Professional Documents
Culture Documents
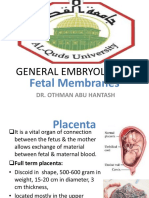
Fetal Membranes-WPS Office
Uploaded by
Ahemigisha James0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views6 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views6 pagesFetal Membranes-WPS Office
Uploaded by
Ahemigisha JamesCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
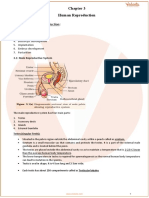
Fetal membranes
Fetal membranes are also called extraembryonic
membranes
Fetal membranes continues
• Fetal membranes consist of two layers ie
• The chorion
• The amnion
The chorion
• This is the outer layer of the two fetal membranes
• It's thicker than the amnion, friable and shaggy on
both sides .
• Internally, it's attached to the amnion by loose
areolar tissue and remnant of primitive
mesenchyme
• Externally it's covered by vestiges of trophoblastic
layer and decidual cells of the fused decidua
capsularis and parietalis.
Amnion
• It's the inner layer of the fetal membranes
• Internal surface is smooth and shiny and is in
contact with amniotic fluid.
• A fully formed amnion is 0.02-0.5mm in thickness.
Functions of fetal membranes
. Intact membranes prevent ascending uterine
infections
. Facilitates dilation of the cervix during labor
. Has got enzyme activities for steroid hormonal
metabolism
.They are rich source of glycerophospholipids
containing arachidonic acid which is a precursor of
prostaglandin E2 and F2 alpha
. Contributes to the formation of liquor amnii
Clinical correlates
• Prelabor rupture of membranes (PROM)
• Preterm prelabor rupture of membranes (PPROM)
• Chorioamnionitis
You might also like
- Placenta and Amniotic Fluid Structure FunctionDocument52 pagesPlacenta and Amniotic Fluid Structure FunctionDoli P Hutauruk100% (1)
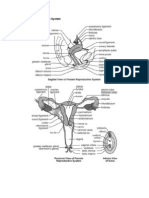
- The Female Reproduction SystemDocument9 pagesThe Female Reproduction Systemjhoanamariequilates182369No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Amnion, Chorion, Amniotic Cavity, Amniotic FluidDocument10 pagesUnit 2 - Amnion, Chorion, Amniotic Cavity, Amniotic FluidN. SivaNo ratings yet
- PlacentaDocument59 pagesPlacentaSulis 'Hp' Kartowidjojo100% (1)
- PlacentaDocument59 pagesPlacentaEdna Jenkins100% (9)
- Unit: 08 Placentation in Mammals: Developmental Biology Cr. Hours: 4 (3+1)Document30 pagesUnit: 08 Placentation in Mammals: Developmental Biology Cr. Hours: 4 (3+1)Task BirdNo ratings yet
- Placenta UpdatedDocument49 pagesPlacenta UpdatedSaad HasanNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Pregnancy: Department of Physiology School of Medicine University of Sumatera UtaraDocument80 pagesPhysiology of Pregnancy: Department of Physiology School of Medicine University of Sumatera UtaraJane Andrea Christiano DjianzonieNo ratings yet
- K11 12 Fisiologi KehamilanDocument75 pagesK11 12 Fisiologi KehamilanAditya PrabawaNo ratings yet
- PlacentaDocument11 pagesPlacentasubashikNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System - Study NotesDocument12 pagesReproductive System - Study NotesSrinibash JenaNo ratings yet
- EMBRYOLOGYDocument9 pagesEMBRYOLOGYmizare29gNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Female Reproductive SystemDocument27 pagesHistology of The Female Reproductive Systemdavidatuluku0No ratings yet
- 8reproductive SystemDocument31 pages8reproductive SystemViola ChepletingNo ratings yet
- Female Repro ReviwerDocument3 pagesFemale Repro ReviwerLincoln LunarNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument42 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemRoeisa SalinasNo ratings yet
- Fetal Membranes IMBBSDocument26 pagesFetal Membranes IMBBSSubham YadavNo ratings yet
- (Anatomy & Physiology Lecture) REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM NOTESDocument21 pages(Anatomy & Physiology Lecture) REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM NOTESZen HeartNo ratings yet
- FERTILIZATIONDocument9 pagesFERTILIZATIONRizalyn Padua ReyNo ratings yet
- ME Sci 10 Q3 1001 PSDocument17 pagesME Sci 10 Q3 1001 PSsino56601No ratings yet
- Human Reproduction (Edustudy Point)Document10 pagesHuman Reproduction (Edustudy Point)Vishal UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- The Placenta BDocument48 pagesThe Placenta BLulano MbasuNo ratings yet
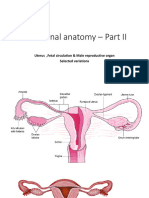
- Functional Anatomy - Part II: Uterus, Fetal Circulation & Male Reproductive Organ Selected VariationsDocument69 pagesFunctional Anatomy - Part II: Uterus, Fetal Circulation & Male Reproductive Organ Selected Variationshfkxbbbty2No ratings yet
- Assessment of PlacentaDocument21 pagesAssessment of PlacentaAarti RajputNo ratings yet
- Embryology, Pathophysiology, and Ultrasound Characteristics of The Placenta ObjectivesDocument13 pagesEmbryology, Pathophysiology, and Ultrasound Characteristics of The Placenta ObjectivesAudrey100% (5)
- Abhinav 3 Obg TeachingDocument22 pagesAbhinav 3 Obg TeachingEkta RajputNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive Physiology 2021Document164 pagesFemale Reproductive Physiology 2021Elijah Kihiu18No ratings yet
- Basic Steps in Human ReproductionDocument14 pagesBasic Steps in Human ReproductionMauz KhanNo ratings yet
- Fetal Membrane and PlacentaDocument77 pagesFetal Membrane and PlacentaIssa AvenaNo ratings yet
- 10 Kuliah PLACENTADocument33 pages10 Kuliah PLACENTAAya KamajayaNo ratings yet
- PlacentaDocument24 pagesPlacentaNibedita 2015No ratings yet
- Fetus Development From Conception To Birth Part2Document40 pagesFetus Development From Conception To Birth Part2jeremyzucker321No ratings yet
- Human Reproduction: 3.1: Male Reproductive SystemDocument27 pagesHuman Reproduction: 3.1: Male Reproductive SystemAvik BhaumikNo ratings yet
- Conception and Fetal DevelopmentDocument22 pagesConception and Fetal DevelopmentChari RivoNo ratings yet
- The Female Reproduction SystemDocument10 pagesThe Female Reproduction Systemrafaelvillacorta100% (1)
- The Antenatal Care-Maternal Changes During Pregnancy 7Document75 pagesThe Antenatal Care-Maternal Changes During Pregnancy 795kscbyqxmNo ratings yet
- Embryology - The PlacentaDocument14 pagesEmbryology - The PlacentaDr. SaG SaugatNo ratings yet
- Selaput EmbrioDocument25 pagesSelaput EmbrioMartupa SidabutarNo ratings yet
- EMBRYOLOGYDocument30 pagesEMBRYOLOGYMSc. PreviousNo ratings yet
- Three Stages of Fetal DevelopmentDocument4 pagesThree Stages of Fetal DevelopmentmellowlilydeeNo ratings yet
- ch.8 Embryo PDFDocument22 pagesch.8 Embryo PDFMohammad GhannamNo ratings yet
- File 2Document104 pagesFile 2Djo RamNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Fertilization, Impantation, Development of Placenta and Its Function, AbnormalityDocument62 pagesUnit 2 - Fertilization, Impantation, Development of Placenta and Its Function, AbnormalityN. Siva100% (1)
- Chapter 9: Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy and Care of The Developing FetusDocument8 pagesChapter 9: Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy and Care of The Developing FetusAlyssaGrandeMontimor100% (1)
- Femalereprod (Author T.globa)Document56 pagesFemalereprod (Author T.globa)Angelina BulaiNo ratings yet
- Year 2 Embryology LectureDocument57 pagesYear 2 Embryology LectureIjeoma Doris100% (1)
- Amnion 1Document2 pagesAmnion 1Oryza SativaniNo ratings yet
- The Growing FetusDocument62 pagesThe Growing Fetuscoosa liquorsNo ratings yet
- Department of Zoology Govt Hss Mylachal: PresentsDocument69 pagesDepartment of Zoology Govt Hss Mylachal: PresentsBiju MylachalNo ratings yet
- 7 Perkembangan EMbrio Manusia PDFDocument57 pages7 Perkembangan EMbrio Manusia PDFFadhilah SiregarNo ratings yet
- Histology of Female Genital System For Reproductive ModuleDocument35 pagesHistology of Female Genital System For Reproductive ModuleTeklemuz KahsayNo ratings yet
- REWIEW OF FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM NewDocument49 pagesREWIEW OF FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM NewnamitaNo ratings yet
- Parturition, Foetal Membranes and Multiple PregnanciesDocument38 pagesParturition, Foetal Membranes and Multiple PregnanciesGeoffreyNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction Class 12 NotesDocument21 pagesHuman Reproduction Class 12 NotesTamanna NayakNo ratings yet
- Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya, Bolangir Biology Assingment Guided by - Swastitapa Kar Prepared by - Sujata Goud Class - Xii Section-A Roll No. - 16Document19 pagesJawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya, Bolangir Biology Assingment Guided by - Swastitapa Kar Prepared by - Sujata Goud Class - Xii Section-A Roll No. - 16preetamgoud225No ratings yet
- A Case Study About Cervical PolypsDocument8 pagesA Case Study About Cervical PolypsJisel-Apple BulanNo ratings yet
- Stages of Fetal DevelopmentDocument42 pagesStages of Fetal DevelopmentKara Ashleigh0% (1)
- BreastDocument104 pagesBreastRamesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Last Minute Embryology: Human embryology made easy and digestible for medical and nursing studentsFrom EverandLast Minute Embryology: Human embryology made easy and digestible for medical and nursing studentsNo ratings yet