Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Genetic-Engineering Part 1
Uploaded by
Wattpadpurposes0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views19 pagesGenetic engineering is the process of manipulating genes from different species and inserting them into an organism's genome to give it desired traits. This involves using recombinant DNA technology to cut and join DNA from different sources. For example, genes encoding pesticidal proteins from Bacillus thuringiensis bacteria have been inserted into corn plants, creating Bt corn which is resistant to certain insect pests. The process involves cutting DNA with restriction enzymes, joining the foreign gene to a vector like a plasmid, transferring the recombinant DNA into a host cell, and screening for cells that express the new gene.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGenetic engineering is the process of manipulating genes from different species and inserting them into an organism's genome to give it desired traits. This involves using recombinant DNA technology to cut and join DNA from different sources. For example, genes encoding pesticidal proteins from Bacillus thuringiensis bacteria have been inserted into corn plants, creating Bt corn which is resistant to certain insect pests. The process involves cutting DNA with restriction enzymes, joining the foreign gene to a vector like a plasmid, transferring the recombinant DNA into a host cell, and screening for cells that express the new gene.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views19 pagesGenetic-Engineering Part 1
Uploaded by
WattpadpurposesGenetic engineering is the process of manipulating genes from different species and inserting them into an organism's genome to give it desired traits. This involves using recombinant DNA technology to cut and join DNA from different sources. For example, genes encoding pesticidal proteins from Bacillus thuringiensis bacteria have been inserted into corn plants, creating Bt corn which is resistant to certain insect pests. The process involves cutting DNA with restriction enzymes, joining the foreign gene to a vector like a plasmid, transferring the recombinant DNA into a host cell, and screening for cells that express the new gene.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
GENETIC ENGINEERING
Describe the process of Genetic Engineering
DNA
(Deoxyribonuclei
c Acid)
Bacteria
Recombina
nt DNA
(rDNA)
Flvar Savr
Bt COrn / Bt Maize
Bt Eggplant
Genetic
Engineering
Genetic engineering is the process of
using recombinant DNA (rDNA)
technology to alter the genetic
makeup of an organism. Genetic
engineering involves the direct
manipulation of one or more genes.
Most often, a gene from another
species is added to an organism's
genome to give it a desired
phenotype.
Classical plant breeding uses
deliberate interbreeding
Classical (crossing) of closely or distantly
related individuals to produce
Breeding new crop varieties or lines with
desirable properties. Plants are
crossbred to introduce traits/genes
from one variety or line into a new
genetic background.
The modification in Genetic Engineering may
involve the following;
Genetic - Introduction of new traits in organisms
Engineering - Enhancement of present trait by
increasing the expression of desired gene
- Enhancement of a present trait by
disrupting the inhibition of the desired genes’
expression
Goal: Solve problem
on pests
Pest resistant corn
Bt corn
Pest resistant corn Non-Pest resistant
corn
Bacillus thuringiensis(Bt)
• is a species of bacteria that
lives in soil
• It makes proteins that are
toxic to some insects when
eaten, but not others
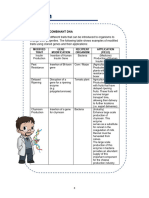
Process of Genetic
Engineering
1. cutting or cleavage of DNA by
restriction enzymes (REs)
2. selection of an appropriate
vector or vehicle which would
propagate the recombinant DNA
(eg. circular plasmid in bacteria
with a foreign gene of interest)
3. ligation (join together) of the
gene of interest (eg. from animal)
with the vector (cut bacterial
plasmid)
4. transfer of the recombinant
plasmid into a host cell (that 5. selection process to screen
would carry out replication to which cells actually contain
make huge copies of the the gene of interest
recombined plasmid)
You might also like
- Applications in Crop ImprovementDocument11 pagesApplications in Crop ImprovementMaria Ella Juliana CapanangNo ratings yet
- Topical Guidebook For GCE O Level Biology 3 Part 2From EverandTopical Guidebook For GCE O Level Biology 3 Part 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Basic Principles of Recombinant DNA Technology (173865)Document69 pagesBasic Principles of Recombinant DNA Technology (173865)Yap Jacky75% (4)
- Genetic Engineering: Junalyn Gale D. TapayaDocument27 pagesGenetic Engineering: Junalyn Gale D. TapayaKyle Refugio100% (1)
- Chapter 6 Plant BiotechnologyDocument39 pagesChapter 6 Plant Biotechnologyshivabt07No ratings yet
- Plant Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument6 pagesPlant Recombinant DNA TechnologyPaula FranciaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Plant BiotechnologyDocument39 pagesChapter 6 Plant BiotechnologyInuyashayahooNo ratings yet
- Module I - GeneticsDocument20 pagesModule I - GeneticsJhay Luiz Cajigal ArquinesNo ratings yet
- 3rd-Quarter General Biology 2 STEMDocument35 pages3rd-Quarter General Biology 2 STEMKassandra MarieNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering and Recombinant Dna: Lesson 1Document5 pagesGenetic Engineering and Recombinant Dna: Lesson 1Dexie MusaNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNADocument2 pagesRecombinant DNAKarylle MaeNo ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument8 pagesGenetic EngineeringKbo SjdiNo ratings yet
- Application of Biotechnology For Improvement of Ornamental CropsDocument92 pagesApplication of Biotechnology For Improvement of Ornamental Cropspavani100% (8)
- A Seminar ON Genetic Engineering and Gene Cloning BY Ayinde Samson MATRIC NUMBER: 168859049 Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Ekiti State University. JUNE, 2021Document12 pagesA Seminar ON Genetic Engineering and Gene Cloning BY Ayinde Samson MATRIC NUMBER: 168859049 Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Ekiti State University. JUNE, 2021SamsonNo ratings yet
- DNA Genetic EngineeringDocument72 pagesDNA Genetic EngineeringEmman Matthew GregorioNo ratings yet
- rDNA and Genetic Engineering NotesDocument6 pagesrDNA and Genetic Engineering NotesEllah Iracielli TevesNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering Part 3 and 4Document42 pagesGenetic Engineering Part 3 and 4KSHITIJ K GAUTAMNo ratings yet
- GenbioDocument9 pagesGenbiovin98625No ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering and BiotechnologyDocument34 pagesGenetic Engineering and BiotechnologyCristy Jean ApdianNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheets in General Biology Ii Quarter 3, Week 1: Department of EducationDocument15 pagesActivity Sheets in General Biology Ii Quarter 3, Week 1: Department of EducationKashima KotaroNo ratings yet
- Bio 3Document3 pagesBio 3CameronNo ratings yet
- Dictionary of BiotechnologyDocument3 pagesDictionary of BiotechnologyMa Lizha RafaelNo ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument8 pagesGenetic EngineeringWynne Cassandra JoverNo ratings yet
- WEEK 4 - Q2 - Earth and LifeDocument16 pagesWEEK 4 - Q2 - Earth and Lifenoreen lubindinoNo ratings yet
- Basics of Genetic Trasgenic Plants DefinitionDocument36 pagesBasics of Genetic Trasgenic Plants DefinitionKeyru LaillampNo ratings yet
- DNA Recombination and DNA TechnologyDocument8 pagesDNA Recombination and DNA TechnologyJhun Lerry TayanNo ratings yet
- Genetically Engineered CellsDocument22 pagesGenetically Engineered CellsRhenzo YuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Genetic Engineering and Recombinant DNADocument20 pagesLesson 2 Genetic Engineering and Recombinant DNAWynnie TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument14 pagesRecombinant DNA TechnologyAnshika SinghNo ratings yet
- STS Week 12 - 13 Part 1 GMOsDocument55 pagesSTS Week 12 - 13 Part 1 GMOsGerman MartinNo ratings yet
- BiotechnologyDocument2 pagesBiotechnologyJenny PastorNo ratings yet
- General Bio HandoutDocument4 pagesGeneral Bio HandoutJamilah BaruangNo ratings yet
- C. Genetic Modification ObjectivesDocument9 pagesC. Genetic Modification ObjectivesFengyiNo ratings yet
- Doc-Pocket K17Document5 pagesDoc-Pocket K17José Ignacio Basilio OlveraNo ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument37 pagesGenetic EngineeringLalita SahNo ratings yet
- 6.molecular Method Cloning, Therapy, RecombinantDocument18 pages6.molecular Method Cloning, Therapy, Recombinantaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Karnatakapuc 110709070353 Phpapp01Document11 pagesBiotechnology Karnatakapuc 110709070353 Phpapp01Lovryan Tadena AmilingNo ratings yet
- Application of Biotechnology in Different Field: By-Vinod KumarDocument33 pagesApplication of Biotechnology in Different Field: By-Vinod KumarElvira Sta. MariaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Techniques of Genetic EngineeringDocument10 pagesAssignment Techniques of Genetic EngineeringmariashekinahdNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2: Quarter 3 - Module 1 GeneticsDocument12 pagesGeneral Biology 2: Quarter 3 - Module 1 GeneticsCamille Castrence Caranay100% (1)
- CHEK Gen Bio 2 - Module 1 - Week 1 4 - Q3finalDocument68 pagesCHEK Gen Bio 2 - Module 1 - Week 1 4 - Q3finalKatherine Mae Martinez0% (1)
- Earth and Life Science NotesDocument3 pagesEarth and Life Science Notesradz quilinganNo ratings yet
- vt59.2708-21424810576 - 1098526164484586 - 5189445820608338690 - n.pdfLESSON-1-and-2-RECOMBINANT-DNA-and-its - 8Document30 pagesvt59.2708-21424810576 - 1098526164484586 - 5189445820608338690 - n.pdfLESSON-1-and-2-RECOMBINANT-DNA-and-its - 8CameronNo ratings yet
- Notes - BiologyDocument41 pagesNotes - BiologyJamie Rose FontanillaNo ratings yet
- A B C: B R: Pplications OF Iotechnology TO Rops Enefits AND IsksDocument8 pagesA B C: B R: Pplications OF Iotechnology TO Rops Enefits AND IsksEnkhbaatar BatmagnaiNo ratings yet
- Gen - Bio W2-Recombinant DnaDocument6 pagesGen - Bio W2-Recombinant DnaLielanie NavarroNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2.5 - Genetic-Engineering (General Biology II)Document34 pagesCHAPTER 2.5 - Genetic-Engineering (General Biology II)Queen Iris Angeline CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering - lessON 1Document32 pagesGenetic Engineering - lessON 1Zion JiasnesNo ratings yet
- Transgenic OrganismsDocument3 pagesTransgenic OrganismsGalino Julia Cristine A.No ratings yet
- Bioteknologi TanamanDocument20 pagesBioteknologi TanamanRahel AlfaniahNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology AssignmentDocument6 pagesBiotechnology AssignmentBerhanu RegassaNo ratings yet
- Q4 - Gen Bio NotesDocument12 pagesQ4 - Gen Bio NotesBeast GamingNo ratings yet
- Term Paper ON: Transgenic PlantsDocument17 pagesTerm Paper ON: Transgenic PlantsVikal RajputNo ratings yet
- Gene Transfer Technologies in Plants: Roles in Improving CropsDocument9 pagesGene Transfer Technologies in Plants: Roles in Improving CropsAbhinav VermaNo ratings yet
- Scope and Application of Genetic Engineering RS Maam HWDocument29 pagesScope and Application of Genetic Engineering RS Maam HWRani SapkotaNo ratings yet
- SHS STEM Bio2 Q3 Week 1 Module 2 Applications of Recombinant DNADocument5 pagesSHS STEM Bio2 Q3 Week 1 Module 2 Applications of Recombinant DNAWynnie TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- Medical TerminologyDocument43 pagesMedical TerminologyJansher Ali ChohanNo ratings yet
- The Simple Addition, Deletion, or Manipulation of A Single Trait in An Organism To Create A Desired ChangeDocument25 pagesThe Simple Addition, Deletion, or Manipulation of A Single Trait in An Organism To Create A Desired ChangeSharang AhujaNo ratings yet
- Gene Transfer Technologies in Plants: Roles in Improving CropsDocument9 pagesGene Transfer Technologies in Plants: Roles in Improving CropsRachanaNo ratings yet
- Plant Biotech Tutorial-Oct30-Nov06 AlsoDocument2 pagesPlant Biotech Tutorial-Oct30-Nov06 Alsorgcgzjj2sdNo ratings yet