Professional Documents
Culture Documents
6-4-07 - A Brief History of Views of Earth's Place in Space
6-4-07 - A Brief History of Views of Earth's Place in Space
Uploaded by
Jovanie Ludioman0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views28 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views28 pages6-4-07 - A Brief History of Views of Earth's Place in Space
6-4-07 - A Brief History of Views of Earth's Place in Space
Uploaded by
Jovanie LudiomanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 28
Astronomy at Grade 6
The “Big Ideas”
Grade 6 Astronomy – Big Ideas
• Develop an understanding of the position of
Earth in Space with respect to its astronomical
“neighbours”
• Investigate space research programs involving
the human presence in space
• Investigate the astronomical causes (motions)
related to day/night, the seasons, moon phases,
and eclipse events
Grade 6 Astronomy – Big Ideas
• Investigate and describe points of reference
in the night sky (e.g., constellation patterns),
and account for the seasonal changes
observed
• Examine changing conceptions, historically,
about Sun, Earth, Moon and Stars (NoS)
• Provide descriptions of certain historical and
cultural views on the cosmos (e.g. cultural
astronomy, astrology) (NoS)
A Brief History of Ideas About
the Universe
The Greek Mind….
• Much of the Greek method of thinking revolved
around philosophy instead of scientific
reasoning
• Greeks valued perfection and therefore any
models of the universe should involve the
perfect shape, the circle
Ptolemy ~140 AD
• Greeks also had no reason to believe that the
Earth was not the center of the universe.
Completely reasonable at the time – and still
reasonable today!
• The only 'scientific' data they had available to
them was the motion of the Sun, Moon, and
planets, which were monitored heavily at the
time
An Earth Centred Cosmos
The Motion of the Planets
…A Problem Emerges
• A model of the universe
would be very simple except
for the fact that the planets Retrograde Motion
undergo a “looping” motion in
their movements as seen
from Earth
• Remember, in one night, all
planets still rise in the east
and set in the west
• However, if you keep track of
the planet's position versus
the background stars night to
night, you will see the planet
'move'
Jupiter and Saturn (June 2000 – May 2001)
• The word 'planetos' means
wanderer in Greek
Ptolemaic Model
• In order to produce the
retrograde motion of the planets,
Ptolemy created a model with
little circles called epicycles
• All the planets orbited the Earth
in a perfect circle
• The planet itself made a smaller
orbit centered upon the larger
orbit around the Earth
• With the right timing, this model
can reproduce the retrograde
motion seen from Earth
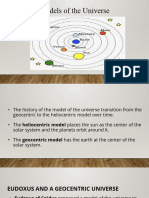
The “Geocentric” Model
Geocentric model
and the
“backwards”
motion of Mars
Ptolemaic Model
• In Ptolemy's complete model,
each planet had its own orbit
around the Earth with its own
epicycle
– By changing the period of the
orbit and the epicycle, the model
could match observations
relatively well
• The Sun and the Moon
traveled around the Earth in
perfect circles
• The entire model was
‘Simplified’ Ptolemaic Model
composed of more than 80
circles and was very
complicated
Ptolemy’s Model Survives
• Since Ptolemy’s model matched
observations sufficiently and no contrary
evidence was produced, it was supported
for nearly 1,500 years!
• After all, if the Earth was moving, shouldn't
we feel it?
• On top of all this, the Dark Ages provided
relatively little advance in any natural
philosophies (sciences) for Europe
Astronomy in the ‘Dark Ages’
• While Europe was
enduring the “Dark Ages”,
Islamic nations were
experiencing a kind of
‘golden age’ of astronomy
• Much of the knowledge of
the Greeks was preserved
and expanded upon during
this time
• Many of the proper names
for stars are relics of this
era
– Rigel, Betelgeuse, Vega ...
and Zuben Al-genubi
“Flat Earth” Models ?
There was never a time in history when the concept
of a flat (disc-shaped) Earth was widely held, either
by priests, prophets, poets, philosophers, scientists,
or the common people…..it would be a myth to
assume this…..and we cannot perpetuate this myth
with our students. The idea has come almost
exclusively from literature.
So, what was known back then by the
Greek and Arab Cultures….and then
lost?
• The earth is round
• Circumference/diameter of the earth; distance to
the moon
• The solar system is heliocentric (“sun-centred”)
• An estimate of the distance to the sun (while
wrong, the Sun was much further away than
commonly thought)
• Length of the year to a high degree of accuracy
Nikolai Kopernik (1473-1543)
• “Who in this most
beautiful of temples
would put His lamp at
a better place than
from where it can
illuminate them all?.
Thus the Sun sitting
as on a Royal throne,
leads the surrounding
family of stars!”
The Copernican Revolution
• At the end of the Dark Ages, a
Polish Catholic priest named
Nikolai Kopernik (Copernicus)
came up with a new model of the
universe where the Earth was no
longer at the center
• The heliocentric (Sun centered)
model placed the Earth out of its
central position, yet still maintained
many of the observations we see
• The perceived elegance in his
model was that it was simpler than
Ptolemy’s model, and explained all
the stuff going on very well Nikolai Kopernik (Copernicus) (1473-1543)
Position of Mars over Months….
Motion of Mars as
explained by the
HELIOCENTRIC
model….
The Copernican Model – Retrograde Motion
In the Copernican model, retrograde motion is an
apparent effect caused by the Earth 'overtaking' an
outer planet in its orbit
The Copernican Revolution
• Even though the Copernican model was a ‘simpler’
representation of the solar system, it was not widely
accepted due to the incredible hold Ptolemy had on the
minds of 16th century astronomers
• While it did provide a much simpler description compared to
Ptolemy, it did not necessarily improve the predictive power
of the model
• The religious ideas of the time insisted upon Earth being the
center of the universe (why would God demote us away
from the centre of creation?)
• Copernicus’ works were published in Latin, which was
unreadable by the common public who had no theological
training
Galileo - The Observer
• A century after Copernicus’ work,
other “natural philosophers” began
to make strides toward making the
heliocentric model popular among
ordinary people
• Galileo was the first to use a
telescope to make detailed
observations of the sky – he was as
famous in Italy then as David Suzuki
is now in Canada
• Though he did not invent the
telescope, he made many working
prototypes and trained them on a
variety of celestial bodies Galileo Galilei (1564-1642)
Galileo's Observations - I
• Galileo used his telescopes to make
observations of many heavenly
objects
• The sketch to the right shows
Galileo's observations of the four
largest moons of Jupiter
• He noticed that the position of these
four moons changed night to night, as
if they were revolving around Jupiter
• These moons now bear his name
– The “Galilean” moons of Jupiter are:
• Io
• Europa
• Ganymede
• Callisto
Galileo's Observations - II
• Galileo also noticed that
Venus was not simply a
point of light, but actually a
disk – this was NEW!!
• He watched Venus go
through complete phases,
just like the Moon
• This cycle of phases can
only be satisfied by the
heliocentric model, not the
geocentric one – a critical
The phases of Venus
TEST!
Galileo's Observations - III
• Galileo also pointed his
telescope toward the Sun
– NEVER DO THIS – DUMB!!
• He discovered that the disk of
the Sun was not perfect and
was occasionally dotted with
small black spots
• By making daily sketches of
these spots, he was able to
determine that the Sun itself
was rotating – WOW!
Galileo's Influences….
• All of Galileo's observations were pointing towards a
HELIOCENTRIC view of the universe
• Galileo published his observations and conclusions in multiple works,
including some published in Italian to appeal to a wider audience
• Galileo’s popularization of new ideas about the cosmos threatened
the status quo, and he was forced to stop publicly teaching in favour
of the heliocentric model, and sentenced to house arrest for the rest
of his life; he communicated with his daughter regularly through
letters (she had been given over to cloistered monastic life at age 13)
• The seeds of the Copernican Revolution, however, had been planted
and by the mid-17th century, virtually all philosophers and
astronomers were committed to the Copernican model
You might also like
- Cummins: Fault Code: 122 PID: P102 SPN: 102 FMI: 3Document6 pagesCummins: Fault Code: 122 PID: P102 SPN: 102 FMI: 3Enrrique Lara100% (1)
- EEE229 EEE223 GEE202 Tutorial RevisionDocument2 pagesEEE229 EEE223 GEE202 Tutorial Revisionlordeinst100% (1)
- The Models of The UniverseDocument25 pagesThe Models of The UniversePaolo Xavier Co100% (4)
- Calculation of Strand ElongationDocument1 pageCalculation of Strand Elongationboubress100% (1)
- Iec 62040-3-2011Document216 pagesIec 62040-3-2011gnuga12417100% (2)
- "Full Coverage": Circle Theorems: (Edexcel IGCSE Nov2009-4H Q15ai)Document16 pages"Full Coverage": Circle Theorems: (Edexcel IGCSE Nov2009-4H Q15ai)Krypto MusicNo ratings yet
- Model of The Solar SystemDocument46 pagesModel of The Solar SystemPapa BallsNo ratings yet
- Scientific RevolutionDocument68 pagesScientific Revolutiong pNo ratings yet
- The Universe AND Solar SystemDocument22 pagesThe Universe AND Solar Systemlaurence mendozaNo ratings yet
- Helio-Geo Cer ArticleDocument2 pagesHelio-Geo Cer Articleapi-434008934No ratings yet
- Early Views of The UniverseDocument44 pagesEarly Views of The UniverseAllen KateNo ratings yet
- Science 11-Models of UniverseDocument23 pagesScience 11-Models of UniverseAngelica CamilonNo ratings yet
- A History of AstronomyDocument10 pagesA History of AstronomyHadi Bangash100% (1)
- PHY SCI 2ND QUARTER - Lesson 2-Models of Astronomical Phenomena Copernican, Ptolemaic, and TychonicDocument22 pagesPHY SCI 2ND QUARTER - Lesson 2-Models of Astronomical Phenomena Copernican, Ptolemaic, and TychonicGLADYS SARAELNo ratings yet
- SSHistoryDocument38 pagesSSHistoryCrescent OsamuNo ratings yet
- Early AstronomyDocument70 pagesEarly AstronomyDigie AspricNo ratings yet
- Early AstronomyDocument70 pagesEarly AstronomyMALOU ELEVERA100% (1)
- The Cosmic Perspective: Seventh EditionDocument70 pagesThe Cosmic Perspective: Seventh EditionSehrelilNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument19 pagesPhysical Scienceron NocheNo ratings yet
- Geo Theoryvs Helio TheoryDocument19 pagesGeo Theoryvs Helio TheoryJaicel ClaudetteNo ratings yet
- Physics: Earth Is Not The Center of The UniverseDocument14 pagesPhysics: Earth Is Not The Center of The UniverseTracy zorca50% (2)
- 10 1 - Introduction To The Solar SystemDocument8 pages10 1 - Introduction To The Solar Systemapi-236666161No ratings yet
- Topic 2. Intellectual RevolutionDocument10 pagesTopic 2. Intellectual RevolutionKyla GabiolaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science SHS Lesson 14.4 Models of The UniverseDocument23 pagesPhysical Science SHS Lesson 14.4 Models of The UniverseJoy DolorosaNo ratings yet
- The UniverseDocument14 pagesThe Universerosana f.rodriguezNo ratings yet
- A History of AstronomyDocument10 pagesA History of Astronomy3SpotNo ratings yet
- The Copernican RevolutionDocument41 pagesThe Copernican RevolutionRhea Jane Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Models of The UniverseDocument20 pagesModels of The UniverseChristopher Agustin Tambogon Lpt100% (1)
- Copernican RevolutionDocument17 pagesCopernican RevolutionFrances Mary BareñoNo ratings yet
- Johannes Kepler-He Followed The Heliocentric Model and DiscoveredDocument6 pagesJohannes Kepler-He Followed The Heliocentric Model and DiscoveredVon Allen DayoNo ratings yet
- Origins of Modern AstronomyDocument37 pagesOrigins of Modern AstronomyJana BalisalisaNo ratings yet
- How We Come To Realize That The Earth Is Not The Center of The UniverseDocument8 pagesHow We Come To Realize That The Earth Is Not The Center of The UniverseAlexa Aurellano100% (6)
- PS Unit 14 DDocument20 pagesPS Unit 14 DDennis Alfred PascualNo ratings yet
- 1b. Historical Perspective of The E and UDocument38 pages1b. Historical Perspective of The E and UJesiah Pascual100% (1)
- Galileos Astronomical DiscoveryDocument14 pagesGalileos Astronomical DiscoveryAlyssa De Guzman100% (1)
- 1a. History, Prior Believe, Ancientastronomer - Edt2Document50 pages1a. History, Prior Believe, Ancientastronomer - Edt2HyeZuanNo ratings yet
- The History of AstronomyDocument57 pagesThe History of Astronomyludivino escardaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Q4Document41 pagesWeek 1 Q4RIZALINA BATANNo ratings yet
- Geocentrism vs. HeliocentrismDocument17 pagesGeocentrism vs. HeliocentrismJohn FrancisNo ratings yet
- Models of The UniverseDocument17 pagesModels of The UniverseSeanNo ratings yet
- Day 1 Cosmology 2010Document114 pagesDay 1 Cosmology 2010Vio GlavanNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Part II. Intellectual RevolutionDocument19 pagesModule 2 Part II. Intellectual RevolutionEricka MaonNo ratings yet
- The Birth of Modern AstronomyDocument17 pagesThe Birth of Modern AstronomyMarArizalaNo ratings yet
- Ancient Astronomy NVDocument32 pagesAncient Astronomy NVKian GallardoNo ratings yet
- Copernican Revolution ReadingsDocument3 pagesCopernican Revolution ReadingsJarewell Daniel AbaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 The Origin of The Solar SystemDocument6 pagesChapter 7 The Origin of The Solar Systemapi-234121168No ratings yet
- Copernican Intellectual Revolution-European History: Nicolas CopernicusDocument3 pagesCopernican Intellectual Revolution-European History: Nicolas CopernicusIsmael Jr PANGCOGANo ratings yet
- Astronomy PrelimDocument5 pagesAstronomy PrelimdodakomataNo ratings yet
- Astronomy 161: Introduction To Solar System AstronomyDocument26 pagesAstronomy 161: Introduction To Solar System AstronomyLeah AbenerNo ratings yet
- 24 Models of Astronomical PhenomenaDocument10 pages24 Models of Astronomical PhenomenaJomark JimenezNo ratings yet
- 1 - Chapter 04-The Origin of Modern AstronomyDocument87 pages1 - Chapter 04-The Origin of Modern AstronomyKiruba SelvamNo ratings yet
- Task 1: 1.1 Research and Develop A Profile of A Great Innovation/innovatorDocument8 pagesTask 1: 1.1 Research and Develop A Profile of A Great Innovation/innovatorPanduka BandaraNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Lesson #1Document10 pagesEarth and Life Science Lesson #1Gian Carlo RegaladoNo ratings yet
- Copernican RevolutionDocument27 pagesCopernican RevolutionAnonymous OzIYtbjZNo ratings yet
- 4.3.1 Copernican Revolution 2Document12 pages4.3.1 Copernican Revolution 2Karumon UtsumiNo ratings yet
- Copernican RevolutionDocument12 pagesCopernican RevolutionChrishelle De guzmanNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document10 pagesPresentation 2Ismael Jr PANGCOGANo ratings yet
- Scientific RevolutionDocument42 pagesScientific RevolutionKanil De La TorreNo ratings yet
- Ancient AstronomyDocument28 pagesAncient AstronomyZairra Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Copernicus, Kepler, Galileo, NewtonDocument52 pagesCopernicus, Kepler, Galileo, NewtonUltimateWho MobNo ratings yet
- MST 112 Intellectual Revolutions-COPERNICAN REVDocument23 pagesMST 112 Intellectual Revolutions-COPERNICAN REVLord GrimmNo ratings yet
- Laws of Planetary MotionDocument10 pagesLaws of Planetary MotionPAUIG, VANESSA R.No ratings yet
- CHP 2Document73 pagesCHP 2Ata Ernam (Student)No ratings yet
- We're the Center of the Universe!: Science's Biggest Mistakes about Astronomy and PhysicsFrom EverandWe're the Center of the Universe!: Science's Biggest Mistakes about Astronomy and PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document3 pagesPresentation 1Glenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Fire HazardDocument33 pagesFire HazardGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - CARBOHYDRATESDocument47 pagesChapter 4 - CARBOHYDRATESGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- The Six Components of A Capstone PaperDocument5 pagesThe Six Components of A Capstone PaperGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Water ResourcesDocument9 pagesWater ResourcesGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Energy ResourcesDocument25 pagesEnergy ResourcesGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Naming CompoundsDocument44 pagesNaming CompoundsGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- S4 O1 CarbohydratesDocument14 pagesS4 O1 CarbohydratesGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Biology Study Guide 3 - Cell OrganellesDocument2 pagesBiology Study Guide 3 - Cell OrganellesGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio, Gen ChemDocument12 pagesGen Bio, Gen ChemGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- PP 5 Atomic ModelDocument27 pagesPP 5 Atomic ModelGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument3 pagesEarth ScienceGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Cancer 1Document65 pagesCancer 1Glenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- CKSci G5U6 Human-Hormones-and-Reproduction SRDocument54 pagesCKSci G5U6 Human-Hormones-and-Reproduction SRGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Holt MCD Earth Science CHP 2Document28 pagesHolt MCD Earth Science CHP 2Glenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Empirical & Molecular FormulasDocument28 pagesEmpirical & Molecular FormulasGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- GlennDocument1 pageGlennGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- HormonesDocument2 pagesHormonesGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Earth ScienceDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Earth ScienceGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Perform Basic First Aid ProceduresDocument76 pagesPerform Basic First Aid ProceduresGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Cycling of Matter and Flow of EnergyDocument1 pagePhotosynthesis Cycling of Matter and Flow of EnergyGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- The Mole ConceptDocument8 pagesThe Mole ConceptGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Ionic CovalentNameRaceDocument4 pagesIonic CovalentNameRaceGlenn Clemente100% (1)
- Postulates of Special Relativity: Relativity and The Big BangDocument4 pagesPostulates of Special Relativity: Relativity and The Big BangGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Origins of The Universe and Our Solar System Anchor Phenomenon & Performance TaskDocument36 pagesOrigins of The Universe and Our Solar System Anchor Phenomenon & Performance TaskGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- 12.8: Water - A Remarkable Molecule: Learning ObjectivesDocument2 pages12.8: Water - A Remarkable Molecule: Learning ObjectivesGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Newton's Three Laws of Motion: Lesson OutlineDocument10 pagesNewton's Three Laws of Motion: Lesson OutlineGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Classes of Crystalline SolidsDocument4 pagesClasses of Crystalline SolidsGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- 12.6: Intermolecular Forces: Dispersion, Dipole-Dipole, Hydrogen Bonding, and Ion-DipoleDocument11 pages12.6: Intermolecular Forces: Dispersion, Dipole-Dipole, Hydrogen Bonding, and Ion-DipoleGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces,, And: LiquidsDocument72 pagesIntermolecular Forces,, And: LiquidsGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Met201 Tutorial1Document2 pagesMet201 Tutorial1SijuKalladaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 Bernoulli Equation and Applications FinalDocument29 pagesCHAPTER 4 Bernoulli Equation and Applications FinalAung QinkangNo ratings yet
- Tension Member LRFDDocument9 pagesTension Member LRFDgullipalliNo ratings yet
- Molecular Modelling: Principles and Applications: PrefaceDocument12 pagesMolecular Modelling: Principles and Applications: PrefaceHarsha Vardhan JNo ratings yet
- Electrical Components of MHPDocument10 pagesElectrical Components of MHPDiyath VindulaNo ratings yet
- Estiluz - Catalogue Intl 2022Document178 pagesEstiluz - Catalogue Intl 2022Camila Carbajal RomanNo ratings yet
- Pretest For Paper 2Document3 pagesPretest For Paper 2Nan Hay Zun Naung LattNo ratings yet
- Aluminium Aluminum 6061 Alloy (UNS A96061)Document4 pagesAluminium Aluminum 6061 Alloy (UNS A96061)HARIPRASATH PNo ratings yet
- Cavite State University: Laboratory Exercise 2Document2 pagesCavite State University: Laboratory Exercise 2Ryan Shane LangitNo ratings yet
- Failure Analysis of A Bucket Elevator Shaft: Technicalarticle-Peer-ReviewedDocument7 pagesFailure Analysis of A Bucket Elevator Shaft: Technicalarticle-Peer-Revieweddouglasncamilo100% (1)
- Integral Equation AssDocument7 pagesIntegral Equation AssKiran MirzaNo ratings yet
- Acoustical Design and Detailing of Other SpacesDocument42 pagesAcoustical Design and Detailing of Other SpacesSamyuktha SureshNo ratings yet
- Graphite: Types and VarietiesDocument1 pageGraphite: Types and VarietiesXarbie RebadomiaNo ratings yet
- 2016 Exercise On IM (Chapter - 3)Document3 pages2016 Exercise On IM (Chapter - 3)Yonas BelaynehNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation and Economic Analysis of A Gas Turbine Plant Final PaperDocument10 pagesPerformance Evaluation and Economic Analysis of A Gas Turbine Plant Final Papernabil160874No ratings yet
- Turbomachinery Exit Exam TutorialsDocument22 pagesTurbomachinery Exit Exam TutorialsteddiyfentawNo ratings yet
- Engineering Utilities 1: Engr. Jessica Laine M. TumbagaDocument20 pagesEngineering Utilities 1: Engr. Jessica Laine M. TumbagaJessica Laine TumbagaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. The Lorentz System - Paul TobinDocument55 pagesChapter 3. The Lorentz System - Paul TobinN DNo ratings yet
- I Danaila Bose EinsteinDocument38 pagesI Danaila Bose EinsteincocoaramirezNo ratings yet
- E10 User Manual - V1.15 - E10 User ManualDocument28 pagesE10 User Manual - V1.15 - E10 User ManualThiago Teixeira PiresNo ratings yet
- Halliday and Resnick Ch05Document51 pagesHalliday and Resnick Ch05Kalen Gonzales100% (1)
- ADR01!02!03-06 10.0 V5.0 V2.5 V3.0 V Precision Voltage ReferencesDocument20 pagesADR01!02!03-06 10.0 V5.0 V2.5 V3.0 V Precision Voltage ReferencesjavierNo ratings yet
- SOP For Preventive Maintenance of AHU & Ventilation UnitsDocument2 pagesSOP For Preventive Maintenance of AHU & Ventilation UnitsmrugeshjNo ratings yet
- 纯液压技术 英文版讲义 PDFDocument236 pages纯液压技术 英文版讲义 PDFWeeLun TanNo ratings yet
- Shema ElecDocument19 pagesShema ElecelyeszebdaNo ratings yet