0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 views27 pagesIntro to C# Programming Basics
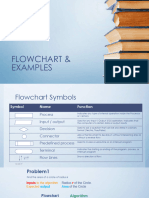
The document discusses flowcharts and pseudocode, providing examples of how to represent algorithms visually and in written form using basic structures like inputs, outputs, decisions, and processing steps; it also gives 10 examples of algorithms and their corresponding flowcharts or pseudocode to illustrate how to design solutions and express program flow for tasks like calculating speeds, triangle properties, and collecting data.
Uploaded by
princessoke141Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 views27 pagesIntro to C# Programming Basics
The document discusses flowcharts and pseudocode, providing examples of how to represent algorithms visually and in written form using basic structures like inputs, outputs, decisions, and processing steps; it also gives 10 examples of algorithms and their corresponding flowcharts or pseudocode to illustrate how to design solutions and express program flow for tasks like calculating speeds, triangle properties, and collecting data.
Uploaded by
princessoke141Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd