Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 3.05 Pressure
Uploaded by
Cayner WongCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 3.05 Pressure
Uploaded by
Cayner WongCopyright:
Available Formats
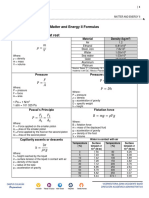
Force acting at right angles to a surface Pressure, P = Force, F
Pressure
Area, A
N / m2 or Pa (Pascal)
Unit
6N
C
2m 3m 2m
A B
2N 2N
Pressure acting on surface A Pressure, P = 2 N = = 0.33 N/m2
3x2
Pressure acting on surface B Pressure, P = 2 N = = 0.5 N/m2
2x2
Pressure acting on surface C Pressure, P = 6 N = = 1.0 N/m2
3x2
Pressure, P = Force, F
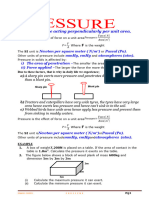
Application of Pressure
Area, A
Pressure Force Pressure Force
Small Large
Small
Large
Area Area
Ski Area : Large
Pressure : Less
Boot Stud Area : Small
Won’t sink in snow
Pressure : High
Better grip on ground
Wall Area : Large
Pressure : Less
Not sink into ground Knife Blade Area :
Washer Area: Large
Pin Area : Small Small
Pressure : Less
Pressure : High Pressure : High
Nut won’t pull into
Easily push through Easily push through
wood
wood material
Pressure, P = Force, F
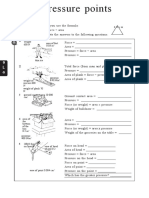
If either shoes steps on your feet, which one is more painful?
Area, A
20 kPa 500 kPa
Pressure, P = Force, F
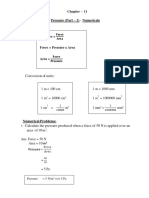
Problem
Area, A
Problem 1 : The wind pressure on the wall Problem 2 : A concrete block has a mass
on the right is 100 Pa. If the wall has an of 2600 kg. If the block measures 0.5 m by
area of 6 m2, what is the force on it? 1.0 m by 2.0 m, what is the maximum
pressure it can exert when resting on the
ground? (g = 10 N/kg)
Pressure, P = F = Pressure, P = F =
A A
100 = F = P = 2600 x 10 =
6 0.5 x 1
F = 6 x 100 P = 26000 =
= 600 N 0.5
P = 52000 N/m2
P = 52 kPa (Max)
You might also like
- Pressure PointsDocument2 pagesPressure PointsindakNo ratings yet
- PressureDocument16 pagesPressureKeyur GalaNo ratings yet
- Pressure Notes EditedDocument7 pagesPressure Notes EditedSharuvindan NairNo ratings yet
- Pressure NotesDocument11 pagesPressure NotesVaishnavi BannurNo ratings yet
- Unit 3.06 Pressure in LiquidsDocument5 pagesUnit 3.06 Pressure in LiquidsCayner WongNo ratings yet
- G9 H) Pressure in Fluids 1Document14 pagesG9 H) Pressure in Fluids 1Alhasan AlmoaqalehNo ratings yet
- Pusat Tuisyen Meka Bestari & Indera: Bab 3: Daya & Tekanan Chapter 3: Force & PressureDocument11 pagesPusat Tuisyen Meka Bestari & Indera: Bab 3: Daya & Tekanan Chapter 3: Force & PressuresadyehNo ratings yet
- Water and Soil Pressure Calculation For EtabsDocument3 pagesWater and Soil Pressure Calculation For EtabsBijendra Man Pradhan MRBNo ratings yet
- Design of Banded Drystone Gravity Wall (H 2M) Designed by Approved byDocument3 pagesDesign of Banded Drystone Gravity Wall (H 2M) Designed by Approved bynikki naiduNo ratings yet
- Final DemoDocument14 pagesFinal DemoWennie ManzaneroNo ratings yet
- Fluid PressureDocument3 pagesFluid PressureMuhammad AsifNo ratings yet
- Pressure RevisedDocument5 pagesPressure ReviseddanielNo ratings yet
- Water and Soil Pressure Calculation For EtabsDocument3 pagesWater and Soil Pressure Calculation For Etabsबिजेन्द्र प्रधान67% (6)
- PressureDocument30 pagesPressurerodel.verzosaNo ratings yet
- Design of Drystone Gravity WALL (H 2m) Designed by Approved byDocument3 pagesDesign of Drystone Gravity WALL (H 2m) Designed by Approved bynikki naiduNo ratings yet
- Pressure - Year 8Document13 pagesPressure - Year 8MamdouhNo ratings yet
- Design of Banded Drystone Gravity Wall (H 3M) Designed by Approved byDocument3 pagesDesign of Banded Drystone Gravity Wall (H 3M) Designed by Approved bynikki naiduNo ratings yet
- Sheet Pile Granular Excel SheetDocument9 pagesSheet Pile Granular Excel SheetNishan GajurelNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE Physics (3rd Edition) by Tom Duncan and Heather Kennett-2Document3 pagesCambridge IGCSE Physics (3rd Edition) by Tom Duncan and Heather Kennett-2Usman Ali0% (2)
- 7 Pressure OrigDocument165 pages7 Pressure Origrodel.verzosaNo ratings yet
- 11.1 Gases & PressureDocument7 pages11.1 Gases & PressureOmar AlwaerNo ratings yet
- PRESSURE - Part 2 (Numericals)Document5 pagesPRESSURE - Part 2 (Numericals)ARSHAD JAMIL87% (15)
- Design of A Cement Masonry Gravity Wall (H 4M) Designed by Approved byDocument3 pagesDesign of A Cement Masonry Gravity Wall (H 4M) Designed by Approved bynikki naiduNo ratings yet
- ME2 FormulasDocument12 pagesME2 Formulaspau verdugoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 2022Document27 pagesChapter 2 2022Nhật KhangNo ratings yet
- Pressure Standard 7Document35 pagesPressure Standard 7Jash Pasad100% (1)
- Design of A Cement Masonry Gravity Wall (H 2M) Designed by Approved byDocument3 pagesDesign of A Cement Masonry Gravity Wall (H 2M) Designed by Approved bynikki naiduNo ratings yet
- Pile DesignDocument9 pagesPile DesignIndraHoedayaNo ratings yet
- Footing Biaxial 2Document25 pagesFooting Biaxial 2knight1729No ratings yet
- Design Load CalculationsDocument5 pagesDesign Load CalculationsHabsi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Retaining Wall DesignDocument11 pagesRetaining Wall Designeric bargasNo ratings yet
- Structure Design FormulaDocument7 pagesStructure Design FormulaMIslamMonirNo ratings yet
- Reese-Wang EqnsDocument5 pagesReese-Wang Eqnsali jamiilNo ratings yet
- Pool Calculation SheetDocument6 pagesPool Calculation SheetSuman Resolved NeupaneNo ratings yet
- 3E Sci Phy Chapter 6 Pressure - TRDocument16 pages3E Sci Phy Chapter 6 Pressure - TRXu JianhangNo ratings yet
- 2023 Lect1 FLUID STATIC Application of Hydro StaticDocument80 pages2023 Lect1 FLUID STATIC Application of Hydro StaticmegatrotronNo ratings yet
- Pile Cuttack-1Document4 pagesPile Cuttack-1KANHA100% (1)
- Pressure Gauges and ManometersDocument13 pagesPressure Gauges and ManometersJoe NjoreNo ratings yet
- Design of A Cement Masonry GRAVITY WALL (H 3m) Designed by Approved byDocument3 pagesDesign of A Cement Masonry GRAVITY WALL (H 3m) Designed by Approved bynikki naiduNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 1Document1 pagePdfa3 1aizatNo ratings yet
- Brinch Hansen Lateral CapacityDocument18 pagesBrinch Hansen Lateral CapacityHamza MamiNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 With Slides Added PDFDocument70 pagesChapter2 With Slides Added PDFNur Syahira Afini Binti RamliNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Input 1.1 Design Soil Parameters: 0.0 0.0 Ground LevelDocument5 pages1.0 Input 1.1 Design Soil Parameters: 0.0 0.0 Ground LevelsuratwaritNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Input 1.1 Design Soil Parameters: 0.0 0.0 Ground LevelDocument10 pages1.0 Input 1.1 Design Soil Parameters: 0.0 0.0 Ground LevelsuratwaritNo ratings yet
- PressureDocument12 pagesPressuretrojanfrpNo ratings yet
- Hidrolika I (IL-2101) Slide 3Document32 pagesHidrolika I (IL-2101) Slide 3adhit46No ratings yet
- Ch. 4 Pressure in Fluids & Atm Pr.Document13 pagesCh. 4 Pressure in Fluids & Atm Pr.rudranilm2008No ratings yet
- Wind Analysis For Open Structure (Solar Panels) Based On ASCE 7-16 Input DataDocument8 pagesWind Analysis For Open Structure (Solar Panels) Based On ASCE 7-16 Input DataDonald HamiltonNo ratings yet
- Design of Toe Wall 1.5 M Above Ground LevelDocument4 pagesDesign of Toe Wall 1.5 M Above Ground LevelManupriya KapleshNo ratings yet
- Review of Soil Mechanics PDFDocument98 pagesReview of Soil Mechanics PDFLorence OmbaoNo ratings yet
- Type - 1 OptionDocument2 pagesType - 1 Optionmuhammed sabir v aNo ratings yet
- Retaining Wall ACI 318-08Document4 pagesRetaining Wall ACI 318-08Joseph AsfourNo ratings yet
- Statika FluidaDocument23 pagesStatika Fluidacarlos manikNo ratings yet
- Basement Wall SPR NewDocument12 pagesBasement Wall SPR NewAnonymous O404LiV4CNo ratings yet
- 2 - 5 MCsN106 Qd2 Dwall - Toe StabilityDocument1 page2 - 5 MCsN106 Qd2 Dwall - Toe StabilityBuvanendran SanjeevanNo ratings yet
- LEP3Document34 pagesLEP3renadNo ratings yet
- BayangolDocument7 pagesBayangolVenkat RaoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Pressure Concept & MeasurementDocument55 pagesFluid Pressure Concept & MeasurementAfiq IrfanNo ratings yet
- Design of A Gabion Wall Height 2m Designed by Approved byDocument5 pagesDesign of A Gabion Wall Height 2m Designed by Approved bynikki naiduNo ratings yet
- Carbon Compound Summary NotesDocument2 pagesCarbon Compound Summary NotesCayner WongNo ratings yet
- Unit 4.01 Work and EnergyDocument4 pagesUnit 4.01 Work and EnergyCayner WongNo ratings yet
- Unit 3.10 Pressure ProblemDocument4 pagesUnit 3.10 Pressure ProblemCayner WongNo ratings yet
- Tokyo Itinerary - 110123Document5 pagesTokyo Itinerary - 110123Cayner WongNo ratings yet
- Unit 4.02 Energy TransformationDocument3 pagesUnit 4.02 Energy TransformationCayner WongNo ratings yet
- Unit 4.03 Calculating PE and KEDocument4 pagesUnit 4.03 Calculating PE and KECayner WongNo ratings yet
- Fye Y7p4 2020 PDFDocument18 pagesFye Y7p4 2020 PDFCayner WongNo ratings yet
- PARK PERMITS GwenDocument1 pagePARK PERMITS GwenCayner WongNo ratings yet
- Spectrum-Brochure 220825Document10 pagesSpectrum-Brochure 220825Cayner WongNo ratings yet
- FAQ For Unlimited 5G Data - 14dec2022Document5 pagesFAQ For Unlimited 5G Data - 14dec2022Cayner WongNo ratings yet
- To FrameDocument5 pagesTo FrameMuhaimin RohizanNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Around The Table Negotiations 1 By: Hadaitulalh BaqriDocument14 pagesCH 3 Around The Table Negotiations 1 By: Hadaitulalh BaqriHadait Ullah Baqri80% (5)
- Crafting The Service Environment: Text Book Chapter 10Document25 pagesCrafting The Service Environment: Text Book Chapter 10Sneha DussaramNo ratings yet
- THESISDocument21 pagesTHESISMell Heiston GensonNo ratings yet
- D502K5+4 Operators ManualDocument68 pagesD502K5+4 Operators ManualOscar RamirezNo ratings yet
- GAP Guidelines: Management Programs (Overview)Document27 pagesGAP Guidelines: Management Programs (Overview)LleiLlei100% (1)
- PGDBA From MIT PuneDocument2 pagesPGDBA From MIT PuneMIT,PuneNo ratings yet
- Reptilian Astral WarsDocument4 pagesReptilian Astral WarsAlienraces1No ratings yet
- 015 Sami ZubaidaDocument2 pages015 Sami ZubaidaJuan Manuel CarriónNo ratings yet
- Rumus Fizik 2021Document1 pageRumus Fizik 2021Azizi Abdullah100% (1)
- Rockmass Strength PropertiesDocument32 pagesRockmass Strength PropertieskannonzkNo ratings yet
- Chap 3Document40 pagesChap 3eshbliNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Fall 2017Document68 pagesLab Manual Fall 2017Nil SabbirNo ratings yet
- TEST PearsonsDocument4 pagesTEST Pearsonsazertytyty000No ratings yet
- Political Discourse A Critical Discourse Discourse A Critical Discourse AnalysisDocument13 pagesPolitical Discourse A Critical Discourse Discourse A Critical Discourse AnalysisJennina MazoNo ratings yet
- Aurelia Vallier SlidesDocument42 pagesAurelia Vallier SlidesSaddy KhanNo ratings yet
- M16a3 Upper SpecsDocument1 pageM16a3 Upper SpecsMosinNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle Asset ManagementDocument1 pageLife Cycle Asset ManagementJuan EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Table of SpecificationDocument5 pagesTable of SpecificationEvangeline Delos Santos50% (2)
- CitiBank ApplicationDocument15 pagesCitiBank ApplicationJordan P HunterNo ratings yet
- Shaker SK L180 SDocument1 pageShaker SK L180 SUPT LABKESDA KAB PADANG PARIAMANNo ratings yet
- Egs630-6 Komatsu GensetDocument2 pagesEgs630-6 Komatsu GensetimamfadiliNo ratings yet
- WESCAM MX-15-0503AA-SpecDocument2 pagesWESCAM MX-15-0503AA-SpecAIT FARIDNo ratings yet
- CIRPs Ending in Resolution - 30sept 2022Document10 pagesCIRPs Ending in Resolution - 30sept 2022dip downNo ratings yet
- Eclipse Ring Planning Guide - Any To AnyDocument8 pagesEclipse Ring Planning Guide - Any To AnyAnsar ShafiiNo ratings yet
- Score Fusion of Finger Vein and Face For Human Recognition Based On Convolutional Neural Network ModelDocument9 pagesScore Fusion of Finger Vein and Face For Human Recognition Based On Convolutional Neural Network ModelFressy NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Geometry of Middle SurfaceDocument29 pagesGeometry of Middle SurfaceParth ShahNo ratings yet
- ADSA Assignment-1 Group - 3Document16 pagesADSA Assignment-1 Group - 3Animesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument6 pagesArtificial IntelligencesaraNo ratings yet
- Analog 01 Lab Exp 08 FullDocument6 pagesAnalog 01 Lab Exp 08 FullShuvro Sankar SenNo ratings yet