Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biome Final
Uploaded by
Megha Shivaraj0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views27 pagesOriginal Title
biome final
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views27 pagesBiome Final
Uploaded by
Megha ShivarajCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 27
Biomes
Biomes
A biome is defined as a large natural ecosystem which
is distinct in its climatic conditions and has its specific
type of plant and animal life.
thus, biomes are the major ecosystems of the world
which are the largest ecological units.
Factors determining characteristic of biome
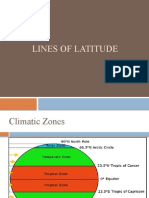
Temperature range
Latitude and altitude
Intensity and duration of summer and winter
Amount and periodicity of rainfall
Soil characteristics
Geographical barriers like mountain or sea
Topography
Water mass
Types of biomes
Terrestrial biome-area of land with similar climatic
condition
Aquatic biome-biome found in water
Terrestrial biome
They are large terrestrial communities which are influenced
by latitude, amount and periodicity of rainfall.
The major terrestrial biomes are:
Tundra
Taiga
Deciduous forest
Tropical rain forest
Chapparal
Tropical savannah
Grassland
desert
Tundra
It lies at 60o N latitude below the polar ice
Tundra occupies 8 million km2 area of land extending
across N America, Europe and Asia.
It occurs only in arctic region and is, therefore, also
called arctic tundra.
Physical characteristics-the area receives very little
precipitation, mostly in the form of snow.
The area is covered by snow for most part of the year.
Winter temperature will be -30o C to -40o C.
Summer is for short duration of 45-75 days.
Highest temperature in summer is 10oC.
Tundra
Soil is permanently frozen(permafrost).
North tundra is often called as arctic desert.
The tress found in tundra will complete their life cycle
in brief summer or can remain alive even when
covered by snow for 8-10 months.
Mosses and lichens show best development in the area.
Other plants growing in tundra are grasses, sedges,
heaths and a few shrubs.
The plants possess xeropyhtic characters.
Taiga
The biome occurs just south of tundra across N America,
Europe and Asia.
It is also found in southern hemisphere and contains
roughly 10% of land mass.
The area contains both rainfall and snowfall.
Lakes and marshes are quite common in the wetter parts.
The average winter temperature does not exceed 6 oC.
Summers are pleasant with long hours of day light and
an average temperature of less than 20 oC.
The growing season is about 150 days.
Taiga
Dominant vegetation consist of evergreen conifers
which are able to tolerate wide fluctuation of
temperature, light and soil.
The area contains pine, fir, hemlock, spruce,
juniper and deodar.
Where conditions are more favourable dense
coniferous forests is present with little light
reaching the ground.
Birch and maple are found at several places.
Temperate deciduous forest
It is found in both northern hemisphere( Canada, Eastern
USA, North Central Europe, Eastern Asia) and Southern
Hemisphere(New Zealand and Eastern Australia).
The areas have warm summer and moderately cold winter.
Annual rainfall lies between 75-150cm.
The dominant climax vegetation consists of broad leaved trees
like oak, elm, maple, birch, beech etc.
The trees and shrubs usually shed their leaves with the onset
of autumn.
New leaves are spread in early spring.
Where conditions are favourable four storeyed forest is
formed.
Tropical Rain Forest
It is mainly found in central America, along amazon
and Orinoco rivers. South America, Congo river basin
of Africa and South East Asia including India.
The biome occurs in equatorial or sub equatorial
regions where both rainfall and warmth and abundant.
Rainfall is above 140cm per year usually between 200-
500cm per year. Therefore, humidity is good.
Plant growth is luxuriant.
The forest is thick and almost impenetrable. Hence,
they are called as jungle.
Tropical Rain Forest
Diversity of life is so high that a hectare of forest may
have as many as 200 species of trees, 70-80% of all
insects and 80-85% of all birds are known from tropical
forests.
The vegetation shows stratification which means
grouping of plants in a forest into 2 or more well
defined layers.
Tropical rain forest is multi storey and mainly contains
broad leaved evergreen plants.
The important plants found here are rosewood,
mahogany, ebony, rubber tree, cinnamon and bamboos.
Chaparral
The biome occurs in Mediterranean area, pacific coast of
North America, Chile, South Africa and South Australia.
It is a broad leaved evergreen shrub forest of hard and thick
leaved small trees and shrubs which usually contain resin but
are resistant to fires.
It receives humid air from nearby oceans which keeps the
temperature moderate.
Rainfall is during winter only.
The plants are adopted to frequent and long period of
drought.
The common plants are sage, carnithus, adenosdema, oak
and eucalyptus
Tropical Savannah
The savannah is found in equatorial and sub tropical
regions of the world especially South America, Central
Africa and Australia.
It is a warm climate plain which contains coarse
grasses with scattered trees and shrubs.
It receives rainfall for about 100-150cm per year.
The organisms of the biome are drought tolerant.
A savannah does not have much species diversity.
Commonly found trees are Acacia and Eucalyptus.
Grassland
A grassland posses different types of grasses, non -
graminaceous herbs and a few scattered bushes or
occasional trees.
Depending upon the types of grasses and non
graminaceous flora, grasslands have been differentiated
into Prairies of Canada and USA, Pampas of South
America, Steppes of Eurasia, Iussocks of New Zealand
and Veldds of South Africa.
Climate is continental with cold winters and hot summers.
Rainfall is 25-75cm.
Dominant plants are short and tall grasses.
Desert
Deserts are found all over the world in areas bordering cold
oceanic currents, lacking cloud intercepting mountains, lying far
from cloud seeding regions or rain shadow.
Major desert occur in Asia(Gobi, Thar etc.), central western
Australia, North Africa(Sahara), South Western USA, Mexico,
coastal areas of Chile and Peru.
Deserts contain low annual rainfall of less than 25cm.
Depending upon temperature, deserts are of two types namely:
cold and hot deserts.
Nights are cold but days are very hot with temperature reaching
60oC.
Hardy grasses, echinops, cacti are common plants grow in desert.
You might also like
- 6 Major Biomes of The WorldDocument8 pages6 Major Biomes of The WorldSyed Hassan Raza JafryNo ratings yet
- Tundra Ecosystems PaperDocument20 pagesTundra Ecosystems PaperDragana SekulicNo ratings yet
- National Geographic UK - September 2019-CompressedDocument133 pagesNational Geographic UK - September 2019-CompressedEmily Tan67% (3)
- BiomesDocument117 pagesBiomesgeissingert93% (14)
- Biome Coloring Pages ADocument7 pagesBiome Coloring Pages ALennyn Andres Montecinos Ferrada100% (3)
- The Complete U.S. Army Survival Guide to Tropical, Desert, Cold Weather, Mountain Terrain, Sea, and NBC EnvironmentsFrom EverandThe Complete U.S. Army Survival Guide to Tropical, Desert, Cold Weather, Mountain Terrain, Sea, and NBC EnvironmentsNo ratings yet
- Major Biomes of The WorldDocument4 pagesMajor Biomes of The WorldNaga Chary100% (1)
- Zoology BiomesDocument11 pagesZoology BiomesDennie Zody LoganNo ratings yet
- Biomes InformationDocument15 pagesBiomes Informationapi-26319781050% (2)
- t3 G 93 World Biomes and Climate Zones Powerpoint - Ver - 6Document16 pagest3 G 93 World Biomes and Climate Zones Powerpoint - Ver - 6Calm SeekNo ratings yet
- World BiomesDocument11 pagesWorld Biomesapi-198070814No ratings yet
- Major Biomes: Tundra, Forests, Grasslands & DesertsDocument22 pagesMajor Biomes: Tundra, Forests, Grasslands & DesertsMujeebMemonNo ratings yet
- Major Biomes of The World: Coniferous ForestDocument36 pagesMajor Biomes of The World: Coniferous ForestShourya JainNo ratings yet
- Types of Forest Ecosystems: Tropical Rainforest, Temperate, Boreal & MoreDocument13 pagesTypes of Forest Ecosystems: Tropical Rainforest, Temperate, Boreal & MoreKarthick Ramamoorthy100% (1)
- World VegetationDocument11 pagesWorld VegetationAixha MallickNo ratings yet
- Tropical Thorn and Scrubs ForestDocument6 pagesTropical Thorn and Scrubs ForestAnkit Ram100% (2)
- Answer KeyDocument10 pagesAnswer Keyapi-283605071No ratings yet
- BIOMESDocument20 pagesBIOMESrysii gamesNo ratings yet
- TERRRESTIAL-ECOSSYTEMDocument32 pagesTERRRESTIAL-ECOSSYTEMAldrin CantigaNo ratings yet
- Terrestrial Biomes and EcosystemDocument2 pagesTerrestrial Biomes and EcosystemJohn CortezNo ratings yet
- Reyes Rhaisesun R. BS-HRM Grassland: LOCATION: The Name For This BiomeDocument6 pagesReyes Rhaisesun R. BS-HRM Grassland: LOCATION: The Name For This BiomeRhaisesunRamiloReyesNo ratings yet
- Latitude and Climatic ZonesDocument26 pagesLatitude and Climatic ZonesTheresa BrownNo ratings yet
- Temperate & Taiga-EditedDocument40 pagesTemperate & Taiga-EditedLADY MARIELLE GAYOSANo ratings yet
- Tropical Rainforests and Other Forest TypesDocument10 pagesTropical Rainforests and Other Forest TypesasdfghjkNo ratings yet
- Biome CharacteristicsDocument2 pagesBiome CharacteristicsTolu 'Fridgey' KuforijiNo ratings yet
- Wednesday Vocab KeyDocument5 pagesWednesday Vocab KeyRachaelNo ratings yet
- Forest Types (FHU3219) : Razak TerhemDocument21 pagesForest Types (FHU3219) : Razak TerhemPrasna NairNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 7 & 8Document67 pagesLecture Notes 7 & 8Marvin JeaNo ratings yet
- Biomes Are Large Community Unit Where The Plant Species Are More or Less Uniform Which Provides A Basis For EcologicalDocument2 pagesBiomes Are Large Community Unit Where The Plant Species Are More or Less Uniform Which Provides A Basis For EcologicalMelissa Marie CustodioNo ratings yet
- Tropical Rainforests: Hot, Wet, and Home To MillionsDocument9 pagesTropical Rainforests: Hot, Wet, and Home To MillionsHuni RaphaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Forest?: 1. Tropical ForestsDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Forest?: 1. Tropical ForestsAgilandeshwari RamalinggamNo ratings yet
- LESSON 8Document9 pagesLESSON 8Dianna Rose Villar LaxamanaNo ratings yet
- Panel SolarDocument13 pagesPanel SolarRosa Andrea CumezNo ratings yet
- Biotic RegionsDocument43 pagesBiotic RegionsSachin ShrivastavNo ratings yet
- With Relevant Examples, Discuss Different BiomesDocument2 pagesWith Relevant Examples, Discuss Different BiomesKipkirui BonifaceNo ratings yet
- DocsumoDocument1 pageDocsumoKrish ThakkerNo ratings yet
- Presentation2 2Document25 pagesPresentation2 2api-340417349No ratings yet
- Group 6 Environmental ScienceDocument29 pagesGroup 6 Environmental SciencejessiejohnfelixNo ratings yet
- EnamDocument8 pagesEnamzahid HassanNo ratings yet
- Biomes of Our EarthDocument5 pagesBiomes of Our EarthMayaNo ratings yet
- BiomesDocument14 pagesBiomesJerico MarcosNo ratings yet
- Delicious Deciduous ForestsDocument12 pagesDelicious Deciduous ForestsdcsquaredNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 BiomesDocument14 pagesLesson 1 BiomesJim Roger Malabo LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Biomes ProjectDocument11 pagesBiomes Projectapi-306090320No ratings yet
- Lorca, Princess Anne H. Environmental Science ACT. 4Document6 pagesLorca, Princess Anne H. Environmental Science ACT. 4Princess LorcaNo ratings yet
- Geography AssignmentDocument4 pagesGeography AssignmentMehak Liaqat AliNo ratings yet
- Major Biomes: Patterns of Global Life ZonesDocument22 pagesMajor Biomes: Patterns of Global Life ZonesFelipe Cury MarquesNo ratings yet
- Natural Vegetation- 3102Document13 pagesNatural Vegetation- 3102Khandoker mariatul IslamNo ratings yet
- Meaning of Biomes: ClimateDocument10 pagesMeaning of Biomes: ClimateAtika ParvazNo ratings yet
- What Is Biomes? BiomesDocument2 pagesWhat Is Biomes? BiomesAngelica Mae CornejoNo ratings yet
- Natural Region - WorksheetDocument3 pagesNatural Region - WorksheeteswarmbbeNo ratings yet
- Tundra Is The Coldest of All The BiomesDocument24 pagesTundra Is The Coldest of All The BiomesAira GarciaNo ratings yet
- Hot Wet Equatorial ClimateDocument63 pagesHot Wet Equatorial ClimateRitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Hot Wet Equatorial ClimateDocument3 pagesHot Wet Equatorial ClimateharryNo ratings yet
- ENGG 413 Environmental Science and Engineering Major Ecosystem of The WorldDocument20 pagesENGG 413 Environmental Science and Engineering Major Ecosystem of The WorldFatima Therese ManaloNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Biomes and Biodiversity (AutoRecovered)Document12 pagesTopic 2 - Biomes and Biodiversity (AutoRecovered)Jomari TawatNo ratings yet
- Types of ForestsDocument4 pagesTypes of Forestsmaria arockiamNo ratings yet
- Forest: Coniferous ForestsDocument3 pagesForest: Coniferous ForestsRutuja BhalekarNo ratings yet
- Rainforest & DeciduousDocument6 pagesRainforest & DeciduousLADY MARIELLE GAYOSANo ratings yet
- Terrestrial EcosystemDocument27 pagesTerrestrial EcosystemCamille FaustinoNo ratings yet
- 7 Major Biomes of EarthDocument2 pages7 Major Biomes of EarthMark Adrian ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Explore the Cold Tundra BiomeDocument33 pagesExplore the Cold Tundra BiomeBenedict Stephen Tabisaura BattungNo ratings yet
- habitats more noteDocument3 pageshabitats more notesorealfarmsNo ratings yet
- The Tree-Mendous Rainforest! All about the Rainforests | Children's Nature BooksFrom EverandThe Tree-Mendous Rainforest! All about the Rainforests | Children's Nature BooksNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science - EcosystemDocument31 pagesEnvironmental Science - EcosystemtashNo ratings yet
- Neral Issues On Environment and EcologyDocument43 pagesNeral Issues On Environment and EcologyArchakam RakshithaNo ratings yet
- 06 Nov 2015 - RS GIS Applications in Forestry and Ecology - Dr. Arjit RoyDocument38 pages06 Nov 2015 - RS GIS Applications in Forestry and Ecology - Dr. Arjit RoyrphmiNo ratings yet
- 23 Terrestrial EcosystemDocument5 pages23 Terrestrial EcosystemBrian PaguiaNo ratings yet
- Ib Ess Summer Pack 2023: This Paper Is Your Summer HomeworkDocument39 pagesIb Ess Summer Pack 2023: This Paper Is Your Summer Homeworkhalit özbelliNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Consensus Among ScientistsDocument121 pagesGlobal Warming Consensus Among ScientistsAtraSicariusNo ratings yet
- Apes-Introduction To The Worlds Biomes RepairedDocument7 pagesApes-Introduction To The Worlds Biomes Repairedapi-235658421No ratings yet
- Practice Test 19 I. MULTIPLE CHOICE (8.0 Points)Document4 pagesPractice Test 19 I. MULTIPLE CHOICE (8.0 Points)Ngan Anh NgNo ratings yet
- Zooniverse Book 2022Document28 pagesZooniverse Book 2022Dr Pankaj DhussaNo ratings yet
- NK HCM 13-14Document10 pagesNK HCM 13-14Hồng Hoa Trần ThịNo ratings yet
- North America GeographyDocument31 pagesNorth America GeographyWaRda AzizNo ratings yet
- An Arctic Tale Guided Viewing WorksheetDocument4 pagesAn Arctic Tale Guided Viewing WorksheetPia Regine Calope BellezaNo ratings yet
- NAtural Vegetation and Wildlife NotesDocument18 pagesNAtural Vegetation and Wildlife NotesnikhatskhanNo ratings yet
- Answer KeyDocument10 pagesAnswer Keyapi-283605071No ratings yet
- Polar ecology and contaminant pathways in the ArcticDocument16 pagesPolar ecology and contaminant pathways in the ArcticRaajeswaran BaskaranNo ratings yet
- The Alaska Pipeline Starts at The Frozen Edge of The Arctic OceanDocument3 pagesThe Alaska Pipeline Starts at The Frozen Edge of The Arctic OceanCrystal BeataNo ratings yet
- World Biomes WebQuest: Explore Terrestrial Biome EnvironmentsDocument5 pagesWorld Biomes WebQuest: Explore Terrestrial Biome EnvironmentsCristhian Silva CastellonNo ratings yet
- Canada BiomesDocument3 pagesCanada BiomesJessi NavarroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Climate Change and MicrobesDocument9 pagesChapter 7 - Climate Change and MicrobesUTTAMNo ratings yet
- Earth's Major BiomesDocument2 pagesEarth's Major BiomesSAAM_BLDNo ratings yet
- Natural Vegetation Final VersionDocument87 pagesNatural Vegetation Final VersionAqsa SyrNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. Introduction To Asian Studies AbstractionDocument13 pagesUnit 1. Introduction To Asian Studies AbstractionEuthel Jhon FinlacNo ratings yet
- Ensc 0100 NotesDocument66 pagesEnsc 0100 NotesGrace MwangiNo ratings yet
- Components of EcosytemDocument20 pagesComponents of EcosytemRosselle May JumayaoNo ratings yet
- BiomesDocument5 pagesBiomesMaya TareqNo ratings yet