasuddin Maniyar, S. P. UgaleDr Meena BoyNo ratings yet
- Electric Vehicle Collaboration - Toyota Motor Corporation and Tesla MotorsDocument6 pagesElectric Vehicle Collaboration - Toyota Motor Corporation and Tesla Motorsalejandro perdomoNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Electric VehicleDocument18 pagesHybrid Electric VehiclePrudhvi PrinceNo ratings yet
- Energy Management Strategies For Modern Electric Vehicles Using MATLAB SimulinkDocument8 pagesEnergy Management Strategies For Modern Electric Vehicles Using MATLAB SimulinkAli aliNo ratings yet
- AesDocument5 pagesAesshreyas129No ratings yet
- EV Everywhere - Vehicle Charging - Department of EnergyDocument3 pagesEV Everywhere - Vehicle Charging - Department of EnergyAshwin DhanotiyaNo ratings yet
- Presentation Smart India by CS Electric PDFDocument55 pagesPresentation Smart India by CS Electric PDFGuru Nadh DoneparthyNo ratings yet
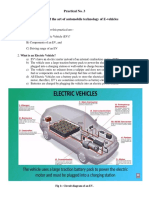
- Practical No. 3 EV'sDocument2 pagesPractical No. 3 EV'sAjay VermaNo ratings yet
- AC Level 2 Electric Vehicle Charging Station: The Most Robust, FL Exible Offering of EVSE On The MarketDocument2 pagesAC Level 2 Electric Vehicle Charging Station: The Most Robust, FL Exible Offering of EVSE On The MarketاحمدميدوNo ratings yet
- DST Report EV Standards Aug2021Document26 pagesDST Report EV Standards Aug2021Sanket DevleNo ratings yet
- EV's Charging Sations Infrastructures-CE451Document39 pagesEV's Charging Sations Infrastructures-CE451tmornNo ratings yet
- Definition of Project 6.0Document21 pagesDefinition of Project 6.0MOHAMMAD ALINo ratings yet
- Crashworthiness Aspects of Electric Vehicle DesignDocument21 pagesCrashworthiness Aspects of Electric Vehicle DesigngfdczxNo ratings yet
- 1 ADocument12 pages1 Asharjeel hassanNo ratings yet
- PV and Grid Interfaced Plugin EV Battery Charger Operating in PVG PV and VG ModesInternational Journal of Recent Technology and EngineeringDocument13 pagesPV and Grid Interfaced Plugin EV Battery Charger Operating in PVG PV and VG ModesInternational Journal of Recent Technology and EngineeringApolo GreenNo ratings yet