Professional Documents
Culture Documents
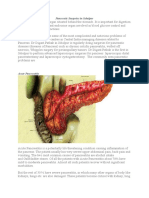
Gastric Tumor
Uploaded by
Shujina Zainab0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views16 pagesThis document discusses gastric tumors and cancer. It provides learning objectives about describing clinical features of stomach cancer, investigating stomach cancer through various methods like barium meals and CT scans, staging stomach cancer, complications of stomach removal surgery, surgical treatment options, and managing stomach cancer. Key points are that stomach cancer causes weight loss, appetite loss, vomiting blood, and abdominal masses. Investigation methods include endoscopy and biopsies. Surgical options include full or partial stomach removal with lymph node dissection or palliative treatments. Management involves surgery with the goal of removal.
Original Description:
Original Title
2. Gastric Tumor
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses gastric tumors and cancer. It provides learning objectives about describing clinical features of stomach cancer, investigating stomach cancer through various methods like barium meals and CT scans, staging stomach cancer, complications of stomach removal surgery, surgical treatment options, and managing stomach cancer. Key points are that stomach cancer causes weight loss, appetite loss, vomiting blood, and abdominal masses. Investigation methods include endoscopy and biopsies. Surgical options include full or partial stomach removal with lymph node dissection or palliative treatments. Management involves surgery with the goal of removal.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views16 pagesGastric Tumor
Uploaded by
Shujina ZainabThis document discusses gastric tumors and cancer. It provides learning objectives about describing clinical features of stomach cancer, investigating stomach cancer through various methods like barium meals and CT scans, staging stomach cancer, complications of stomach removal surgery, surgical treatment options, and managing stomach cancer. Key points are that stomach cancer causes weight loss, appetite loss, vomiting blood, and abdominal masses. Investigation methods include endoscopy and biopsies. Surgical options include full or partial stomach removal with lymph node dissection or palliative treatments. Management involves surgery with the goal of removal.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
GASTRIC TUMOR
Prof. Dr. Mansab Ali
HOD, General Surgery Department
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Describe clinical features of Ca
Stomach.
Enlist the various methods of
investigation in Ca stomach.
Enlist the stages of Ca stomach.
Describe complications of gastrectomy.
Describe different surgical treatment
options for Ca stomach.
Describe management plan of CA
stomach.
Describe clinical features of Ca
stomach.
Weight Loss
Appetite Loss
Haemetesis
Malena
Mass Abdomen
Ascities
Metastatic Disease
Enlist the various methods of
investigation in Ca stomach.
Barium Meal and Follow Through
Endoscopy & Biopsy
CT Scan Abdomen
Endoscopy Ultrasonography
PET Scan
Laparoscopy
USG Abdomen
Enlist the stages of Ca stomach.
Describe complications of
gastrectomy.
Dumping Syndrome
Pernicious Anemia / Nutritional Deficiencies
Dysphagia
Describe different surgical treatment
options for Ca stomach.
Gastrectomy
Total Gastrectomy
Sub Total Gastrectomy
Lymph node dissection
Palliative treatment
Describe management plan of CA
stomach.
Gastrectomy
Total Gastrectomy
Sub Total Gastrectomy
Lymph node dissection
Palliative treatmentS
TAKE HOME MESSAGE
●● Gastric cancer is one of the most common causes of cancer death in the world
●● The outlook is generally poor, owing to the advanced stage of the tumour at
presentation
●● Better results are obtained in Japan, which has a high population incidence,
screening programmes and a high quality surgical treatment
●● The etiology of gastric cancer is multifactorial, but H. pylori is an important
factor for distal but not proximal gastric cancer
●● Early gastric cancer is associated with very high cure rates
●● Gastric cancer can be classified into intestinal and diffuse types, the latter
having a worse prognosis
●● In western resource-rich countries, proximal gastric cancer is now more
common than distal cancer and is usually of the diffuse type
●● Spread may be by lymphatics, blood, transcoelomic or direct, but distant
metastases are uncommon in the absence of lymph node involvement
●● The treatment of curable cases is by radical surgery and removal of the second
tier of nodes (around the principal arterial trunks) may be advantageous
●● Gastric cancer is chemosensitive and chemotherapy improves survival in
patients having surgery for the condition and in advanced disease
Summary box 63.5
Gastric outlet obstruction
●● Gastric outlet obstruction is most commonly associated with
longstanding peptic ulcer disease and gastric cancer
●● The metabolic abnormality of hypochloraemic alkalosis is
usually only seen with peptic ulcer disease and should be
treated with isotonic saline with potassium
●● Endoscopic biopsy is essential to determine whether the
cause of the problem is malignancy
●● Aggressive medical therapy for peptic ulcer disease often
leads to resolution
●● Endoscopic dilatation of the gastric outlet may be effective in
less severe cases of benign stenosis
●● Operation is frequently required, with a drainage procedure
being performed for benign disease and appropriate
resectional surgery if malignant
THANKS
You might also like
- Current and Future Developments in Surgery: Volume 2: Oesophago-gastric SurgeryFrom EverandCurrent and Future Developments in Surgery: Volume 2: Oesophago-gastric SurgeryNo ratings yet
- Upper GI Malignancy - TutorDocument28 pagesUpper GI Malignancy - Tutoramoody95No ratings yet
- Gastric Outlet ObstructionDocument96 pagesGastric Outlet ObstructionAbdulsalam DostNo ratings yet
- Stomach Cancer: de Jesus, Justine V. Malicay, Anne Mari Nicole ADocument34 pagesStomach Cancer: de Jesus, Justine V. Malicay, Anne Mari Nicole AhelloaNo ratings yet
- Gastric Carcinoma: H. Pylori InfectionDocument7 pagesGastric Carcinoma: H. Pylori InfectionMuvenn KannanNo ratings yet
- Colorectal CancerDocument7 pagesColorectal Cancerjames garciaNo ratings yet
- OncologyDocument7 pagesOncologyKit NameKoNo ratings yet
- Diagnose of Stomach CancerDocument24 pagesDiagnose of Stomach CancerSameem MunirNo ratings yet
- Oncology Esophag Stomach PancreasDocument281 pagesOncology Esophag Stomach PancreasManav AryaNo ratings yet
- Gastric Outlet ObstructionDocument59 pagesGastric Outlet Obstructionmaryam tariqNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument29 pagesPeptic Ulcer DiseasesoumayacallenderNo ratings yet
- Pancreatic CancerDocument9 pagesPancreatic CancerSergio Sar1gumbaNo ratings yet
- Diseases of PancreasDocument3 pagesDiseases of PancreasLaparoscopic surgeon jabalpur digant pathakNo ratings yet
- Cancer Research - Jay XieDocument10 pagesCancer Research - Jay XieJay XieNo ratings yet
- GASTRECTOMYDocument3 pagesGASTRECTOMYMaria Ydela MeradoresNo ratings yet
- Gastric Linitis PlasticaDocument22 pagesGastric Linitis PlasticaPhy RdaousNo ratings yet
- EtiologyDocument2 pagesEtiologyJanice EligioNo ratings yet
- Clinical Features, Diagnosis, and Staging of Gastric Cancer - UpToDateDocument31 pagesClinical Features, Diagnosis, and Staging of Gastric Cancer - UpToDateCileni NuñezNo ratings yet
- Gastric Ulcers: Presented By: Dr. Jawaria Memon & Dr. Deep KumarDocument31 pagesGastric Ulcers: Presented By: Dr. Jawaria Memon & Dr. Deep KumarDeep KhemaniNo ratings yet
- Gastric Tumors (Notes)Document23 pagesGastric Tumors (Notes)Priyanka GosaiNo ratings yet
- Gastric CancerDocument7 pagesGastric CancerMicah PingawanNo ratings yet
- CA Stomach OverviewDocument84 pagesCA Stomach OverviewDr Shafiq Ahmad ChughtaiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Features, Diagnosis, and Staging of Gastric Cancer - UpToDateDocument41 pagesClinical Features, Diagnosis, and Staging of Gastric Cancer - UpToDateTatiana CumbicosNo ratings yet
- STOMACCANCEREDITEDDocument12 pagesSTOMACCANCEREDITEDhelloaNo ratings yet
- Gastric CancerDocument27 pagesGastric Cancermackiecc100% (2)
- Gastrointestinal MalignanciesDocument59 pagesGastrointestinal Malignanciesadamu mohammadNo ratings yet
- Periampullary TumorDocument22 pagesPeriampullary Tumorlovelots1234No ratings yet
- Pancreas: DR Sigid Djuniawan, SPBDocument40 pagesPancreas: DR Sigid Djuniawan, SPBditaayupNo ratings yet
- Cancro GastricoDocument6 pagesCancro GastricoDani SNo ratings yet
- Neoplasma of PankreasDocument33 pagesNeoplasma of PankreasGina Sonia RahmahNo ratings yet
- Official Reprint From Uptodate ©2018 Uptodate, Inc. And/Or Its Affiliates. All Rights ReservedDocument39 pagesOfficial Reprint From Uptodate ©2018 Uptodate, Inc. And/Or Its Affiliates. All Rights ReservedFabio CabreraNo ratings yet
- 17-09-2019 Lower GI FINALDocument32 pages17-09-2019 Lower GI FINALNaima HabibNo ratings yet
- PancreatitisDocument51 pagesPancreatitisMizrab NadeemNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia For Pancreatic SurgeryDocument11 pagesAnaesthesia For Pancreatic SurgeryyenuginNo ratings yet
- Capstone Sample - 3-26-2019-2Document15 pagesCapstone Sample - 3-26-2019-2Tiffany McFarlandNo ratings yet
- Esophageal CancerDocument23 pagesEsophageal Cancerabhandlung100% (3)
- Billroth I & IIDocument5 pagesBillroth I & IIRoxieparkerNo ratings yet
- Gastric CarcinomaDocument43 pagesGastric CarcinomaPragadeswaran SNo ratings yet
- 20.MBBS Pancreatic CancerDocument52 pages20.MBBS Pancreatic Cancermrajah95No ratings yet
- Casestudy Gastric CarcinomaDocument56 pagesCasestudy Gastric CarcinomaMJ Amarillo92% (12)
- Notes On Colon and Liver CancerDocument12 pagesNotes On Colon and Liver CancerNynko Nino ElazeguiNo ratings yet
- Cholangiocarcinoma 2 Juni 2018Document40 pagesCholangiocarcinoma 2 Juni 2018Anonymous 1UgsHkUNo ratings yet
- Absite 21 Answers - StomachDocument2 pagesAbsite 21 Answers - Stomachsiriopa08No ratings yet
- Pancreatic CancerDocument4 pagesPancreatic Cancersdf100% (1)
- Dr. Saleh M. Al SalamahDocument27 pagesDr. Saleh M. Al SalamahKudingLimMingYaoNo ratings yet
- Periampullary CarcinomaDocument35 pagesPeriampullary Carcinomaminnalesri100% (2)
- 3 NCM+116n+Lecture+Care+of+the+Clients+with+Problems+GI+Function+and+NutritionDocument4 pages3 NCM+116n+Lecture+Care+of+the+Clients+with+Problems+GI+Function+and+NutritionKylle AlimosaNo ratings yet
- ANAESTHESIA FOR GASTROINTESTINAL CANCER SURGERIES AutosavedDocument40 pagesANAESTHESIA FOR GASTROINTESTINAL CANCER SURGERIES AutosavedKavyasree KatamNo ratings yet
- Casestudy Gastric CarcinomaDocument53 pagesCasestudy Gastric CarcinomaAngelaTrinidadNo ratings yet
- Gall Bladder CarcinomaDocument29 pagesGall Bladder CarcinomaUsman FarooqNo ratings yet
- Internal MedDocument8 pagesInternal MedFind my Profession zambiaNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading SurgeryDocument21 pagesJournal Reading Surgerydr.liraNo ratings yet
- Gastric Cancer by BalaDocument17 pagesGastric Cancer by BalaArundeep AsaithambiNo ratings yet
- Pancreatic Cancer OverviewDocument6 pagesPancreatic Cancer OverviewpoerbaantonNo ratings yet
- Tumours of The Pancreas: Dr. Saleh M. Al SalamahDocument33 pagesTumours of The Pancreas: Dr. Saleh M. Al SalamahAdil ShabbirNo ratings yet
- Cancer of The Colon and RectumDocument37 pagesCancer of The Colon and Rectumapi-19641337100% (1)
- En Stomach Cancer Guide For PatientsDocument51 pagesEn Stomach Cancer Guide For Patientsmanuaf2000No ratings yet
- Whipple Surgical ReportDocument4 pagesWhipple Surgical Reportapi-332047001No ratings yet
- Esophageal CADocument17 pagesEsophageal CASesrine BuendiaNo ratings yet
- Stomach CancerDocument7 pagesStomach CancerSyazmin KhairuddinNo ratings yet
- Trauma Informed Care: Importance of TICDocument10 pagesTrauma Informed Care: Importance of TICJenNo ratings yet
- Types of MedicineDocument5 pagesTypes of MedicineAndrei BădulescuNo ratings yet
- No Scalpel PDFDocument70 pagesNo Scalpel PDFSantosh BabuNo ratings yet
- NCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Document4 pagesNCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Jessamine EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Scenar Testimonials (Updated)Document10 pagesScenar Testimonials (Updated)Tom Askew100% (1)
- AndaDocument26 pagesAndaNagula Naresh100% (1)
- Therapy With ChildrenDocument12 pagesTherapy With Childrenantalmarialuana_67750% (1)
- Equine Tetanus 202CDocument4 pagesEquine Tetanus 202Cvah5018No ratings yet
- Damar SDocument175 pagesDamar SSIVANo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing DrillDocument6 pagesFundamentals of Nursing DrillHassen Zabala100% (1)
- Janet Sayers' Freud's Art - Book ReviewDocument4 pagesJanet Sayers' Freud's Art - Book ReviewNeha ChoksiNo ratings yet
- Letterhead of Referring ESI Hospital (P-I) : Referral Form (Permission Letter)Document8 pagesLetterhead of Referring ESI Hospital (P-I) : Referral Form (Permission Letter)Arpit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Juicing For LifeDocument40 pagesJuicing For Lifeinfo_altenaNo ratings yet
- Infection Control AnswersDocument6 pagesInfection Control Answersrusski1383% (18)
- Codex Stan A-4-1971Document3 pagesCodex Stan A-4-1971Raisha ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Type IIDocument3 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Type IIJirou BalcitaNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Brain Injury and Increased Intracranial Pressure: Continuing EducationDocument9 pagesTraumatic Brain Injury and Increased Intracranial Pressure: Continuing EducationNurbaitiNo ratings yet
- CB5c Cardiovascular Disease: Answer The Questions BelowDocument24 pagesCB5c Cardiovascular Disease: Answer The Questions Belowseema chaturvediNo ratings yet
- PTB Osh LectureDocument24 pagesPTB Osh LectureAnonymous 4BDHvgeiNo ratings yet
- Mental Status ExamDocument24 pagesMental Status ExamKevin Leo Lucero AragonesNo ratings yet
- Dengue FeverDocument1 pageDengue Feverapi-266482250No ratings yet
- Dissociation and Dissociative DisordersDocument20 pagesDissociation and Dissociative DisordersRicky DNo ratings yet
- FinalprogrammeokusethisoneDocument185 pagesFinalprogrammeokusethisoneCuc MariaNo ratings yet
- A Complete Book On Cardiovascular System For Homoeopaths DR R Chattopadhyay.03907 2prefaceDocument6 pagesA Complete Book On Cardiovascular System For Homoeopaths DR R Chattopadhyay.03907 2prefaceBillwadal BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Warm Up and Cool DownDocument4 pagesWarm Up and Cool Downapi-315123529No ratings yet
- Budman SH & Gurman As - Theory and Practice of Brief TherapyDocument417 pagesBudman SH & Gurman As - Theory and Practice of Brief TherapyPaulo César Camacho Cáceres100% (1)
- A Myth About Anastomotic LeakDocument3 pagesA Myth About Anastomotic LeakAvinash RoyNo ratings yet
- ESMO Leukemia & Myeloma 2019Document133 pagesESMO Leukemia & Myeloma 2019Rasoul Ghasemian100% (1)
- Teaching Plan: General Santos Doctors' Medical School Foundation IncDocument12 pagesTeaching Plan: General Santos Doctors' Medical School Foundation Incjay kusainNo ratings yet