Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Uganda Evol
Uploaded by
dkoeyj0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views7 pagesRevolution
Original Title
Uganda evol
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentRevolution
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views7 pagesUganda Evol
Uploaded by
dkoeyjRevolution
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
French Revolution (1789 to 1799)
• What was the French Revolution?
The French Revolution was a period of time in
France when the people overthrew the
monarchy and took control of the
government.
When did it take place?
The French Revolution lasted 10 years from
1789 to 1799. It began on July 14, 1789 when
revolutionaries stormed a prison called the
Bastille. The revolution came to an end 1799
when a general named Napoleon overthrew
the revolutionary government and established
the French Consulate (with Napoleon as
leader)
The French Estates
Before the French Revolution, the people of
France were divided into social groups called
"Estates." The First Estate included the clergy
(church leaders), the Second Estate included the
nobles, and the Third Estate included the
commoners. Most of the people were members
of the Third Estate. The Third Estate paid most of
the taxes, while the nobility lived lives of luxury
and got all the high-ranking jobs
Revolutionary Government
• The French Government was in constant turmoil
throughout the revolution. At the start of the revolution,
representatives from the Third Estate established the
National Assembly where they demanded that King
Louis XVI give them certain rights. This group soon took
control of the country. They changed names over time to
the Legislative Assembly and, later, to the National
Convention. After the Reign of Terror, a new government
was formed called the Directory. The Directory ruled
until Napoleon took control.
Reign of Terror
•
The darkest period of the French Revolution is called the
Reign of Terror which lasted from 1793 to 1794. During this
time, a man named Robespierre led the National
Convention and the Committee of Public Safety. He wanted
to stamp out any opposition to the revolution, so he called
for a rule of "Terror." Laws were passed that said anyone
suspected of treason could be arrested and executed by
guillotine. Thousands of people were executed including
Queen Marie Antoinette and many of Robespierre's
political rivals.
Outcome
The French Revolution completely changed the social
and political structure of France. It put an end to the
French monarchy, feudalism, and took political power
from the Catholic church. It brought new ideas to
Europe including liberty and freedom for the commoner
as well as the abolishment of slavery and the rights of
women. Although the revolution ended with the rise of
Napoleon, the ideas and reforms did not die. These new
ideas continued to influence Europe and helped to
shape many of Europe's modern-day governments.
You might also like
- Tanishq Jewellery ProjectDocument42 pagesTanishq Jewellery ProjectEmily BuchananNo ratings yet
- French Revolution Paraphrase TextDocument2 pagesFrench Revolution Paraphrase TextAnonymous i35iwMVFNo ratings yet
- Lec#02 French Revolution. Series Important Sociological ConceptsDocument9 pagesLec#02 French Revolution. Series Important Sociological ConceptsFARHAN MEERNo ratings yet
- The French RevolutionDocument11 pagesThe French RevolutionNilima Aparajita SahuNo ratings yet
- History French Revolution NotesDocument4 pagesHistory French Revolution NotesRanjani J Deepak100% (1)
- School of Education/ English Department Rayak CampusDocument5 pagesSchool of Education/ English Department Rayak CampusDiana MechaalanyNo ratings yet
- French RevolutionDocument5 pagesFrench RevolutionHeart BrokenNo ratings yet
- Class 9th History Chapter 1 NotesDocument3 pagesClass 9th History Chapter 1 NotesNobodyIsHereNo ratings yet
- The French RevolutionDocument4 pagesThe French RevolutionTharani K P100% (1)
- 01 ReadingDocument1 page01 ReadingJosé E. ParedesNo ratings yet
- 09 Social Science Key Notes History Ch1 The French RevolutionDocument3 pages09 Social Science Key Notes History Ch1 The French RevolutionkeshavNo ratings yet
- The French Society During The Late 18th CenturyDocument4 pagesThe French Society During The Late 18th Centuryrashmi ChauhanNo ratings yet
- French Revolution Upsc Notes 21Document4 pagesFrench Revolution Upsc Notes 21sanisingh750568No ratings yet
- Class 9 historyNCERT SummaryDocument64 pagesClass 9 historyNCERT SummaryJYOTISH RAJNo ratings yet
- Test Essay - 2Document2 pagesTest Essay - 2inspiron_1520No ratings yet
- French RevolutionDocument12 pagesFrench RevolutionPavan's IQ GARDENNo ratings yet
- French Revolution, 9, Ch-1Document2 pagesFrench Revolution, 9, Ch-1Khan ArshiNo ratings yet
- French RevolutionDocument27 pagesFrench Revolutionapi-237266847No ratings yet
- French RevolutionDocument21 pagesFrench RevolutionMazhar ul haqNo ratings yet
- World History A Level Essays PDFDocument38 pagesWorld History A Level Essays PDFMohammed Ali raza KhanNo ratings yet
- French Revolution of 1789Document1 pageFrench Revolution of 1789Ahmed AliNo ratings yet
- French RevolutionDocument2 pagesFrench RevolutionTirade RuefulNo ratings yet
- His CH 1Document3 pagesHis CH 1geetNo ratings yet
- French RevolutionDocument16 pagesFrench RevolutionRohit SaxenaNo ratings yet
- The French RevolutionDocument8 pagesThe French RevolutionJithin RanganiNo ratings yet
- The French RevolutionDocument2 pagesThe French Revolutiontatecharlie48No ratings yet
- WedDocument2 pagesWedDorian VoineaNo ratings yet
- French Revolution - Compiled NotesDocument14 pagesFrench Revolution - Compiled NotesZain ShamimNo ratings yet
- The French RevolutionDocument26 pagesThe French RevolutionApoorva JakharNo ratings yet
- French Revolution Grade 9 - PPT PresentationDocument10 pagesFrench Revolution Grade 9 - PPT Presentationfdkfja dafklaNo ratings yet
- 09 Social Science Key Notes History Ch1 The French RevolutionDocument3 pages09 Social Science Key Notes History Ch1 The French RevolutionManisha SinghNo ratings yet
- The French Revolution and NapoleonDocument23 pagesThe French Revolution and Napoleonnusaibahhasan222No ratings yet
- The French Revolution Class 9 Notes History Chapter 1Document6 pagesThe French Revolution Class 9 Notes History Chapter 1atharvashende806No ratings yet
- The French Revolution Part 2: Robespierre To NapoleonDocument55 pagesThe French Revolution Part 2: Robespierre To NapoleonmissseesNo ratings yet
- The French RevolutionDocument3 pagesThe French RevolutionNaman SinghNo ratings yet
- The French Revolution Was A Period of Time in France When The People Overthrew The Monarchy and Took Control of The GovernmentDocument3 pagesThe French Revolution Was A Period of Time in France When The People Overthrew The Monarchy and Took Control of The GovernmentDahian VargasNo ratings yet
- French Revolution:: 1. Cultural CauseDocument2 pagesFrench Revolution:: 1. Cultural CauseAHZAM SALEEMNo ratings yet
- French Revolution IntroductionDocument25 pagesFrench Revolution IntroductionJbaron066100% (1)
- HIST 101 - Midterm Abstract BookletDocument9 pagesHIST 101 - Midterm Abstract Bookletznour alyNo ratings yet
- Rise of Nationalism in Europe NotesDocument6 pagesRise of Nationalism in Europe NotesAarshi SNo ratings yet
- World History A-Level EssaysDocument38 pagesWorld History A-Level EssaysRukha Salman100% (1)
- A Narrative History of The French RevolutionDocument2 pagesA Narrative History of The French RevolutionDumb CoffeeNo ratings yet
- French RevolutionDocument2 pagesFrench Revolutiondkmusicdk1No ratings yet
- The French RevolutionDocument6 pagesThe French Revolutiongeeggerw4ttrgNo ratings yet
- Why We Chose The French RevolutionDocument2 pagesWhy We Chose The French Revolutionapi-612716745No ratings yet
- The French Revolution: People Power in Action - History 5th Grade | Children's European HistoryFrom EverandThe French Revolution: People Power in Action - History 5th Grade | Children's European HistoryNo ratings yet
- French RevolutionDocument8 pagesFrench Revolutionfatimawaqar657No ratings yet
- French RevolutionDocument1 pageFrench Revolution7g5bh5djbqNo ratings yet
- The French Revolution HistoryDocument14 pagesThe French Revolution HistoryMaría Campal GarcíaNo ratings yet
- History Chapter 1-The French Revolution NotesDocument3 pagesHistory Chapter 1-The French Revolution NotesKhushi TanejaNo ratings yet
- Effects & Legacies of The French RevolutionDocument2 pagesEffects & Legacies of The French RevolutionBrij Narain JhaNo ratings yet
- Aalekh Class 9th HistoryDocument64 pagesAalekh Class 9th HistoryAALEKH RANANo ratings yet
- The French Revolution - Timeline and Major Events-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesThe French Revolution - Timeline and Major Events-WPS OfficeMarklein DumangengNo ratings yet
- 1848 People's SpringDocument23 pages1848 People's Springnusaibahhasan222No ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled DocumentLeoNo ratings yet
- French Society Before The RevolutionDocument4 pagesFrench Society Before The RevolutionMR. EXPLORERNo ratings yet
- Captura 2023-02-23 A Las 2.08.35Document37 pagesCaptura 2023-02-23 A Las 2.08.35Aitana RlNo ratings yet
- French Revolution and Role of EnlightenmentDocument5 pagesFrench Revolution and Role of Enlightenmentbored galNo ratings yet
- What Was The French Revolution?: The Storming of The BastilleDocument8 pagesWhat Was The French Revolution?: The Storming of The BastilleSagar SunuwarNo ratings yet
- French RevolutionDocument12 pagesFrench Revolutionshaileshawasthi100% (1)
- French RevolutionDocument2 pagesFrench Revolutionhaniyaindira3No ratings yet
- CSC Leave Form 6 BlankDocument3 pagesCSC Leave Form 6 BlankARMANDO NABASANo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Starting Your BusinessDocument8 pagesModule 4 - Starting Your BusinessJHERICA SURELLNo ratings yet
- 3-16-16 IndyCar Boston / Boston Grand Prix Meeting SlidesDocument30 pages3-16-16 IndyCar Boston / Boston Grand Prix Meeting SlidesThe Fort PointerNo ratings yet
- Philippine Phoenix Surety vs. WoodworksDocument1 pagePhilippine Phoenix Surety vs. WoodworksSimon James SemillaNo ratings yet
- Top 7506 SE Applicants For FB PostingDocument158 pagesTop 7506 SE Applicants For FB PostingShi Yuan ZhangNo ratings yet
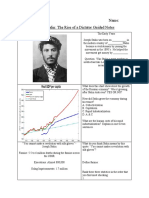
- Stalin Guided NotesDocument2 pagesStalin Guided Notesapi-536892868No ratings yet
- Wrongful ForeclosureDocument8 pagesWrongful Foreclosurefaceoneoneoneone100% (2)
- Role of The Govt in HealthDocument7 pagesRole of The Govt in HealthSharad MusaleNo ratings yet
- Frias Vs Atty. LozadaDocument47 pagesFrias Vs Atty. Lozadamedalin1575No ratings yet
- Financial Management: Usaid Bin Arshad BBA 182023Document10 pagesFinancial Management: Usaid Bin Arshad BBA 182023Usaid SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Colville GenealogyDocument7 pagesColville GenealogyJeff MartinNo ratings yet
- Cir Vs PagcorDocument3 pagesCir Vs PagcorNivra Lyn Empiales100% (2)
- TolemicaDocument101 pagesTolemicaPrashanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Page 1 of The Mafia and His Angel Part 2 (Tainted Hearts 2)Document2 pagesPage 1 of The Mafia and His Angel Part 2 (Tainted Hearts 2)adtiiNo ratings yet
- Basic Fortigate Firewall Configuration: Content at A GlanceDocument17 pagesBasic Fortigate Firewall Configuration: Content at A GlanceDenisa PriftiNo ratings yet
- KPMG Our Impact PlanDocument44 pagesKPMG Our Impact Planmuun yayo100% (1)
- African American LiteratureDocument9 pagesAfrican American LiteratureStephen Ali BarkahNo ratings yet
- A Review Essay On The European GuildsDocument11 pagesA Review Essay On The European GuildsAnonymous xDPiyENo ratings yet
- Acknowledgment, Dedication, Curriculum Vitae - Lanie B. BatoyDocument3 pagesAcknowledgment, Dedication, Curriculum Vitae - Lanie B. BatoyLanie BatoyNo ratings yet
- The Aesthetic Revolution and Its Outcomes, Jacques RanciereDocument19 pagesThe Aesthetic Revolution and Its Outcomes, Jacques RanciereTheoria100% (1)
- WAS 101 EditedDocument132 pagesWAS 101 EditedJateni joteNo ratings yet
- ENT300 - Module07 - BUSINESS PLANDocument23 pagesENT300 - Module07 - BUSINESS PLANSahira AdwaNo ratings yet
- The Reformation MovementDocument5 pagesThe Reformation MovementJulie Anne TasicNo ratings yet
- Educ 203 CHAPTER 6 Lesson 1Document13 pagesEduc 203 CHAPTER 6 Lesson 1charmen rogando100% (4)
- Ground Floor Plan Second Floor Plan: Bedroom 1 T & B Service Area Closet T & BDocument1 pageGround Floor Plan Second Floor Plan: Bedroom 1 T & B Service Area Closet T & BAbegail Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Discipline, Number of Vacancies, Educational Qualification and ExperienceDocument8 pagesDiscipline, Number of Vacancies, Educational Qualification and ExperienceMohammedBujairNo ratings yet
- Ais CH5Document30 pagesAis CH5MosabAbuKhater100% (1)
- Tiktok PresentationDocument17 pagesTiktok Presentationapi-681531475No ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension: Skills Weighted Mean InterpretationDocument10 pagesReading Comprehension: Skills Weighted Mean InterpretationAleezah Gertrude RegadoNo ratings yet