Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Business Finance Lessons, 2,3,7,8,9, and 10
Uploaded by
dollizonmishaeliezer0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views56 pagesThis file contains lessons for Business Finances for the GRADE 12 ABM STUDENTS.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis file contains lessons for Business Finances for the GRADE 12 ABM STUDENTS.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views56 pagesBusiness Finance Lessons, 2,3,7,8,9, and 10
Uploaded by
dollizonmishaeliezerThis file contains lessons for Business Finances for the GRADE 12 ABM STUDENTS.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 56
Financial Planning
Tools and Concepts
Parts1&2
Week 10
Introduction
Every business unit whether it is an industrial
establishment, a trading concern or a construction
company needs funds for carrying on its activities
successfully.
It requires funds to acquire fixed assets like machines, equipment,
furniture etc. and to purchase raw materials or finished goods, to pay
its creditors, to meet its day-to-day expenses, and so on. In fact,
availability of adequate finance is one of the most important factors
for success in any business.
However, the requirement of finance, nowadays, is so
large that no individual is in a position to provide the
whole amount from his personal sources.
So the businessman has to depend on other sources
and use various ways to raise the necessary amount of
funds.
Every businessman has to be very careful not only in
assessing the firm’s requirement of finance but also in
deciding on the forms in which funds are raised and
utilized.
Planning
Planning is an important aspect of the firm’s
operations because it provides road maps for
guiding, coordinating, and controlling the
firm’s actions to achieve its objectives
(Gitman & Zutter, 2012).
Planning is a systematic way of deciding
about and doing things in a purposeful
manner. When this approach is applied
exclusively for financial matter, it is termed
as financial planning.
In simple words Financial Planning can be
defined as:
“the process of estimating the capital required
and determining it’s composition. It is the
process of framing financial policies in relation
to procurement, investment and administration
of funds of an enterprise.”
-Management planning is about setting
the goals of the organization and identifying
ways on how to achieve them (Borja&
Cayanan, 2015).
There are two phases of financial
planning:
Financial planning starts with long
term plans which would then
translate to short term plans.
Importance of Financial Planning
To ensure adequate funds
Help in making growth and expansion program
which will aid the long-run survival of the company.
Assures the suppliers of funds that their
investments are well managed.
Maintain a secure balance between outflow and
inflow of funds for stability.
Strategic financial
management
Strategic financial management
focuses on developing long-term
goals through forecasting market
changes.
Strategic financial
management is about
creating profits for the
business over the long
run.
It seeks to maximize
return on investment
for stakeholders.
Tactical financial
management
Tactical financial management focuses on more
short-term goals by making decisions and creating
an action plan based on current market conditions.
which relate to short-term positioning.
Long-term financial plans
-These are a set of goals that lay out the overall
direction of the company.
-A long-term financial plan is an integrated
strategy that takes into account various
departments such as sales, production, marketing,
and operations for the purpose of guiding these
departments towards strategic goals.
-Those long-term plans consider proposed outlays for
fixed assets, research and development activities,
marketing and product development actions, capital
structure, and major sources of financing.
-Also included would be termination of existing
projects, product lines, or lines of business; repayment
or retirement of outstanding debts; and any planned
acquisitions (Gitman & Zutter, 2012)
Short-term financial plans
-Specify short-term financial actions and the anticipated
impact of those actions. Part of short term financial
plans include setting the sales forecast and other forms
of operating and financial data. This would then
translate into operating budgets, the cash budget, and
pro forma financial statements (Gitman & Zutter, 2012).
-For the purpose of this topic, emphasis will be made on
short-term financial planning
Comparison of Short-Term and Long-Term Planning
the planning process as follows:
1)Set goals or objectives.
•For corporations, long term and short term
objectives are usually identified. These can be
seen in the company’s vision and mission
statements. The vision statement states where the
company wants to be while the mission statement
states the plans on how to achieve the vision.
Goal setting is a process that starts with
careful consideration of what you want to
achieve and ends with a lot of hard work to
accomplish it. In setting goals, you have to
identify the long-term and short-term plans
in order to achieve your mission and vision.
Examples of a company’s Vision-Mission
statements are as follows:
Jollibee Foods Corporation (JFC)
Vision: To excel in providing great tasting food that
meets local preferences better than anyone; To
become one of the three largest and most profitable
restaurant companies in the world by 2020.
Mission: To serve great tasting food, bringing the
joy of eating to everyone.
McDonalds Philippines
Vision: First to respond to the fast changing needs of the
Filipino family; First choice when it comes to food and dining
experience; First mention as the ideal employer and socially
responsible company; First to respond to the changing lifestyle
of the Filipino family
Mission: To serve the Filipino community by providing great-
tasting food and the most relevant customer delight experience.
2)Identify Resources
Resources include production capacity,
human resources who will man the
operations and financial resources (Borja
& Cayanan, 2015).
3)Identify goal-related tasks
In this step, management should focus
on completing a task in order to achieved
planned objectives. Task-driven or
results-driven uses targets to stay
motivated in their work.
• the goal-related task is to
prepare an event to increase
awareness of (whatever issue
you want)
4)Establish responsibility centers for
accountability and timeline
If the task is already identified, the next step is to identify
which department should be held accountable. For
example, if your goal is to achieve 30% in sales, this
should be the responsibility of the head of sales and
marketing department and there should also be another
departments who take the responsibility in achieving the
goal.
there must be a timeline for the
planned activities, especially
activities which are not normally
done.
5)Establish the evaluation system for
monitoring and controlling
In financial planning, the management must establish
a monitoring and controlling evaluation system so that
there is a clear plan for the program or activity. It will
help the staffs decide how they are going to track and
analyze data. Quantified plans for budget and
projected financial statements should also be done.
For corporations, the management must establish
a mechanism which will allow plans to be
monitored. This can be done through quantified
plans such as budgets and projected financial
statements. The management will then compare
the actual results to the planned budgets and
projected financial statements. Any deviations
from the budgets should be investigated.
6)Determine contingency plans
A contingency plan is often referred to as
PLAN B because it can be used as an
assumption for an unexpected result.
Determining a contingency plan helps an
organization respond effectively to a future
event or situation that may or may not occur.
•In planning, contingencies must be considered as
well.
•Budgets and projected financial statements are
anchored on assumptions. If these assumptions
do not become realities, management must have
alternative plans to minimize the adverse effects
on the company (Borja & Cayanan, 2015)
Financial Planning Tools
and Concepts Part 2
Characteristics of an Effective Plan
• In planning, the goal of maximizing shareholders’
wealth must always be put in mind. The following
criteria may be used for effective planning:
• •Specific – target a specific area for improvement.
• •Measurable – quantify or at least suggest an
indicator of progress.
• •Assignable – specify who will do it.
• •Realistic – state what results can
realistically be achieved, given available
resources.
• •Time-related – specify when the result(s)
can be achieved.
1. Sales Budget
• The most important account in the financial
statement in making a forecast is sales since most of
the expenses are correlated with sales.
• Given the importance of the sales forecast, the
financial manager must be able to support this
figure with reasonable assumptions. The following
external and internal factors should be considered in
forecasting sales:
Factors that Influence Sales
the following external and internal factors
influencing sale, among others:
-Macroeconomic Variables (external)
Macroeconomic variables such as the GDP rate,
inflation rate, and interest rates, among others
play an important role in forecasting sales
because it tells us how much the consumers are
willing to spend.
• A low GDP rate coupled by a high inflation
rate means that consumers are spending
less on their purchases of goods and
services. This means that we should not
forecast high sales of the periods of low
GDP.
-Developments in the Industry (external)
Products and services which have more
developments in its industry would likely have a
higher sales forecast than a product or service in
slow moving industry. Consumer trends are always
changing, thus the industry should be competitive
to be able to appeal to more customers and stay in
the market.
-Competition (external)
Suppose you are selling bread and you know that
each person in your community eats an average of
one loaf of bread a day. The population of your
community is 500 people. If you are the only person
selling bread in your town, then your sales forecast is
500 units of bread. However, you also have to take
account your competition.
What if there are 4 other sellers of bread? You will
need to have to divide the sales between the 5 of
you. Does this mean your new forecast should be
100 units of bread? Not necessary. You should also
know the preference of your consumers. If more of
them would prefer to buy more bread from you,
then you should increase your sales forecast
-Production Capacity and man power
(internal)
Suppose that you have already evaluated the
macroeconomic factors and identified that there is a
very strong market for your product and consumers
are very likely to buy from you. You forecasted that
you will be able to sell 1,000 units of your product.
However, you only have 20 employees who are
able to produce 20 units each. Your capacity
cannot cover your expected demand hence, you
are limited by it. To be able to increase
capacity, you should be able to expand your
operations.
What are the implications if the sales budget
is not correct? If understated, there can be
lost opportunities in the form of forgone
sales. If it is too optimistic, the management
may decide to unnecessarily increase
capacity or hire more employees and end up
with more inventories.
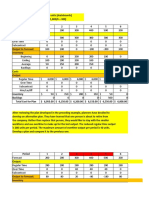
2. Production Budget
-A production budget provides
information regarding the number of
units that should be produced over a
given accounting period based on
expected sales and targeted level of
ending inventories.
It is computed as follows:
Example:
-[A] Company forecasts sales in units for
January to May as follows:
-Moreover, [A] Company would like to maintain
100 units in its ending inventory at the end of
each month.
-Beginning inventory at the start of January
amounts to 50 units.
-How many units should [A] Company produce in
order to fulfill the expected sales of the company?
Answer:
Example of a Production Budget
As an example of a production budget, ABC
Company plans to produce an array of plastic
pails during the upcoming budget year, all of
which fall into the general Product A category.
Its production needs are outlined as follows:
Calculation of the Production Budget
The production budget is typically presented in either a monthly
or quarterly format. The basic calculation used by the production
budget is:
+ Forecasted unit sales
+ Planned finished goods ending inventory balance
= Total production required
- Beginning finished goods inventory
= Products to be manufactured
The planned ending finished goods inventory at the end of
each quarter declines from an initial 1,000 units to 500
units, since the materials manager believes that the
company is keeping too many finished goods in stock.
Consequently, the plan calls for a decline from 1,000 units
of ending finished goods inventory at the end of the first
quarter to 500 units by the end of the second quarter,
despite a projection for rising sales. This may be a risky
forecast, since the amount of safety stock on hand is being
cut while production volume increases by over 30 percent.
Given the size of the projected inventory decline, there is a
fair chance that ABC will be forced to increase the amount
of ending finished goods inventory later in the year.
3. Budgeting Cash
Operating Budget An operating budget is a
forecast of the revenues and expenses
expected for one or more future periods.
An operating budget is typically formulated by
the management team just prior to the
beginning of the year and shows expected
activity levels for the entire year.
This budget may be supported by a
number of subsidiary schedules that contain
information at a more detailed level.
For example, there may be separate
supporting budgets that address payroll, the
cost of goods sold, and inventory. Actual results
are then compared to the operating budget to
determine the extent of any variances from
expectations. Management may alter its actions
during the year to bring actual results into line
with the operating budget.
-Operations budget refers to the variable
and fixed costs needed to run the
operations of the company but are not
directly attributable to the generation of
sales.
-Examples of this are the following:
•Rent payments •Wages and Salaries of selling
and administrative personnel •Administrative
Costs •Travel and representation expenses
•Professional fees •Interest Payment
Activity 10 (30 pts.) to be presented in
class
• Suppose you are planning an event
(birthday, debut, wedding, etc.)
prepare a step-by-step activity
following the financial process.
You might also like
- Business Forecasting 9th Edition Hanke Solution ManualDocument9 pagesBusiness Forecasting 9th Edition Hanke Solution ManualMisha Lezhava67% (6)
- Assignment 2 IndividualDocument10 pagesAssignment 2 IndividualShahrul AzrinNo ratings yet
- Financial Planning Tools and ConceptsDocument30 pagesFinancial Planning Tools and ConceptsEarl Concepcion89% (9)
- The Importance of Accurate Sales ForecastingDocument8 pagesThe Importance of Accurate Sales ForecastingVipul KothariNo ratings yet
- Operations Management: Contemporary Concepts and Cases Fifth EditionDocument6 pagesOperations Management: Contemporary Concepts and Cases Fifth EditionShahriar Alam100% (1)
- Bagong Patype EditedDocument21 pagesBagong Patype EditedJoyluxxi100% (1)
- Sample Questions of MSCDocument6 pagesSample Questions of MSCJacob hauhengNo ratings yet
- SOAL DAN JAWABAN: MANAJEMEN OPERASIONALDocument106 pagesSOAL DAN JAWABAN: MANAJEMEN OPERASIONALrenyzahridar63% (8)
- OPIM5671 Case Study ReportDocument76 pagesOPIM5671 Case Study ReportJobin GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Case #1 Farmers RestaurantDocument63 pagesCase #1 Farmers RestaurantPaulina Naranjo83% (6)
- Converging Factor Racing FormulasDocument53 pagesConverging Factor Racing Formulashomomysticus67% (3)
- Financial Planning Tools and Concepts - and andDocument25 pagesFinancial Planning Tools and Concepts - and andChristian ZebuaNo ratings yet
- Financial PlanningDocument48 pagesFinancial PlanningKeanna Ashley Grace GutingNo ratings yet
- Business Finance: 1 Quarter Lesson 3: Financial Planning ProcessDocument6 pagesBusiness Finance: 1 Quarter Lesson 3: Financial Planning ProcessReshaNo ratings yet
- Local Media6428844306473856818Document38 pagesLocal Media6428844306473856818Maura Lizabeth Gawili BalunggayNo ratings yet
- Financial MGMT MODULE 2Document7 pagesFinancial MGMT MODULE 2Isabelle MariaNo ratings yet
- Financial Planning: WK04-LAS1-BF-II-12Document19 pagesFinancial Planning: WK04-LAS1-BF-II-12Benj Jamieson DuagNo ratings yet
- Financial Planning and ToolsDocument41 pagesFinancial Planning and ToolsShalom BuenafeNo ratings yet
- BUDGETING PresentationDocument6 pagesBUDGETING PresentationJandJ's Art BoxNo ratings yet
- Page 1 of 9Document9 pagesPage 1 of 9Gemechis LemaNo ratings yet
- Budgets and Their Ability To Support Organisational ObjectivesDocument38 pagesBudgets and Their Ability To Support Organisational ObjectivesranjithNo ratings yet
- What Is Budgeting?: Strategy Into Targets and BudgetsDocument11 pagesWhat Is Budgeting?: Strategy Into Targets and BudgetsAriela DavisNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Financial Forecasting For Strategic GrowthDocument17 pagesGroup 1 Financial Forecasting For Strategic GrowthZirah Mae NiepesNo ratings yet
- Financial Forecasting for Strategic GrowthDocument17 pagesFinancial Forecasting for Strategic GrowthArmand RoblesNo ratings yet
- FM II - Chapter 03, Financial Planning & ForecastingDocument14 pagesFM II - Chapter 03, Financial Planning & ForecastingHace AdisNo ratings yet
- Finance Module 03 - Week 3Document16 pagesFinance Module 03 - Week 3Christian ZebuaNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Importance of Financial Planning for BusinessesDocument98 pagesUnderstanding the Importance of Financial Planning for Businessesrey mark hamacNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Financial Forecasting For Strategic GrowthDocument20 pagesTopic 5 Financial Forecasting For Strategic GrowthIrene KimNo ratings yet
- Financial Planning: Prepared By: Luigi Miguel B. Antonio, MBADocument20 pagesFinancial Planning: Prepared By: Luigi Miguel B. Antonio, MBAThriztan Andrei BaluyutNo ratings yet
- Importance of Financial PlanningDocument18 pagesImportance of Financial PlanningSyam LaNo ratings yet
- Fiscal Management WF Dr. Emerita R. Alias Edgar Roy M. Curammeng Financial Forecasting, Corporate Planning and BudgetingDocument10 pagesFiscal Management WF Dr. Emerita R. Alias Edgar Roy M. Curammeng Financial Forecasting, Corporate Planning and BudgetingJeannelyn CondeNo ratings yet
- Sterling Institute of Management StudiesDocument29 pagesSterling Institute of Management StudiesPraNita AmbavaneNo ratings yet
- Business Finance For Video Module 2Document16 pagesBusiness Finance For Video Module 2Bai NiloNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Accounting Lesson 14 Operational BudgetingDocument36 pagesIntroduction to Accounting Lesson 14 Operational Budgetingluo jamesNo ratings yet
- Fin Assignment1 CunananDocument4 pagesFin Assignment1 CunananJowen Para CruzNo ratings yet
- Financial Planning and ForecastingDocument15 pagesFinancial Planning and Forecastingalkanm750100% (1)
- Cost II Chapter Two by SisayDocument20 pagesCost II Chapter Two by SisaySisay Belong To JesusNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 SummaryDocument6 pagesChapter 5 SummaryDiana Mark AndrewNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two-SalesDocument9 pagesChapter Two-SalesBelay AdamuNo ratings yet
- Costing FinalfffDocument39 pagesCosting FinalfffSaloni Aman SanghviNo ratings yet
- Corporate PlanningDocument22 pagesCorporate PlanningYumna HashmiNo ratings yet
- Assignment SMDocument3 pagesAssignment SMshahrukhakhterNo ratings yet
- Master Budget Framework for Planning and ControlDocument5 pagesMaster Budget Framework for Planning and ControlJeson MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Budgets and Managing MoneyDocument51 pagesBudgets and Managing MoneyIrtiza Shahriar ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- CMI ManagementDirect - BudgetsDocument34 pagesCMI ManagementDirect - BudgetsAnonymous 2AK0KTNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Financial Forecasting For Strategic GrowthDocument18 pagesChapter 9 Financial Forecasting For Strategic GrowthMa. Jhoan DailyNo ratings yet
- Financial Planning and BudgetingDocument45 pagesFinancial Planning and BudgetingRafael BensigNo ratings yet
- Financial Performance ToolsDocument30 pagesFinancial Performance ToolsJason RecanaNo ratings yet
- Master Budget Strategy GuideDocument20 pagesMaster Budget Strategy Guideitsdaloveshot naNANAnanaNo ratings yet
- H9 Master Budget and ForecastingDocument17 pagesH9 Master Budget and ForecastingGodwin Jil CabotajeNo ratings yet
- Budget and BudgetryDocument6 pagesBudget and Budgetryram sagar100% (1)
- Financial Strategizing Contributes To ProfitsDocument3 pagesFinancial Strategizing Contributes To ProfitsSaleeth Muhammed SaleethNo ratings yet
- Financial Forecasting For Strategic GrowthDocument3 pagesFinancial Forecasting For Strategic GrowthVergel MartinezNo ratings yet
- MB 0045Document32 pagesMB 0045Kawal Preet Singh OberoiNo ratings yet
- Role of Financial Management WorkbookDocument15 pagesRole of Financial Management WorkbookAditri MahajanNo ratings yet
- Cost Ii CH 2Document23 pagesCost Ii CH 2TESFAY GEBRECHERKOSNo ratings yet
- Financial Planning and Forecasting StudyDocument16 pagesFinancial Planning and Forecasting Studyprince yadavNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER FOUR Financial Forcasting and PlanningDocument15 pagesCHAPTER FOUR Financial Forcasting and PlanningSoftware Lab MISKERNo ratings yet
- Accounting and Finance for Managers: Budgeting and Budgetary ControlDocument12 pagesAccounting and Finance for Managers: Budgeting and Budgetary ControlSiraj MohammedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PptsDocument111 pagesChapter 4 PptsKimberly Quin Cañas100% (1)
- Abm 4 Module 6Document6 pagesAbm 4 Module 6Argene AbellanosaNo ratings yet
- Plan Your EnterpriseDocument9 pagesPlan Your EnterpriseJerwin SamsonNo ratings yet
- Financial Planning and Control ProcessDocument3 pagesFinancial Planning and Control ProcessPRINCESS HONEYLET SIGESMUNDONo ratings yet
- Unit 7Document11 pagesUnit 7Shaik UsmanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 Financial PlanningDocument7 pagesCHAPTER 3 Financial Planningflorabel parana0% (1)
- Chapter 3Document14 pagesChapter 3Tariku KolchaNo ratings yet
- Financial Planning and Budgeting GuideDocument29 pagesFinancial Planning and Budgeting GuidejsemlpzNo ratings yet
- Master Budgeting and Forecasting for Hospitality Industry-Teaser: Financial Expertise series for hospitality, #1From EverandMaster Budgeting and Forecasting for Hospitality Industry-Teaser: Financial Expertise series for hospitality, #1No ratings yet
- Management AccountingDocument3 pagesManagement AccountingRobert HensonNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Forecasting relies on opinionsDocument10 pagesQualitative Forecasting relies on opinionsLiezel Panganiban TaralaNo ratings yet
- The Role of Planning and Forecasting in Business OrganizationDocument43 pagesThe Role of Planning and Forecasting in Business OrganizationAyalsew MekonnenNo ratings yet
- Forecasting Seasonal Time SeriesDocument11 pagesForecasting Seasonal Time SeriesManuel Alejandro Sanabria AmayaNo ratings yet
- The ROI Fieldbook - Strategies For Implementing ROI in HR and Training (PDFDrive) PDFDocument412 pagesThe ROI Fieldbook - Strategies For Implementing ROI in HR and Training (PDFDrive) PDFBe DawsonNo ratings yet
- CH 7. Demend Estimation and ForecastingDocument27 pagesCH 7. Demend Estimation and ForecastingdanarNo ratings yet
- Holt WinterDocument5 pagesHolt Winterjohanna silabanNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0301479723016791 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0301479723016791 MainAmal AouadiNo ratings yet
- CounselLink - Law Department Budgeting and ForecastingDocument12 pagesCounselLink - Law Department Budgeting and ForecastingBuddhika PereraNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Planning Example SolvedDocument16 pagesAggregate Planning Example SolvedAbdullah ShahidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Quantitative AnalysisDocument35 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Quantitative AnalysisAbo FawazNo ratings yet
- Forecast Time Series With R LanguageDocument98 pagesForecast Time Series With R Languageec04017No ratings yet
- Overview BPC 11.00 For Sapbw4hanaDocument56 pagesOverview BPC 11.00 For Sapbw4hanaAriel Linetzky0% (1)
- Practice NumericalsDocument12 pagesPractice NumericalsAvinash SubramanianNo ratings yet
- PM Unit IiiDocument106 pagesPM Unit IiiAnonymous kwi5IqtWJNo ratings yet
- Energies 14 06336 v2Document23 pagesEnergies 14 06336 v2Ashar AwanNo ratings yet
- Insights into forecasting models for PET bottle stock ordersDocument8 pagesInsights into forecasting models for PET bottle stock ordersTwinkle ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Flowcasting The Retail Supply Chain PDFDocument115 pagesFlowcasting The Retail Supply Chain PDFCésar Zapata R100% (2)
- Traffic Growth Rate EstimationDocument6 pagesTraffic Growth Rate Estimationmanu1357No ratings yet
- 5 MPC-Aggregate PlanningDocument16 pages5 MPC-Aggregate Planningpkj009No ratings yet
- Elliott 2007Document30 pagesElliott 2007Eko AdhityoNo ratings yet