Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Muscular System
Uploaded by
kocisiamisia0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views12 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views12 pagesThe Muscular System
Uploaded by
kocisiamisiaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
The Muscular System
• The muscular system is responsible for
functions such as maintenance of posture,
locomotion, and control of various circulatory
systems.
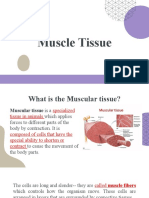
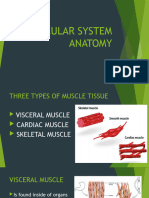
• Muscle tissue can be divided functionally
(voluntarily or involuntarily controlled) and
morphologically (striated or non-striated).
• These classifications describe three distinct
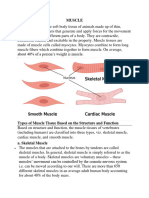
muscle types: skeletal, cardiac and smooth.
Skeletal muscle is voluntary and striated,
cardiac muscle is involuntary and striated,
and smooth muscle is involuntary and non-
striated.
Vocabulary:
• Myofibril - miofibryla
• Myofilament - miofilament
• Myosin - miozyna
• Actin - aktyna
• Striated - prążkowany
• Voluntary - świadomy
• Involuntary - mimowolny
• Myocyte – miocyt. A muscle cell.
Skeletal muscle mainly attaches to the
skeletal system via tendons to maintain
posture and control movement. They can
contract and relax without breaking, they are
elastic, they also protect our organs. Muscles
connect together with our bones with fibres
called tendons (ścięgna). The connection of
both systems directed by the nervous system
allows us to move.
The properties of muscles:
• they are excitable (pobudliwy, wrażliwy na
bodźce) or irritable
this means that they are capable of receiving
stimulation and responding to stimulation
from the nerves.
• Contractible (kurczliwe)
After receiving stimulation, they are capable
of contracting, or shortening
• Extensible (rozciągliwy)
A muscle can be stretched without damage by
the application of force.
• Elasticity
A muscle is able to return to its original
resting shape and length after being extended
or contracted
• Adaptability (możliwość przystosowania)
The muscular system is adaptable to, it can be
changed on response to how it is used.
The skeletal muscle is built of belly of muscle
(brzusiec) and tendons. The belly of muscle is
built of muscle bundles (pęczków włókien
mięśniowych) which consist of myofibrils.
Myofibrils are built of thin actin filaments
and thick myosin filaments.
These filaments slide past one another as the
muscle contracts and expands. On each
myofibril, regularly occurring dark bands,
called Z lines, can be seen where actin and
myosin filaments overlap. The region
between two Z lines is called a sarcomere;
sarcomeres can be considered the primary
structural and functional unit of muscle tissue.
ATP is the main source of energy required for
both muscle contraction and muscle
relaxation.
You might also like
- Muscular SystemDocument26 pagesMuscular Systemlubnab75% (4)
- Lesson-VI-The-Muscular-SystemDocument13 pagesLesson-VI-The-Muscular-Systemmikaelladoles02No ratings yet
- Embryology: Abdulrahman Uday AbdulfatahDocument27 pagesEmbryology: Abdulrahman Uday AbdulfatahAbdulrahman UdayNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle Structure and FunctionDocument12 pagesSkeletal Muscle Structure and FunctiondilsharakaviNo ratings yet
- Muscle PhysiologyDocument6 pagesMuscle Physiologytewogbadeomobuwajo005No ratings yet
- Muscle TissuesDocument9 pagesMuscle Tissuesangelo beldaNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of MusclesDocument58 pagesBiomechanics of MusclesAsad Chaudhary100% (2)
- Functions and Properties of Muscle TissuesDocument5 pagesFunctions and Properties of Muscle TissuesJoseph RefuerzoNo ratings yet
- Muscles and Its ClassificationDocument25 pagesMuscles and Its ClassificationJunaid ShahNo ratings yet
- Exercise PhysiologyDocument4 pagesExercise PhysiologyHya LaniogNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument8 pagesMuscular SystemZoological science classesNo ratings yet
- Pe 1 Module 4 Muscular System-PjsDocument26 pagesPe 1 Module 4 Muscular System-PjsJulie anne De jesusNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The MusclesDocument41 pagesAnatomy of The Musclestayabaiqbal66No ratings yet
- Report Summary and QuestionsDocument7 pagesReport Summary and QuestionsSkyNayvieNo ratings yet
- BM of Softtissue AftrmsDocument52 pagesBM of Softtissue AftrmsborrellanoNo ratings yet
- Module 5 MUSCULAR SYSTEMDocument20 pagesModule 5 MUSCULAR SYSTEMMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Zoology Notes: 011 Chapter 7Document4 pagesZoology Notes: 011 Chapter 7humanupgradeNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument13 pagesMuscular SystemAksidaksiNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue VnaDocument55 pagesMuscle Tissue Vnavaryvira6677No ratings yet
- 6.0 Muscular SystemDocument76 pages6.0 Muscular System[R2A] Khadijah AzlanNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue: Lecturer Reham M.M. Almosawi Medical MicrobiologyDocument10 pagesMuscle Tissue: Lecturer Reham M.M. Almosawi Medical Microbiologymustafa7calligrapherNo ratings yet
- Muscular Tissue Anatomy and Physiology LectureDocument25 pagesMuscular Tissue Anatomy and Physiology LecturehanzNo ratings yet
- Muscle Physiology: Human Physiology By-Liul M. ForDocument63 pagesMuscle Physiology: Human Physiology By-Liul M. ForKhant Si ThuNo ratings yet
- General Veterinary Macroscopic Anatomy: MYOLOGYDocument38 pagesGeneral Veterinary Macroscopic Anatomy: MYOLOGYneanna100% (1)
- Anatomy of The Muscular SystemDocument38 pagesAnatomy of The Muscular Systemأمال داودNo ratings yet
- MUSCLE B.Sc-IIDocument13 pagesMUSCLE B.Sc-IIAjinkya BansodeNo ratings yet
- GROSS General Concepts of MusclesDocument28 pagesGROSS General Concepts of MusclesDell E6430No ratings yet
- The Muscular System ExplainedDocument5 pagesThe Muscular System ExplainedHannah Mae Supeña CatedrillaNo ratings yet
- Movement Biopsych NotesDocument18 pagesMovement Biopsych NotesRealyn ZambasNo ratings yet
- READING MATERIAL - Muscular TissuesDocument2 pagesREADING MATERIAL - Muscular TissuescharuislostNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument9 pagesDefinitionaimiorreNo ratings yet
- PDF Document 9Document41 pagesPDF Document 9Eliese Marie Antonnie TiuNo ratings yet
- Kharkov National Medical University: Muscle TissueDocument42 pagesKharkov National Medical University: Muscle TissueSyed Irfan ArifNo ratings yet
- Skeletal MuscleDocument32 pagesSkeletal MuscleArfiNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On The Muscular SystemDocument46 pagesLecture Notes On The Muscular SystemDennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RM100% (1)
- 20201027-20201103-1149-Muscular SystemDocument21 pages20201027-20201103-1149-Muscular Systemdrin zekaNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged 1 13Document13 pagesIlovepdf Merged 1 13Abdulrahman UdayNo ratings yet
- Introduction to the Muscular SystemDocument17 pagesIntroduction to the Muscular SystemChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue 1Document93 pagesMuscle Tissue 1YOSHINo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology W3 - EmmanuelaDocument5 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology W3 - EmmanuelaRamizNo ratings yet
- 11J - Caybot - Jash Jovian - Task10Document11 pages11J - Caybot - Jash Jovian - Task10JASH JOVIAN CAYBOTNo ratings yet
- The Muscular TissueDocument23 pagesThe Muscular TissueMuhammad Salisu IliyasuNo ratings yet
- SDL MuscularDocument6 pagesSDL MuscularMonique Eloise GualizaNo ratings yet
- MYOLOGYDocument20 pagesMYOLOGYNatty ChikumbaNo ratings yet
- Locomotion and MovementDocument58 pagesLocomotion and MovementdddNo ratings yet
- Ana 221 Muscle TissueDocument12 pagesAna 221 Muscle TissueAmadi CedarNo ratings yet
- Support and Locomotion SystemDocument59 pagesSupport and Locomotion SystemBerrak AydınNo ratings yet
- Muscular System AnatomyDocument23 pagesMuscular System Anatomymichaelryann madayagNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 7: Muscular System EXPLORE:: Cardiac - The Autonomic Nervous System Also Regulates The Cardiac Muscle ThatDocument4 pagesAssignment # 7: Muscular System EXPLORE:: Cardiac - The Autonomic Nervous System Also Regulates The Cardiac Muscle ThatKassandra Shayne CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Muscle Contraction ExplainedDocument172 pagesMuscle Contraction ExplainedEmebet DebissaNo ratings yet
- Muscular System Chapter 6 SummaryDocument2 pagesMuscular System Chapter 6 SummaryMyat NyanNo ratings yet
- Muscle and Nervous TissueDocument12 pagesMuscle and Nervous TissueTom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- العضلاتDocument8 pagesالعضلاتNajwa AbdualgaderNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle - WikipediaDocument42 pagesSkeletal Muscle - Wikipediacomedy videoNo ratings yet
- Muscular TissueDocument5 pagesMuscular Tissuenitesh.th15005No ratings yet
- UNIT-6 Muscular SystemDocument48 pagesUNIT-6 Muscular SystemChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- Reading 4 The Muscular SystemDocument16 pagesReading 4 The Muscular Systemlephuongvy1406No ratings yet
- Soft Tissue Mechanics: Types and PropertiesDocument14 pagesSoft Tissue Mechanics: Types and PropertiesKripa NNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Unit 6 - The Muscular SystemDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Unit 6 - The Muscular Systemnur100% (1)