0% found this document useful (0 votes)
296 views44 pagesBLS Training for Healthcare Pros
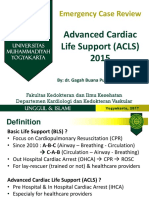
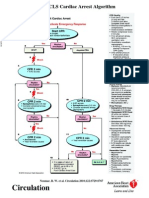
The document provides information about Basic Life Support (BLS) training. It states that BLS training teaches how to recognize life-threatening emergencies, perform high-quality chest compressions, deliver appropriate ventilations, and use an automated external defibrillator (AED). The course is designed for healthcare professionals and others who may need to perform CPR. Key skills taught include performing chest compressions, opening the airway, giving breaths, and using an AED. Sample test questions assess knowledge of proper hand placement for compressions, compression rates and depths, pulse checking locations, ventilation techniques, and AED use.
Uploaded by
mistyguiquingCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
296 views44 pagesBLS Training for Healthcare Pros
The document provides information about Basic Life Support (BLS) training. It states that BLS training teaches how to recognize life-threatening emergencies, perform high-quality chest compressions, deliver appropriate ventilations, and use an automated external defibrillator (AED). The course is designed for healthcare professionals and others who may need to perform CPR. Key skills taught include performing chest compressions, opening the airway, giving breaths, and using an AED. Sample test questions assess knowledge of proper hand placement for compressions, compression rates and depths, pulse checking locations, ventilation techniques, and AED use.
Uploaded by
mistyguiquingCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd