Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Final 3d 4d
Uploaded by
iomarmostafa27Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Final 3d 4d
Uploaded by
iomarmostafa27Copyright:
Available Formats
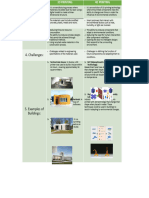
3D PRINTING 4D PRINTING
It is a manufacturing process where materials are added layer by • It is an evolution of 3D printing technology where the pri
layer using a digital model to create a three-dimensional components have the ability to change over time or unde
structure. influence of environmental conditions.
The materials used include modified concrete, plastic, metals and • Smart polymers that interact with environmental factors
resins. heat, humidity, or light are involved.
Reducing time and resource consumption. The ability to produce components that adapt to environ
The ability to produce complex designs that cannot be achieved conditions.
through traditional methods. Reducing the need for human intervention after compon
Using recycled waste materials in the construction process. installation.
Opening the door to intelligent designs that respond to t
surrounding environment.
Challenges related to engineering specifications of the materials • Challenges in defining the function of future components
used. adapting them to conditions.
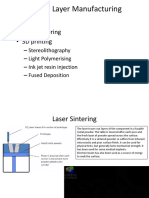
Extrusion method: 1-stereolithography
Through the extruder of the printing machine, small pellets of Allows you to create solid, plastic, three-dimensional (3-D)
material that harden immediately to form layers are extruded and from CAD drawings in a matter of hours. Whether you are
he extruder is connected to threads of thermoplastic or metal mechanical engineer wanting to verify the fit of a part or a
wire, which are used to heat the printing material before the looking to create a plastic prototype of an invention,
extrusion process. stereolithography gives you a fast, easy way to turn CAD dr
into real objects.
Association powder method:
Execution method: - Each layer is built with the prose of the raw
powder.
Those layers use material bound to the ores to bind the granules 2- Fused Filament Fabrication
o the model is formed Filament should be dried adequately before, and kept drie
The piston presses the base layer to stabilize it and then rises to the printing process. As filament is fed through the extrud
ompress the next layer that has been scattered and then binds its heating zones, the material begins to liquify and is driven t
granules using a bond material nozzle where it is deposited along the digitally defined too
Each layer's construction is repeated until the required mass
ormation is completed.
3- Selective laser melting
The cross-section area of the designed 3D part is built by s
You might also like
- 3D Printing Lab Manual: WorkingDocument7 pages3D Printing Lab Manual: WorkingJithin67% (3)
- Cura User-Manual v1.0Document41 pagesCura User-Manual v1.0kaosad75% (4)
- Final 3d 4dDocument1 pageFinal 3d 4diomarmostafa27No ratings yet
- Final 3d 4dDocument1 pageFinal 3d 4diomarmostafa27No ratings yet
- Matecconf Orsdce2018 01013 PDFDocument9 pagesMatecconf Orsdce2018 01013 PDFanon_682200357No ratings yet
- Additive Layer ManufacturingDocument21 pagesAdditive Layer ManufacturingHo JustinNo ratings yet
- 3D Printing Practice LabDocument36 pages3D Printing Practice LabvidyaNo ratings yet
- Additive ManufacturingDocument15 pagesAdditive ManufacturingCaleb QuaynorNo ratings yet
- (2022, Review, Saran) 3D Printing of Composite Materials - A Short ReviewDocument5 pages(2022, Review, Saran) 3D Printing of Composite Materials - A Short ReviewNam Huu TranNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2666412721000441 MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S2666412721000441 MainBM20623 Wan Mohamad Danial Bin Wan SyariffudinNo ratings yet
- Anjuman College of Engineering & TechnologyDocument12 pagesAnjuman College of Engineering & TechnologyZaky MuzaffarNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Study On 3D Printing Technology Investigation of Heat Storage Performance of A Solar Pond With P..Document8 pagesA Comprehensive Study On 3D Printing Technology Investigation of Heat Storage Performance of A Solar Pond With P..Garapati MurarjiNo ratings yet
- Specialised Print Applications Part 3Document57 pagesSpecialised Print Applications Part 3Sreejith KNo ratings yet
- Shallan2014 - Cost-Effective Three-Dimensional Printing of Visibly Transparent Microchips Within MinutesDocument7 pagesShallan2014 - Cost-Effective Three-Dimensional Printing of Visibly Transparent Microchips Within MinutesDinoNo ratings yet
- On 3 D Printing and DronesDocument72 pagesOn 3 D Printing and DronesDurgesh TripathiNo ratings yet
- 3d Printing BADRDocument16 pages3d Printing BADRbadrNo ratings yet
- Additive ManufacturingDocument31 pagesAdditive ManufacturingDaeNo ratings yet
- 65 Course Project ReportDocument8 pages65 Course Project ReportAditya SonkusareNo ratings yet
- Additive Manufacturing of Metallic Based On Extrusion Process - A ReviewDocument10 pagesAdditive Manufacturing of Metallic Based On Extrusion Process - A ReviewVidyanti AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- 3dprintingpracticelab 230710091102 b46f4fddDocument36 pages3dprintingpracticelab 230710091102 b46f4fddchantiNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Study On 3D Printing Technology: August 2016Document7 pagesA Comprehensive Study On 3D Printing Technology: August 2016Tran LucNo ratings yet
- 3D PrintingDocument29 pages3D PrintingAbdul QualeqNo ratings yet
- AMP Experiment No. 1 Case StudyDocument5 pagesAMP Experiment No. 1 Case StudyDeep SasaniNo ratings yet
- Proceedings of The 3rd Biennial Research Through Design ConferenceDocument16 pagesProceedings of The 3rd Biennial Research Through Design ConferenceLuizaNo ratings yet
- State of The Artof3DprintingtechnologyofcementitiousDocument22 pagesState of The Artof3DprintingtechnologyofcementitiousSofia DelacroixNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of XYZ Scanner For 3D PrintingDocument5 pagesDesign and Development of XYZ Scanner For 3D PrintingMAHESH VNo ratings yet
- Material PropertiesDocument7 pagesMaterial Propertiesdummy staticNo ratings yet
- 3D Printing Technology: R.H.M.K.R.S. RajakarunaDocument3 pages3D Printing Technology: R.H.M.K.R.S. RajakarunaVishalyaNo ratings yet
- 3D PrintingDocument27 pages3D Printingnaveen_kumar29173017No ratings yet
- AComprehensive Studyon 3 DPrinting TechnologyDocument7 pagesAComprehensive Studyon 3 DPrinting TechnologyKaushal PanchalNo ratings yet
- 3D Printer InformationDocument16 pages3D Printer Informationmahesh mulikNo ratings yet
- Impact and Application of 3D Printing Technology: Key Words: AM, FDM, PLA, ABS, and CADDocument6 pagesImpact and Application of 3D Printing Technology: Key Words: AM, FDM, PLA, ABS, and CADpradeep rocksNo ratings yet
- MMBC 8Document4 pagesMMBC 8C G Chaithanya 1JA20AT010No ratings yet
- Ijser: Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) MechanismDocument3 pagesIjser: Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) MechanismSamir BoseNo ratings yet
- 3D Printing and NanotechnologyDocument18 pages3D Printing and NanotechnologyJoyitaNo ratings yet
- 4D Rods 3D Structures Via Programmable 1D Composite R 2018 Materials DesiDocument10 pages4D Rods 3D Structures Via Programmable 1D Composite R 2018 Materials DesiJorge Luis Garcia ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- Nano Electromechanical Systems 3d Metal PrintingDocument11 pagesNano Electromechanical Systems 3d Metal PrintingEman Lampago AntoNo ratings yet
- Prasanna 160416051023 PDFDocument43 pagesPrasanna 160416051023 PDFArchan rajNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Study On 3D Printing Technology: August 2016Document7 pagesA Comprehensive Study On 3D Printing Technology: August 2016SE ProductionNo ratings yet
- 3D Printing For Math Professors and Their StudentsDocument18 pages3D Printing For Math Professors and Their StudentsHabtamu GeremewNo ratings yet
- InternshipDocument16 pagesInternshipĀbd DùttNo ratings yet
- Report 8Document7 pagesReport 8Saniya AhmadNo ratings yet
- 3D Printer PDFDocument5 pages3D Printer PDFfaizNo ratings yet
- Metal 3d Printing Services in MumbaiDocument15 pagesMetal 3d Printing Services in MumbaiInnovae3dNo ratings yet
- RandomsDocument2 pagesRandomsiomarmostafa27No ratings yet
- Additive Manufacturing: Processes and Standard TerminologyDocument6 pagesAdditive Manufacturing: Processes and Standard TerminologyABDELHAKIMNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study On The Thermal Performance of 3Document22 pagesExperimental Study On The Thermal Performance of 3Sofia DelacroixNo ratings yet
- VOLCOA Predictive Model For 3D Printed MicroarchitectureDocument14 pagesVOLCOA Predictive Model For 3D Printed MicroarchitectureRaimon Mir Al BesNo ratings yet
- Soa ReportDocument21 pagesSoa Reportashutosh.2022cc09No ratings yet
- 3d Printable Concrete Mixture Design Simulation Test Methods IJERTCONV11IS02048Document13 pages3d Printable Concrete Mixture Design Simulation Test Methods IJERTCONV11IS02048Rachit vermaNo ratings yet
- SM 08 - Nature Flower PolymerDocument11 pagesSM 08 - Nature Flower Polymerrodrigoqcarv2No ratings yet
- 3D Printing The Dawn of A New Era in ManufacturingDocument4 pages3D Printing The Dawn of A New Era in ManufacturingEditor IJRITCCNo ratings yet
- Applications and Prospects of 3D Printing in The Packaging IndustryDocument7 pagesApplications and Prospects of 3D Printing in The Packaging IndustryIJAERS JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Improved Productivity and Efficient Manufacturing Using Injection Molding and 3D Printing A ReviewDocument12 pagesImproved Productivity and Efficient Manufacturing Using Injection Molding and 3D Printing A ReviewIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Additive Manufacturing: Dr. B.Sudarshan Associate Professor. Cri, KsrmceDocument9 pagesAdditive Manufacturing: Dr. B.Sudarshan Associate Professor. Cri, KsrmceDrBollapu SudarshanNo ratings yet
- Best Engineering JournalsDocument10 pagesBest Engineering JournalsSaritaNo ratings yet
- 3D Printed Fabric: Techniques For Design and 3D Weaving Programmable TextilesDocument9 pages3D Printed Fabric: Techniques For Design and 3D Weaving Programmable Textilesswati15sharmaNo ratings yet
- Understand The BasicsDocument2 pagesUnderstand The BasicswiwpiNo ratings yet
- 6 Nagendra Narayan and NeerajaDocument14 pages6 Nagendra Narayan and NeerajaNeeraja Desai SinghNo ratings yet
- Design and Test Strategies for 2D/3D Integration for NoC-based Multicore ArchitecturesFrom EverandDesign and Test Strategies for 2D/3D Integration for NoC-based Multicore ArchitecturesNo ratings yet
- Impact of Additive Manufacturing On Supply Chain Network of Automotive IndustryDocument31 pagesImpact of Additive Manufacturing On Supply Chain Network of Automotive IndustryRUPAVATH SRIKANTHNo ratings yet
- Manhattan Style Electronics Prototyping - An OverviewDocument10 pagesManhattan Style Electronics Prototyping - An Overviewshu2uNo ratings yet
- Why Lighter Parts Matter: EbookDocument19 pagesWhy Lighter Parts Matter: EbookThebe HanyaneNo ratings yet
- Main Street November 2013Document40 pagesMain Street November 2013Anne SecorNo ratings yet
- Patching Catmull-Clark MeshesDocument72 pagesPatching Catmull-Clark MeshesAndrey BeskrovnykhNo ratings yet
- 3D Printing Presentation by Jonayed AhmedDocument15 pages3D Printing Presentation by Jonayed AhmedJonayed Ahmed 96No ratings yet
- Patient Specific Implants (Psi) in Maxillofacial Rehabilitation - A Systematic ReviewDocument10 pagesPatient Specific Implants (Psi) in Maxillofacial Rehabilitation - A Systematic ReviewIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- ZPrinter 450 Color 3D PrinterDocument21 pagesZPrinter 450 Color 3D PrintertarunavasyaniNo ratings yet
- Fabrication and Functionality Integration Technologies For Small Scale Soft RobotsDocument32 pagesFabrication and Functionality Integration Technologies For Small Scale Soft RobotsZhuoheng WeiNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On 3d PrintingDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On 3d Printingefeq3hd0100% (2)
- Creo 6.0 oDocument33 pagesCreo 6.0 oAscentNo ratings yet
- New Resume RJ PDFDocument13 pagesNew Resume RJ PDFRoel P. Dolaypan Jr.No ratings yet
- Construction 4.0Document43 pagesConstruction 4.0Hamda GhaffarNo ratings yet
- Robotic Sketching A Study On Robotic Clay 3D PrintDocument9 pagesRobotic Sketching A Study On Robotic Clay 3D PrintHazem SamehNo ratings yet
- Soal - 3D - Game - Art - LKS - JATENG - 2022Document8 pagesSoal - 3D - Game - Art - LKS - JATENG - 2022Ika LutfianaNo ratings yet
- 5 Parameters That Decide The Success of YourDocument4 pages5 Parameters That Decide The Success of Yourjayanth.raoNo ratings yet
- 3D Print Design Guide ENDocument5 pages3D Print Design Guide ENmichelepazzaglia80No ratings yet
- TOYDIY 4in1 User Guide200706Document78 pagesTOYDIY 4in1 User Guide200706everestoNo ratings yet
- CTC Diy I3 Printer Installation and Operation InstructionsDocument46 pagesCTC Diy I3 Printer Installation and Operation InstructionsAndy AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Aspects of 3D Printed Drugs: Journal of Medical Engineering & TechnologyDocument10 pagesAspects of 3D Printed Drugs: Journal of Medical Engineering & TechnologyRanjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Upload 1 Document To Download Upload Your Original Presentations, Research Papers, Class Notes, or Other Documents To Download Embassy Perimeter Improvement Concepts & Design GuidelinesDocument5 pagesUpload 1 Document To Download Upload Your Original Presentations, Research Papers, Class Notes, or Other Documents To Download Embassy Perimeter Improvement Concepts & Design GuidelinesvictorNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Aircraft DesignDocument14 pagesSustainable Aircraft DesignХардип ЗинтаNo ratings yet
- Imp - Robert Shepherd - Faculty Profile - School of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering - Cornell EngineeringDocument3 pagesImp - Robert Shepherd - Faculty Profile - School of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering - Cornell EngineeringSkmackNo ratings yet
- CW November 2017 PDF For Download PDFDocument88 pagesCW November 2017 PDF For Download PDFАлексей СюкринNo ratings yet
- AMFG Additive Manufacturing MES Software The Essential Guide 3Document20 pagesAMFG Additive Manufacturing MES Software The Essential Guide 3legoon1No ratings yet
- DUP - 706 3D Opportunity Aerospace Defense - MASTER2 PDFDocument28 pagesDUP - 706 3D Opportunity Aerospace Defense - MASTER2 PDFyigitilgazNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Mitigation of Residual Stress in Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing: A Review of Macro Scale Continuum Modelling ApproachDocument25 pagesMeasurement and Mitigation of Residual Stress in Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing: A Review of Macro Scale Continuum Modelling ApproachBhawesh SthaNo ratings yet
- The Future For WAAM-WEBDocument5 pagesThe Future For WAAM-WEBCharlie AltaNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Lattice Structures For Additive Manufacturing TechnologiesDocument10 pagesOptimization of Lattice Structures For Additive Manufacturing TechnologiesJavier Andres Munoz ChavesNo ratings yet