Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture Plate Tectonic Earth Interior Science 10 q1
Uploaded by
echevarrialorainne0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views14 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views14 pagesLecture Plate Tectonic Earth Interior Science 10 q1
Uploaded by
echevarrialorainneCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
According to the plate tectonics model, the
entire lithosphere of the Earth is broken
into numerous segments called plates.
• Each plate is slowly but continuously
moving.
• As a result of the motion of the plates,
three types of plate boundaries were
formed: Divergent, Convergent, and
Transform fault boundaries.
• Divergent boundary is formed when
plates move apart, creating a zone of
tension.
• Convergent boundary is present when
two plates collide.
• Transform fault is characterized by plates
that are sliding past each other.
• Plate tectonics give rise to several
geologic features and events
Glossary of Terms:
Continental volcanic arc mountains
formed in part by igneous activity
associated with subduction of oceanic
lithosphere beneath a continent
Convergent boundary a boundary in
which two plates move toward each
other, causing one of the slabs of the
lithosphere to subduct beneath an
overriding plate.
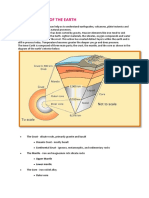
Crust the outer portion of the
earth.
Continental Crust the thick part
of the Earth’s crust, not located
under the ocean.
Oceanic Crust the thin part of
the Earth’s crust located under
the oceans.
Divergent boundary a region where
the crustal plates are moving apart.
Earthquake vibration of Earth due to
the rapid release of energy.
Fault a break in a rock along which
movement has occurred Fracture
any break in a rock in which no
significant movement has taken
place.
Geology the science that studies
Earth.
Hot spot a concentration of heat
in the mantle capable of creating
magma.
Magma a mass of molten rock
formed at depth, including
dissolved gases and crystals.
Mid-ocean ridge a continuous mass of
land with long width and height on the
ocean floor.
Plates rigid sections of the lithosphere
that move as a unit.
Plate tectonics a theory which suggests
that Earth’s crust is made up of plates that
interact in various ways, thus producing
earthquakes, mountains, volcanoes, and
other geologic features.
Primary (P) wave the first type of seismic wave
to be recorded in a seismic station.
Rocks consolidated mixture of minerals.
Secondary (S) wave second type of earthquake
wave to be recorded in a seismic station.
Seismogram a record made by a seismograph.
Seismograph a device used to record
earthquake waves
Subduction an event in which a slab of
rock thrusts into the mantle.
Transform fault boundary a boundary
produced when two plates slide past each
other.
Trench a depression in the seafloor
produced by subduction process. Volcanic
Island arc a chain of volcanoes that
develop parallel to a trench.
Asthenosphere soft, weak upper
portion of the mantle where the
lithospheric plates float and move
around.
Continental Drift Theory states that
all the continents were once one
large landmass that broke apart, and
where the pieces moved slowly to
their current locations.
Convection current in the
mantle because of the heat from
the inner layers of the Earth, and
is the force that drives the plates
to move around.
Lithosphere the topmost, solid
part of the Earth that is
composed of several plates.
Lithospheric Plates the moving,
irregularly-shaped slabs that fit
together to form the surface of the
Earth.
Mid-ocean ridge area in the middle
of the ocean where a new ocean
floor is formed when lava erupts
through the cracks in the Earth’s
crust.
Mohorovičić Discontinuity (Moho)
the boundary that separates the
crust and the mantle.
Plasticity the ability of solid to
flow. Seafloor spreading process by
which new ocean floor is formed
near the mid-ocean ridge and
moves outward.
Subduction the process in which
the crust plunges back into the
Earth.
Tectonics branch of geology that
deals with the movements that
shape the Earth’s crust
You might also like
- Lebs ScienceDocument9 pagesLebs ScienceVince Casison Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic TheoryDocument5 pagesPlate Tectonic TheoryDenise Anne SolidadNo ratings yet
- Science g10Document4 pagesScience g10Julia Amor DestuaNo ratings yet
- Plates Tectonics 2Document57 pagesPlates Tectonics 2Mark LourenceNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics: Name: Krisia Marie Amac Bsge 3ADocument5 pagesPlate Tectonics: Name: Krisia Marie Amac Bsge 3AMark Rienzo HingpisNo ratings yet
- The Turbulent Earth I. Questions To Pose: An Uneasy PlanetDocument32 pagesThe Turbulent Earth I. Questions To Pose: An Uneasy PlanetsshoeburrahmanNo ratings yet
- Science Discussion NotesDocument4 pagesScience Discussion NotesIvan TroyNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Week 2 - General Geology PDFDocument35 pagesLecture Notes For Week 2 - General Geology PDFRuby LenNo ratings yet
- Elements of Earthquake EngineeringDocument41 pagesElements of Earthquake EngineeringAnjaliNo ratings yet
- EndogenicDocument38 pagesEndogenicAngelica SeñaNo ratings yet
- Hand OutsDocument6 pagesHand OutsMJ DejosNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics and Seismography Class 7.5Document27 pagesPlate Tectonics and Seismography Class 7.5Monica SreeNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 First Quarter SummaryDocument3 pagesGrade 10 First Quarter SummaryAdrian Tastar100% (1)
- Marine Geology AssignmentDocument11 pagesMarine Geology AssignmentAlusine TommyNo ratings yet
- Tectonic EarthquakeDocument25 pagesTectonic EarthquakeMark Aaron AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Elements of Sisomology: Understanding EarthquakesDocument11 pagesElements of Sisomology: Understanding EarthquakesRohan ShreshthiNo ratings yet
- Earth and PlateTectonicsDocument34 pagesEarth and PlateTectonicsJohn BenedictNo ratings yet
- Tectonic Processes:: Theories and Plate BoundariesDocument33 pagesTectonic Processes:: Theories and Plate BoundariesYari Hillary Herbias TamarayNo ratings yet
- Plates Volcanoes EarthquakesDocument45 pagesPlates Volcanoes EarthquakesAbigail HernandezNo ratings yet
- Theory of Global Plate TectonicsDocument11 pagesTheory of Global Plate TectonicsHannylet OcateNo ratings yet
- Impact of Geographical Phenomena - Form 6Document139 pagesImpact of Geographical Phenomena - Form 6Conrod Wayne Smith100% (1)
- Plate Tectonics: A Revolutionary Earth Science TheoryDocument8 pagesPlate Tectonics: A Revolutionary Earth Science TheoryJoyNo ratings yet
- What is Plate Tectonics? The Theory that Shapes Our PlanetDocument30 pagesWhat is Plate Tectonics? The Theory that Shapes Our PlanetJhen Bon82% (17)
- Unit1 0Document71 pagesUnit1 0Rishi RamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Tectonic Hazards: Structure of The EarthDocument3 pagesTectonic Hazards: Structure of The EarthHoops Elite UKNo ratings yet
- Plate BoundariesDocument4 pagesPlate BoundariesRoland Rawlins IgaborNo ratings yet
- Why Do Tectonic Plates Crash and Slip? Geology Book for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandWhy Do Tectonic Plates Crash and Slip? Geology Book for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- DSTMDocument18 pagesDSTMDesh Deepak kantNo ratings yet
- DP Cheat Sheet 2017Document5 pagesDP Cheat Sheet 2017HollyNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument4 pagesPlate TectonicsNicole TaroyNo ratings yet
- From Continental Drift To Plate TectonicsDocument6 pagesFrom Continental Drift To Plate TectonicsyabaeveNo ratings yet
- Week-3 - Plate TectonicsDocument81 pagesWeek-3 - Plate TectonicsRashid AhmedovNo ratings yet
- Geology For Civil EngineersDocument5 pagesGeology For Civil EngineersTania Cate AranteNo ratings yet
- Distribution of Active Volcanoes and Major Mountain Belts in the PhilippinesDocument14 pagesDistribution of Active Volcanoes and Major Mountain Belts in the PhilippinesSam V.No ratings yet
- SciencemidtermDocument9 pagesSciencemidtermapi-281100019No ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Theory Explained in 10 ModulesDocument4 pagesPlate Tectonics Theory Explained in 10 ModulesArgie Mabag100% (2)
- Lithosphere. The Sideways and Downward Movement of The Edge of A Plate of The Earth's Crust Into TheDocument2 pagesLithosphere. The Sideways and Downward Movement of The Edge of A Plate of The Earth's Crust Into TheJaycee MeerandaNo ratings yet
- 6th Grade Science-Plate Tectonics and Earths InteriorDocument41 pages6th Grade Science-Plate Tectonics and Earths Interiorleojohn2100% (1)
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument57 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicshatdoghatdogNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document3 pagesChapter 4luisloredoperez156No ratings yet
- C1L4 - Elementary Knowledge On Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics (By MG Biscocho)Document19 pagesC1L4 - Elementary Knowledge On Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics (By MG Biscocho)Marnoel MalapitanNo ratings yet
- Plate MovementDocument49 pagesPlate Movementapi-25965024No ratings yet
- Earthquake Basics ModuleDocument65 pagesEarthquake Basics ModuleZankhana DaveNo ratings yet
- Continental & Oceanic Crust CharacteristicsDocument38 pagesContinental & Oceanic Crust CharacteristicsEvelyn MayorNo ratings yet
- Article On Plate Tectonics and Plate BoundariesDocument2 pagesArticle On Plate Tectonics and Plate BoundariesGUILLER BELENNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Q1Document80 pagesReviewer Q1Keanna marie GanaNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic Theory States That The EarthDocument2 pagesPlate Tectonic Theory States That The EarthPRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- PlatesDocument37 pagesPlatesJohn BenedictNo ratings yet
- PlatesDocument37 pagesPlatesvinod pNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Plate TectonicsDocument37 pagesLesson 2 Plate Tectonicsrobyngaylebautista2No ratings yet
- EndogenicDocument23 pagesEndogenicVicki PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics by Zeeshan AnsariDocument21 pagesPlate Tectonics by Zeeshan AnsariZeeshan AnsariNo ratings yet
- G10 Science Notes - Plate TectonicsDocument2 pagesG10 Science Notes - Plate TectonicsCairo DiazNo ratings yet
- Geology Final Exam NotesDocument14 pagesGeology Final Exam NotesKuhoo UNo ratings yet
- Subject:: ModèleDocument10 pagesSubject:: ModèleAnouar ChraibiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Earthquakes: Causes, Effects and TerminologyDocument22 pagesUnderstanding Earthquakes: Causes, Effects and TerminologyRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Tectonic Plates NotesDocument3 pagesTectonic Plates NotesAngelica CamilonNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument37 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsgildeddivaNo ratings yet
- Tectonic PlatesDocument17 pagesTectonic PlatesMaria Isabel LunaNo ratings yet
- The Earths MechanismDocument6 pagesThe Earths MechanismechevarrialorainneNo ratings yet
- Authors Purpose Oct. 31 2023 English 10 SHJDocument8 pagesAuthors Purpose Oct. 31 2023 English 10 SHJechevarrialorainneNo ratings yet
- Authors Purpose Oct. 31 2023 English 10 SHJDocument8 pagesAuthors Purpose Oct. 31 2023 English 10 SHJechevarrialorainneNo ratings yet
- Ict 10 Reviewer For Second Monthly ExamDocument3 pagesIct 10 Reviewer For Second Monthly ExamechevarrialorainneNo ratings yet
- IPTC 10878 Experiences Using EQR Modelling For Saturation Predictions in A Middle East Carbonate ReservoirDocument13 pagesIPTC 10878 Experiences Using EQR Modelling For Saturation Predictions in A Middle East Carbonate ReservoirStuart WilsonNo ratings yet
- English Material For Senior High School XI ClassDocument27 pagesEnglish Material For Senior High School XI ClassIqbal Hidayat Noor50% (2)
- SEM 1 - QUARTER 1 Learning Gains & Evaluation - Grade 11 ABMDocument46 pagesSEM 1 - QUARTER 1 Learning Gains & Evaluation - Grade 11 ABMkyla perezNo ratings yet
- Vanadium DepositsDocument10 pagesVanadium DepositsAnonymous bcHKSCr100% (1)
- Ebk - TPC 48 - F PDFDocument3 pagesEbk - TPC 48 - F PDFAnshuman SinghNo ratings yet
- Moonstone (Gemstone)Document3 pagesMoonstone (Gemstone)AlexMNo ratings yet
- Soal Bahasa Inggris Kelas XDocument9 pagesSoal Bahasa Inggris Kelas XNovika ArdhiantiNo ratings yet
- Love Across The Salt DesertDocument6 pagesLove Across The Salt DesertMehraj UdinNo ratings yet
- PH-MWBD-077 Borehole LogDocument5 pagesPH-MWBD-077 Borehole LogsawwahwahNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering-Ii: BSC Civil Engineering - 5 SemesterDocument22 pagesGeotechnical Engineering-Ii: BSC Civil Engineering - 5 SemesterSaid-Mansour MohamedNo ratings yet
- SAT UploadDocument11 pagesSAT UploadIskandar SetiadiNo ratings yet
- Astm Soil PenetrometerDocument8 pagesAstm Soil PenetrometerAlaaFaragAllahNo ratings yet
- JKR Design CriteriaDocument5 pagesJKR Design CriteriaAnonymous 6vZfB9pfza100% (2)
- Al-Azhar Engineering International ConferenceDocument2 pagesAl-Azhar Engineering International ConferenceEgyptian ResearcherNo ratings yet
- Casa GrandeDocument6 pagesCasa GrandeXendra AqeylaaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science Summary From BookDocument3 pagesGrade 10 Science Summary From BookRyzhenSanchez-Infante80% (20)
- Kerala Gem Testing Lab Guide to Commonly Used GemstonesDocument16 pagesKerala Gem Testing Lab Guide to Commonly Used GemstonesPiyush KumarNo ratings yet
- 3207 Part A ThrissurDocument376 pages3207 Part A ThrissurAbhay v.s100% (1)
- M49 Unit5 3D Seismic Attributes2 Fall2009Document89 pagesM49 Unit5 3D Seismic Attributes2 Fall2009Omair AliNo ratings yet
- Natural GAs Handbook CH-03Document212 pagesNatural GAs Handbook CH-03yashin21100% (2)
- Lecture3 MagneticAnomalies PDFDocument44 pagesLecture3 MagneticAnomalies PDFMithunNo ratings yet
- Analyses of Pig Iron 1900Document230 pagesAnalyses of Pig Iron 1900OceanNo ratings yet
- Giáo Án Antarctica Cho Học Viên Làm 1Document3 pagesGiáo Án Antarctica Cho Học Viên Làm 122073017 Lê Thị Quỳnh TrangNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to Geology Book InfoDocument2 pagesAn Introduction to Geology Book Infomohan kumar100% (1)
- 2017 5263 Moesm1 EsmDocument103 pages2017 5263 Moesm1 EsmVale SchmidtNo ratings yet
- Cracking in Drying SoilsDocument4 pagesCracking in Drying SoilsZdobniceNo ratings yet
- Topographic Map of KameyDocument1 pageTopographic Map of KameyHistoricalMapsNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1876610214002185 Main - 2Document7 pages1 s2.0 S1876610214002185 Main - 2Nizar Dwi PrabawaNo ratings yet
- Channel Islands HistoryDocument12 pagesChannel Islands HistoryMaryrobin OsteenNo ratings yet
- 13 Strike Slip FaultsDocument7 pages13 Strike Slip FaultsYohany Carmona MoralesNo ratings yet