Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Affective Assessment
Uploaded by
ressian11190 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views17 pagesOriginal Title
Affective Assessment (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views17 pagesAffective Assessment
Uploaded by
ressian1119Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 17
Affective Assessment
Dr. Edward E. Babasa
What is affective assessment?
• It deals with the affect dimension of students’
learning.
• The word affective comes from the Latin word
“affectus” which means feelings
• It includes a host of constructs such as
attitudes, values, beliefs, opinions, interests
and motivation – they are the non-cognitive
outcomes of learning that are not easily seen
or explicitly demonstrated.
• The type of assessment in this domain is not
aimed to determine what the students have
learned. Rather, it looks into how students feel
while they are learning., have their learning
experiences have influenced their emotions
and future behavior.
• Teaching is not only imparting content
knowledge that requires cognition. It is also
knowing and understanding students as
learners and humans.
• Unlike cognitive and psychomotor assessment,
affective assessment does not determine the
grades the students get. It rather helps
teachers determine what steps need to be
taken to help students attain success.
Taxonomy of Affective Domain in Learning
• Receiving – learner demonstrates an
awareness in an activity that is happening
such that he gives attention to that activity
• Responding – the learner reacts to a given
stimulus or information that has been
received.
• Valuing – learner demonstrates commitment
to the object, knowledge or activity. The
learner internalizes a set of specific values.
• Organizing – learner has internalized and
integrated his or her feelings, emotions,
beliefs, opinions resulting to actions where
new values and traits emerged
• The learner is able to discern independently
the right from wrong
• Characterizing – the learner demonstrates
his / her beliefs and attitudes not only in a
single event or situation but in multiple
events, showing consistency of behavior that
establishes his image or character.
Affective variables in learning
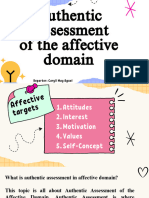
1. Attitudes – we refer to a person’s reaction
whether negative or positive, favorable or
unfavorable toward an object, activity, person
or environment
2. Values and Beliefs
• Values are characteristics or traits that a
person holds in high importance. These
include principles that one considers to be
right and consequently which guides the
person’s future actions and decisions.
• Beliefs refer to our convictions or opinions we
hold to be true even without evidence.
• While beliefs are traditionally associated with
religion, they have been talked about in the
field of education. Beliefs emanate from what
one hears, sees, needs and experiences.
• Values are developed from beliefs. Beliefs and
values can change over time from learned
experiences.
3. Interest – is a psychological state that draws a
person’s attention to an object, idea or event.
• It is interest that drives the learner to be
attentive to the topic of discussion
• Interest may be personal or situational.
4. Motivation is an inner drive, impulse,
emotion, or desire that moves one to a
particular action. It arouses and sustains
behavior.
5. Self-confidence – refers to how a person feels
about his / her abilities to accomplish a task or
reach a goal. It is the person’s perception of
himself / herself and his /her capabilities to
perform successfully the task given to him /
her.
• https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-
oNdeUNi5AA
You might also like
- The Intelligent Investor NotesDocument19 pagesThe Intelligent Investor NotesJack Jacinto100% (6)
- 18 Ex Parte Applic Shorten Time Consolidate 11/01/21Document13 pages18 Ex Parte Applic Shorten Time Consolidate 11/01/21José DuarteNo ratings yet
- Product Design and DevelopmentDocument14 pagesProduct Design and Developmentajay3480100% (1)
- Motivation in Learning and TeachingDocument18 pagesMotivation in Learning and TeachingWan MaisarahNo ratings yet
- Fouts Federal LawsuitDocument28 pagesFouts Federal LawsuitWXYZ-TV DetroitNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Heart ReviewerDocument8 pagesCardiovascular System Heart ReviewerImmanuel Cris PalasigueNo ratings yet
- Developmental Dimensions of LearningDocument22 pagesDevelopmental Dimensions of Learningzandra capio100% (1)
- Nicolopoulou-Stamati - Reproductive Health and The EnvironmentDocument409 pagesNicolopoulou-Stamati - Reproductive Health and The EnvironmentGiorgos PapasakelarisNo ratings yet
- Types of Non Verbal CommunicationDocument7 pagesTypes of Non Verbal Communicationgaurav gharat100% (1)
- Steps in The Valuing ProcessDocument4 pagesSteps in The Valuing ProcessTerie Ann Goyeneche100% (13)
- Value IndicatorsDocument11 pagesValue IndicatorsKhatthy InocNo ratings yet
- Module 2M Applying Learning Theories To Healthcare PracticeDocument48 pagesModule 2M Applying Learning Theories To Healthcare PracticeAubrey Justine Galeon100% (1)
- Affective AssessmentDocument17 pagesAffective AssessmentMa Cecilia TransfiguracionNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Assessment in The Affective DomainDocument46 pagesLesson 4 - Assessment in The Affective DomainMila GamidoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Affective AssessmentDocument11 pagesLesson 4 - Affective AssessmentMary Grace CanlasNo ratings yet
- Assessment in The Affective DomainDocument36 pagesAssessment in The Affective DomainIson Ocampo100% (1)
- Affective Assessment 1Document42 pagesAffective Assessment 1franceearl.claron.studentNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Techniques For Affective ObjectivesDocument15 pagesEvaluation Techniques For Affective ObjectivesAnne MoralesNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Assessment in Learning 2Document22 pagesGroup 4 Assessment in Learning 2Angelique Nicole CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Krathwohl'S Taxonomy: of Objectives in The Affective DomainDocument29 pagesKrathwohl'S Taxonomy: of Objectives in The Affective Domainyen alfafaraNo ratings yet
- English Analysing Themes and Ideas Presentation Beige Pink Lined StyleDocument24 pagesEnglish Analysing Themes and Ideas Presentation Beige Pink Lined StyleKhyla Mae Bassig CondeNo ratings yet
- L5 Affective AssessmentDocument34 pagesL5 Affective Assessmentbyunbacooon456No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document29 pagesUnit 2AnkurNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 ppt-1Document40 pagesUnit 2 ppt-1AnkurNo ratings yet
- Health Ed - Chapter 3Document33 pagesHealth Ed - Chapter 3Kevin CamilozaNo ratings yet
- EDU36 Lesson 4Document8 pagesEDU36 Lesson 4Athena Scarlet Hazelyn BaggayNo ratings yet
- Finals ModuleDocument15 pagesFinals Modulechristianborlaza23No ratings yet
- Lessson 4Document7 pagesLessson 4Love MaribaoNo ratings yet
- Ob Un3Document83 pagesOb Un3Janani ChandrasekaranNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 & 4 PDFDocument46 pagesUnit 3 & 4 PDFJean MarceloNo ratings yet
- Assessment in Affective DomainDocument6 pagesAssessment in Affective Domainfries riveraNo ratings yet
- Attitudes & ValuesDocument17 pagesAttitudes & ValuesNeha AroraNo ratings yet
- Concept of Motivation and Motivational Strategies in The ClassroomDocument33 pagesConcept of Motivation and Motivational Strategies in The ClassroomHope Wilson AgbezukeNo ratings yet
- Affective AssessmentDocument57 pagesAffective AssessmentJenea EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Health Educ3Document36 pagesHealth Educ3Querubin DandoyNo ratings yet
- II-Attitudes and Job SatisfactionDocument35 pagesII-Attitudes and Job SatisfactionAkshat Sharma Roll no 21No ratings yet
- Assessment in Learning 2 FINALDocument8 pagesAssessment in Learning 2 FINALJethroNo ratings yet
- Blue and Yellow Playful Doodle Digital Brainstorm Presentation - 20240227 - 122333 - 0000Document12 pagesBlue and Yellow Playful Doodle Digital Brainstorm Presentation - 20240227 - 122333 - 0000neiljustinlacorte2003No ratings yet
- Adverbs and Verbs: Prepared By: RJC DullanoDocument27 pagesAdverbs and Verbs: Prepared By: RJC DullanoRod Jean Claire DullanoNo ratings yet
- Nature and Characteristics of Learning: Dr. Maheswari JaikumarDocument41 pagesNature and Characteristics of Learning: Dr. Maheswari JaikumarCrisnelynNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Student MotivationDocument32 pagesUnit 3 Student MotivationIqra ShehzadiNo ratings yet
- Attitudes and ValuesDocument19 pagesAttitudes and ValuesPragyan SarangiNo ratings yet
- Learning PerceptionDocument20 pagesLearning PerceptionSaran GodcilNo ratings yet
- Concepts & Dimensions of LearningDocument40 pagesConcepts & Dimensions of LearningRaghav SinghalNo ratings yet
- Activity 6Document2 pagesActivity 6Rose Ann N. CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Prof. Ed. 6Document19 pagesProf. Ed. 6Antonette Gilboy CabrillasNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Learning, Perception and AttributionDocument60 pagesModule 3 Learning, Perception and AttributionMarjon DimafilisNo ratings yet
- SG4-Focus On ClassroomDocument5 pagesSG4-Focus On ClassroomFate VargasNo ratings yet
- Approaches in Teaching Values Education: Inculcation ApproachDocument4 pagesApproaches in Teaching Values Education: Inculcation ApproachKeny DeanNo ratings yet
- Approaches in Teaching Values Education: Inculcation ApproachDocument4 pagesApproaches in Teaching Values Education: Inculcation ApproachKeny DeanNo ratings yet
- Blooms Taxonomy AffectiveDocument10 pagesBlooms Taxonomy AffectiveSindisiwe YaloNo ratings yet
- Presentation2. MAAm MARJALINODocument32 pagesPresentation2. MAAm MARJALINOTricia MorgaNo ratings yet
- Classroom ProcessesDocument36 pagesClassroom ProcessesMary Misty Rose PediangcoNo ratings yet
- LearningDocument251 pagesLearningRamila MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Human Values Unit 1Document14 pagesHuman Values Unit 1ritikatomar241No ratings yet
- Motivation and Ind. Diff, Self-Regulation and Assessment - Ashley R.Document37 pagesMotivation and Ind. Diff, Self-Regulation and Assessment - Ashley R.Ashley RañesesNo ratings yet
- Motivating Adult Learners: Learner Motivation Principles of Motivating InstructionDocument13 pagesMotivating Adult Learners: Learner Motivation Principles of Motivating InstructionParmis AsgaryNo ratings yet
- Motivation Resources and ActivitiesDocument18 pagesMotivation Resources and ActivitiesMaria Felisadae Lorenzo-RomanNo ratings yet
- Human LearningDocument9 pagesHuman Learningapi-268185812No ratings yet
- Attitude NotesDocument9 pagesAttitude NotesULtraSwoRDFiSHNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Affective Assessment: Learning OutcomesDocument3 pagesLesson 5 Affective Assessment: Learning OutcomesJayson Kerth Italia SeveroNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument33 pagesAssessmentDar WinNo ratings yet
- BECED S4 Motivational Techniques PDFDocument11 pagesBECED S4 Motivational Techniques PDFAmeil OrindayNo ratings yet
- All NotesDocument185 pagesAll Notespranab sakarNo ratings yet
- Domainsandobjectives 190505124443Document60 pagesDomainsandobjectives 190505124443Imran KhanNo ratings yet
- mgn-581 Unit 4Document54 pagesmgn-581 Unit 4Ashish kumar ThapaNo ratings yet
- Mamaoui PassagesDocument21 pagesMamaoui PassagesSennahNo ratings yet
- PREETI and RahulDocument22 pagesPREETI and Rahulnitinkhandelwal2911No ratings yet
- Mag Issue137 PDFDocument141 pagesMag Issue137 PDFShafiq Nezat100% (1)
- Remarkings AirportsDocument1 pageRemarkings AirportsJuan Jose CaleroNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Effectiveness of Heat Exchanger Shell and Tube Type One Shell Two Tube Pass As Cooling OilDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Effectiveness of Heat Exchanger Shell and Tube Type One Shell Two Tube Pass As Cooling OilHendrik V SihombingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 101-160Document297 pagesChapter 101-160Dipankar BoruahNo ratings yet
- How To Manage Asthma: A GuideDocument44 pagesHow To Manage Asthma: A GuideSrinivas YerriboinaNo ratings yet
- Marriage and Divorce Conflicts in The International PerspectiveDocument33 pagesMarriage and Divorce Conflicts in The International PerspectiveAnjani kumarNo ratings yet
- Telesis Events - Construction Contract Essentials - WorkbookDocument52 pagesTelesis Events - Construction Contract Essentials - WorkbookassmonkeysNo ratings yet
- Invasive Species RubricDocument1 pageInvasive Species Rubricapi-463570013No ratings yet
- Info Cad Engb FestoDocument14 pagesInfo Cad Engb FestoBayu RahmansyahNo ratings yet
- Cassandra Training 3 Day CourseDocument5 pagesCassandra Training 3 Day CoursedsunteNo ratings yet
- AL Applied Mathematics 1989 Paper1+2 (E)Document7 pagesAL Applied Mathematics 1989 Paper1+2 (E)eltytanNo ratings yet
- مذكرة التأسيس الرائعة لغة انجليزية للمبتدئين?Document21 pagesمذكرة التأسيس الرائعة لغة انجليزية للمبتدئين?Manar SwaidanNo ratings yet
- Utsourcing) Is A Business: Atty. Paciano F. Fallar Jr. SSCR-College of Law Some Notes OnDocument9 pagesUtsourcing) Is A Business: Atty. Paciano F. Fallar Jr. SSCR-College of Law Some Notes OnOmar sarmiento100% (1)
- Cyclosporin ARCDocument9 pagesCyclosporin ARCSean GreenNo ratings yet
- Accenture 172199U SAP S4HANA Conversion Brochure US Web PDFDocument8 pagesAccenture 172199U SAP S4HANA Conversion Brochure US Web PDFrajesh2kakkasseryNo ratings yet
- Eco 407Document4 pagesEco 407LUnweiNo ratings yet
- Lee. Building Balanced Scorecard With SWOT Analysis, and Implementing "Sun Tzu's The Art of Business Management Strategies" On QFD Methodology PDFDocument13 pagesLee. Building Balanced Scorecard With SWOT Analysis, and Implementing "Sun Tzu's The Art of Business Management Strategies" On QFD Methodology PDFSekar Ayu ParamitaNo ratings yet
- Kematian Di ICUDocument24 pagesKematian Di ICURahmida RahmyNo ratings yet
- Resume - General Manager - Mohit - IIM BDocument3 pagesResume - General Manager - Mohit - IIM BBrexa ManagementNo ratings yet
- 2013 03 01 Maurizio Di Noia PresentationDocument80 pages2013 03 01 Maurizio Di Noia PresentationRene KotzeNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Division of Bohol Department of Education Region VII, Central VisayasDocument12 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Division of Bohol Department of Education Region VII, Central VisayasCecille HernandoNo ratings yet