Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Perdarahan Intrakranial
Uploaded by
Tyas Rivai0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views21 pagesOriginal Title
PERDARAHAN INTRAKRANIAL
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views21 pagesPerdarahan Intrakranial
Uploaded by
Tyas RivaiYou are on page 1of 21
PERDARAHAN INTRAKRANIAL
Oleh : Salsalina Violetha Br Ginting
TRAUMA KEPALA
• Epidural hematoma
Interval lucid (talk and die)
robeknya a.meningeal media
Pupil anisokor
• Subdural hematoma
Hemiparesis dan penurunan kesadaran, cephalgia.
Robeknya bridging vein.
• Subarachnoid hemorrhage (stroke)
Thunderclap headache, tanda meningeal, Penurunan kesadaran –
Etiologi: robeknya aneurysma
• Intracerebral hemorrhage (stroke)
Paresis, hypesthesia, ataxia, penurunan kesadaran
Etiology: Hypertension
Coup-countercoup
injury
Epidural Hematome
Perdarahan extradural diantara periosteum
calvaria dengan duramater.
• Ruptur a. meningea media cabang a. maxillaris
• Terjadi pada daerah temporal (bagian mobile)
• Lebih sering akibat coup
• Gejala : ditemukan lucid interval (talk and die)
• Radiologis : Biconvex/lenticular shape
Epidural hematoma is located between the skull and dura mater
Interval lucid (talk and die)
Subdural Hematome
Perdarahan diantara duramater dan arachnoid mater.
• Ruptur dari bridging vein
• Terjadi pada daerah temporo-occipital
• Lebih sering akibat counter coup
• Gejala : perlahan-lahan menurun kesadaran
• Radiologis : semilunar shape
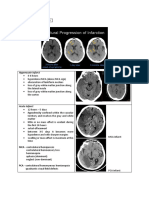
Subdural Hematoma.
Axial CT scan demonstrates a
left parietal subdural hematoma
hyperdense to the brain (white
arrows). There is associated mass
effect with effacement of the left
lateral ventricle and shift of the
midline to the right (red arrows).
Subdural Hematoma.
Image on left at brain
windows shows a slight
increase in density,
crescentric in shape, along
the inner table of the left
cranial vault (red arrows)
with a shift of the midline
structures (white arrow)
indicating mass effect. The
subdural window on the
right clearly shows the high
density crescent-shaped
blood concave toward the
cerebral hemisphere (yellow
arrows).
Subarachnoid Hemmorhage
Perdarahan diantara arachnoid mater
dan piamater
• Ruptur dari arteri biasanya akibat
pecahnya aneurima dan AVM
• Terjadi pada daerah batang otak,
biasanya pada cabang arteria basilaris.
• Gejala : thunderclap headache,
mimik gejala stroke hemorrhagik,
meningeal sign (+)
• Radiologis : Filling the sulci, biasanya
diikuti adanya IVH
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH).
There is high-attenuation blood in
the Sylvian fissures (blue arrows)
and the interhemispheric fissure
(red arrow) seen on this non-
contrast enhanced CT of the brain.
Do not confuse normal, physiologic
calcifications (white and black
arrows) for blood
Intracerebral Hemmorhage
Perdarahan pada parenkim otak
• Biasanya pada stroke
hemorrhagik
• Hemorrhage occurs in about
15% of strokes
• About 60% of hypertensive
hemorrhages occur in the basal
ganglia
Intracerebral hemorrhage, acute.
Freshly extravasated whole blood, as this
bleed into the thalamus (thin white arrow)
will be visible as increased density on non-
enhanced CT scans of the brain due
primarily to the protein in the blood (mostly
hemoglobin). As the clot begins to form, the
blood becomes denser for about 3 days
because of dehydration of the clot. After the
3rd day, the clot gradually decreases in
density from the outside in and becomes
invisible over the next several weeks.
Fraktur
Kranium
Fraktur Linear Fraktur dengan bentuk garis tunggal/stellata pada
tulang tengkorak, mengenai seluruh ketebalan tulang kepala
Fraktur Diastasis Fraktur yang terjadi pada sutura tulang tengkorak
yang mengakibatkan pelebaran sutura
Fraktur Kominutif Fraktur lebih dari 1 fragmen tulang dalam satu
area fraktur
Fraktur Kompresi disertai fragmen patahan tulang terdorong ke dalam
Dianggap bermakna bila segmen tabula eksterna yang impresi
masuk di bawah segmen tabula interna tulang yang sehat (>1 diploe)
Perlu dilakukan CT Scan menentukan dalamnya penekanan,
menyingkirkan adanya hematoma intracranial/kontusio
Indikasi operasi : Fraktur impresi >1 diploea, terdapat lesi intrakanial
dibawah segmen, terdapat deficit neurologis
TERIMA KASIH
You might also like
- STROKE: Handbook with activities, exercises and mental challengesFrom EverandSTROKE: Handbook with activities, exercises and mental challengesNo ratings yet
- Head CT Scan: Dr. Rani MariaDocument42 pagesHead CT Scan: Dr. Rani MariaAnonymous byUCks0OUNNo ratings yet
- BST TraumaDocument41 pagesBST TraumavereriNo ratings yet
- Imaging Techniques and Findings for Head TraumaDocument82 pagesImaging Techniques and Findings for Head TraumaRuki HartawanNo ratings yet
- CT in Head TraumaDocument4 pagesCT in Head TraumasunguramjanjaNo ratings yet
- Intracranial Hemorrhage IntroDocument5 pagesIntracranial Hemorrhage IntroPat Vierneza-CalalangNo ratings yet
- The Radiology Assistant Traumatic Intracranial HemorrhageDocument1 pageThe Radiology Assistant Traumatic Intracranial HemorrhageMahmudah AlkatiriNo ratings yet
- Life Threatening Brain PathologiesDocument33 pagesLife Threatening Brain Pathologiesnithin shenoiNo ratings yet
- CT ScanDocument84 pagesCT ScanHafiz Wajid SadiqNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Dr. Subagia - Neuro RadiologyDocument94 pagesLecture - Dr. Subagia - Neuro RadiologySyaimee Annisa AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Surfacwe Anatomy of Cvs and Arterial Puls AreasDocument6 pagesSurfacwe Anatomy of Cvs and Arterial Puls AreasHisham ChomanyNo ratings yet
- Bim Carok Kuliah CT ScanDocument45 pagesBim Carok Kuliah CT ScanWina HanriyaniNo ratings yet
- Review To CNS Radiology Including SSDocument52 pagesReview To CNS Radiology Including SSBisher Al-halabiNo ratings yet
- CT BrainDocument230 pagesCT BrainpraveenbhavniNo ratings yet
- CT Scan NotesDocument97 pagesCT Scan NotesMr. Hrisab DebNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading Head CT Scan Dengan Dr. Agus Budi, SP - BSDocument34 pagesJournal Reading Head CT Scan Dengan Dr. Agus Budi, SP - BSRizky Ramadhan SofianNo ratings yet
- Neuroimaging PDFDocument71 pagesNeuroimaging PDFMuhammad Syarief HidayatullahNo ratings yet
- NeuroimagingDocument79 pagesNeuroimagingIdris LubisNo ratings yet
- Basic Approach to Brain CT: Key Anatomy, Pathologies & Imaging FindingsDocument62 pagesBasic Approach to Brain CT: Key Anatomy, Pathologies & Imaging FindingsS B SayedNo ratings yet
- CT Scan BrainDocument3 pagesCT Scan BrainanggipuspaNo ratings yet
- #0、aneurysmDocument39 pages#0、aneurysmMargaret ThatcherNo ratings yet
- Head CT Scan PDFDocument89 pagesHead CT Scan PDFLiri AndiyaniNo ratings yet
- 010 Neurology - BRAIN ACUTE INJURYDocument45 pages010 Neurology - BRAIN ACUTE INJURYنوال سائد عبداللطيف مسلماني نوال سائد عبداللطيف مسلمانيNo ratings yet
- Neurology NotesDocument15 pagesNeurology NotesAshley Diane Henry100% (3)
- NeuroradiologyDocument25 pagesNeuroradiologysarguss14100% (2)
- 14 - CNS - 2Document22 pages14 - CNS - 2Saman SarKoNo ratings yet
- k10 - Kuliah Fk-Usu Nervous SystemDocument99 pagesk10 - Kuliah Fk-Usu Nervous SystemwlmhfpNo ratings yet
- Radiological and Other Investigations of The CnsDocument125 pagesRadiological and Other Investigations of The CnsBaguma MichaelNo ratings yet
- Major Arteries of The Head and NeckDocument7 pagesMajor Arteries of The Head and NeckJack MarlowNo ratings yet
- Head TraumaDocument63 pagesHead TraumaHalima AssiNo ratings yet
- CT Scan Kepala EmergencyDocument50 pagesCT Scan Kepala EmergencyRachmayasti RachmatNo ratings yet
- Understanding Subdural Hematomas - Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument54 pagesUnderstanding Subdural Hematomas - Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentNuzhat Noor Ayesha100% (1)
- RADIOLOGICAL SUPPORT Head InjuryDocument33 pagesRADIOLOGICAL SUPPORT Head InjuryNurul NajwaNo ratings yet
- Head Trauma Guide: Epidural, Subdural Hematomas & Brain Injury TypesDocument33 pagesHead Trauma Guide: Epidural, Subdural Hematomas & Brain Injury TypesRupak GhimireNo ratings yet
- Bleed Vs Infarct ComparisonDocument7 pagesBleed Vs Infarct ComparisonJed ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Venous Blood Sinuses Guide: Anatomy, Drainage & Clinical NotesDocument15 pagesVenous Blood Sinuses Guide: Anatomy, Drainage & Clinical NotesJennifer RodriguezNo ratings yet
- (Mantap) Slide Materi Bedah-1 Batch 3 2018 PDFDocument93 pages(Mantap) Slide Materi Bedah-1 Batch 3 2018 PDFKomang Sudiase50% (2)
- Cerebral Aneurysms: Aneurysms Posterior Circulation Basilar Artery Vertebral Arteries Posterior Communicating ArteryDocument10 pagesCerebral Aneurysms: Aneurysms Posterior Circulation Basilar Artery Vertebral Arteries Posterior Communicating ArteryRani SujithNo ratings yet
- (Peserta) Bedah 1 - Mantap Mei 2021Document96 pages(Peserta) Bedah 1 - Mantap Mei 2021ayustian aufaNo ratings yet
- 1 Approachtoheadct 130418093230 Phpapp01Document71 pages1 Approachtoheadct 130418093230 Phpapp01Sikandar Shahzad YousafzaiNo ratings yet
- Stroke and Its Imaging EvaluationDocument38 pagesStroke and Its Imaging EvaluationAnggi KusumawardaniNo ratings yet
- Imaging Findings and Clinical Correlation: Cerebral Herniation SyndromesDocument64 pagesImaging Findings and Clinical Correlation: Cerebral Herniation SyndromessridharNo ratings yet
- CT BRAIN AnatomyDocument32 pagesCT BRAIN AnatomydrsalilsidhqueNo ratings yet
- Head Computed Tomography: Subagia Santoso Sudjono Departement of Radiology Gatot Subroto Central Army HospitalDocument81 pagesHead Computed Tomography: Subagia Santoso Sudjono Departement of Radiology Gatot Subroto Central Army HospitalpebinscribdNo ratings yet
- Head CT Findings and InterpretationDocument31 pagesHead CT Findings and InterpretationElisabeth F. Ojha100% (2)
- 0019 2A Neurologia AngolDocument2 pages0019 2A Neurologia AngolMuhammad Ivan KurniawanNo ratings yet
- GRDA Intro Brain Cranial Nerves P2Document7 pagesGRDA Intro Brain Cranial Nerves P2KingNo ratings yet
- Brain HerniationDocument80 pagesBrain Herniationlamoleverde9297100% (1)
- Cerebral Aneurysm: @C C C CCCCC $C @C C @C ? cc0c @C 0cc @C CC# CC @C ? C CC 'CCC @C /2 CC @C, CC @C C CC CDocument6 pagesCerebral Aneurysm: @C C C CCCCC $C @C C @C ? cc0c @C 0cc @C CC# CC @C ? C CC 'CCC @C /2 CC @C, CC @C C CC Cchardel_08No ratings yet
- (Peserta) Bedah 1 - Mantap Mei 2019Document96 pages(Peserta) Bedah 1 - Mantap Mei 2019nicabiNo ratings yet
- Stroke by DR Hari Om ChandrakarDocument30 pagesStroke by DR Hari Om Chandrakarnavhari2209No ratings yet
- Neuro RadiologyDocument39 pagesNeuro RadiologyAurellia CelineNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Disease TumoursDocument9 pagesCerebrovascular Disease TumoursCindy Van WykNo ratings yet
- Unknown - Unknown - Stroke and Vascular Anatomy - Unknown.1Document42 pagesUnknown - Unknown - Stroke and Vascular Anatomy - Unknown.1Declan O'KaneNo ratings yet
- Trauma ThoraksDocument54 pagesTrauma ThoraksLisana ShidqiNo ratings yet
- CT Scan BasicsDocument28 pagesCT Scan BasicsPauline BurgosNo ratings yet
- Basic Neuroimaging (CT and MRI)Document56 pagesBasic Neuroimaging (CT and MRI)Dave Cronin100% (3)
- 115 Healthcare KPIsDocument19 pages115 Healthcare KPIsAli Elattar100% (2)
- The Strategic Role of Electronic Medical Records "Emr" in Supporting Electronic Health System in Saudi HospitalsDocument11 pagesThe Strategic Role of Electronic Medical Records "Emr" in Supporting Electronic Health System in Saudi HospitalsBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Challenges To Implementation of The Pharmaceutical Care Practice in Davao City.Document11 pagesChallenges To Implementation of The Pharmaceutical Care Practice in Davao City.JessieLynMolinaNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Antibacterial AgentsDocument58 pagesSynthetic Antibacterial AgentsApurba Sarker Apu100% (3)
- Mentorship FinalDocument46 pagesMentorship Finalapi-200572195No ratings yet
- Bi-Preterax Slide Set CI 15 - 16Document35 pagesBi-Preterax Slide Set CI 15 - 16drnasim20088171No ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy MCQ PDFDocument53 pagesPharmacognosy MCQ PDFBassam50% (2)
- Basic ECG Interpretation Practice Test: DIRECTIONS: The Following Test Consists of 20 QuestionsDocument10 pagesBasic ECG Interpretation Practice Test: DIRECTIONS: The Following Test Consists of 20 Questionsmihaela_bondocNo ratings yet
- MRCPI Part II Obstetric & Gynecology Exam FormatDocument3 pagesMRCPI Part II Obstetric & Gynecology Exam FormatNitasha Maqsood100% (1)
- HSCI130 Tutorial Exercise - Incidence & Prevalence ANSWER KEYDocument4 pagesHSCI130 Tutorial Exercise - Incidence & Prevalence ANSWER KEYarurojo100% (1)
- Lingualized Occlusion-A Case ReportDocument4 pagesLingualized Occlusion-A Case ReportSkAliHassanNo ratings yet
- Classification of Sutures: Monofilament MultifilamentDocument17 pagesClassification of Sutures: Monofilament Multifilamentlina_m354No ratings yet
- WNDMutationDB1 12 2wDocument7 pagesWNDMutationDB1 12 2wJyothi ManikNo ratings yet
- Vince McMahon's Testimony To Waxman CommitteeDocument122 pagesVince McMahon's Testimony To Waxman Committeeestannard100% (2)
- Entrepreneurship ProjectDocument21 pagesEntrepreneurship Projectmansi_2460% (5)
- Medical RealDocument1 pageMedical Realapi-252555369No ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: SECTION 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/undertakingDocument10 pagesSafety Data Sheet: SECTION 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/undertakingRamNo ratings yet
- Medicare PAP Documentation Requirements - Supplier Self-Audit ChecklistDocument2 pagesMedicare PAP Documentation Requirements - Supplier Self-Audit CheckliststevierayoNo ratings yet
- Topic 2-Production of Radionuclides & QA QCDocument62 pagesTopic 2-Production of Radionuclides & QA QCEdwin MccainNo ratings yet
- Lab and Blood Bank Safe DisposalDocument8 pagesLab and Blood Bank Safe DisposalShawqi AlmughniNo ratings yet
- RISE MagazineDocument20 pagesRISE MagazineMitch GastinNo ratings yet
- Electrical Conduction System of the HeartDocument7 pagesElectrical Conduction System of the HeartHUAWEI HUAWEINo ratings yet
- Jurnal Gingivitis Vivian 190631174Document5 pagesJurnal Gingivitis Vivian 190631174VivianNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Fever, Cough and Rash ExamDocument3 pagesPediatric Fever, Cough and Rash ExamTheju ReddyNo ratings yet
- 2018 - Guardian Life Claim FormDocument2 pages2018 - Guardian Life Claim FormSherene Boochoon60% (5)
- Irritablebowelsyndrome: What Treatments Really WorkDocument16 pagesIrritablebowelsyndrome: What Treatments Really WorkTeodora RaindropNo ratings yet
- Pediatric AnesthesiaDocument33 pagesPediatric AnesthesiamichaelNo ratings yet
- Youth Advocacy Letter Commission On Narcotic DrugsDocument2 pagesYouth Advocacy Letter Commission On Narcotic DrugsAB-No ratings yet
- Ayurvedic Remedies On Vaginal CandidiasisDocument11 pagesAyurvedic Remedies On Vaginal CandidiasisDipesh GamareNo ratings yet
- Medications Practice Problems (With Answers) : Sheet 1Document11 pagesMedications Practice Problems (With Answers) : Sheet 1Nathaniel PulidoNo ratings yet