Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A1 GC Poster Template (Landscape) (2) - 副本
A1 GC Poster Template (Landscape) (2) - 副本
Uploaded by
wanzhen0527Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A1 GC Poster Template (Landscape) (2) - 副本
A1 GC Poster Template (Landscape) (2) - 副本
Uploaded by
wanzhen0527Copyright:
Available Formats
name: Huang Wanzhen
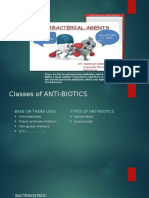
Phages: tiny superheroes combat antibiotic resistant bacteria Tao Shuhan
Ma Tianyu
Xu Jiashang
strengths and weaknesses
introduction Advantages:
Disadvantages:
1. Narrow cleavage spectrum compared
Antibiotic resistance: 1. Excellent lysis of super bacteria: can easily solve to antibiotics(high degree of single-host
•occurs when bacteria evolve and find new ways to beat the medicine(1)=>super bacteria which are the drug-resistant bacteria that antibiotics cannot selectivity)=>It is often necessary to mix
insensitive to antibiotics. kill(1). different strains of phages to broaden
2. Target only harmful bacteria: the host spectrum of phages during the
Global threat: antibiotics, as broad-spectrum fungicides, will kill treatment and some bacteria cannot be
•to global health, food security, and development today(1) both useful and harmful bacteria, thus disrupts killed by phages found up to now(6).
•already killing 700,000 people a year, and it is predicted to cause 10 million deaths per year by 2050 if the the balance of human microbiome(1) 2. Phage tolerance: bacteria can develop
current situation is not improved(2) a specific landing pad=> exclusively target at one tolerance to phages in only 1 or 2
•misuse of antibiotics is still accelerating the process(1) type of bacteria => avoid attack beneficial bacteria days(6).
•growing number of bacterial infections are becoming harder to treat including pneumonia, tuberculosis, in human microbiome 3. May cause an immune response: can
gonorrhoea, and salmonellosis(1) 3. use less medicine dosage during the treatment: be found within the human
longer hospital stays, higher medical costs, and increased mortality rapid replication=> use a small amount can microbiome=> may also be killed by
achieve great lytic effects antibodies against certain phage(1).
Phage therapy as a renewed approach: 4. Reduce antibiotic use: 4. Imperfection of laws and regulations:
•Phages: a type of virus which exclusively infect bacteria(1) bacteria inevitably develop resistance to •As a virus
•Past: Discovered in early 20th century => medical potential realized soon => limited antibiotics. •compared with antibiotics, legal
purification technology=> drawbacks over benefits Carefully select phages to reduce the possibility of supervision and management of phages
•Present: technology development=> identify pathogens => make selectivity as a benefit bacteria develop tolerance(1). is not yet complete(1).
=> avoid side-effects compared to broad-spectrum antibiotics 5. Release dangerous bacterial antigens:
solution :
1. cocktail therapy, also called HAART. large cleavage of targeted bacteria may
2. Antibiotics in combination with phages. result in release of harmful antigens(1).
3. Neutralize antibodies against phages in the body.
Phages Biology 4. Neutralize the toxin produced by bacterial
cleavage(1).
The structure of phage: Infection Process:
1. phage structures are diverse, but most of them share 1. a phage binds to the Bioengineering of phages:
some common characteristics receptor of a specific bacterium increase the therapeutic potential of phages via a range of mechanisms: expanded
2. nucleic acid may be ds DNA, ds RNA, ss DNA, ss RNA and injects its genome into the host range, switching host tropism, delivery of exogenous genes, or modification of
3. The following figure shows the structure of phage T4 bacterium phage capsids(7).
4. it has an icosahedral head called capsid and a linear 2. the genome replicates
double-stranded viral genome are inside(3). 3. the genome transcribes and
5. The capsid of phage T4 is attached to a helical tail translates to produce new shell(4) Industrial phage propagation strain:
through a neck. 4. new genomes are packaged into new future prospect •Bacterial chassis strains: serve as basic platforms for the construction of industrial
6.The Tail contain a series of tail fibers and tail pins at the shell and phage release toxins to lyse phage propagation strains(8).
end. These specialized syringe-like structures bind to bacterium wall(4) •Use bioengineering to construct bacterial chassis strains(8).
receptors on the bacteria surface(3). •Function: ensure the safety of therapeutic phage preparations and reduce the cost
of phage production substantially(8).
People:
4 Active interest and signs of a more open mind are shown to assess the possible
1 benefits of phage therapy(8).
Clinical trials:
•To demonstrate the efficacy and safety of phage application(8).
2 •National and international authorities are opening their doors to such trials, and
3 are prone to regulate phage therapy if it is found to be effective and safe(8).
References
1. Kortright KE, Chan BK, Koff JL, Turner PE. Phage Therapy: A Renewed Approach to Combat Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria. Cell Host Microbe. 2019 Feb 13;25(2):219–32.
2. Antibiotic resistance [Internet]. [cited 2021 Apr 17]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antibiotic-resistance
3. Bacteriophage: Structure, Replication and Uses - Learn Microbiology Online [Internet]. [cited 2021 Apr 18]. Available from: https://microbeonline.com/bacteriophage-structure-replication-use/
4. Bacteriophage: A solution to our antibiotics problem? How we can us a virus to fight bacterial infection [Internet]. [cited 2021 Apr 18]. Available from: https://sitn.hms.harvard.edu/flash/2018/bacteriophage-solution-antibiotics-problem/
5. Viruses [Internet]. [cited 2021 Apr 18]. Available from: https://cronodon.com/BioTech/Virus_Tech.html
Figure 2; the structure of phage T4(5) 6. Gurney J, Brown SP, Kaltz O, Hochberg ME. Steering phages to combat bacterial pathogens. Trends Microbiol. 2020 Feb;28(2):85–94.
7. Gordillo Altamirano FL, Barr JJ. Phage Therapy in the Postantibiotic Era. Clin Microbiol Rev [Internet]. 2019 Jan 16 [cited 2021 Apr 18];32(2). Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6431132/
8. Górski A, Międzybrodzki R, Łobocka M, Głowacka-Rutkowska A, Bednarek A, Borysowski J, et al. Phage Therapy: What Have We Learned? Viruses. 2018 Jun;10(6):288.
You might also like
- Gene TherapyDocument27 pagesGene TherapySergio III Matuguinas Villablanca100% (3)
- Psychiatry PasTest MRCP II 2019Document71 pagesPsychiatry PasTest MRCP II 2019jehemirNo ratings yet
- A1 GC Poster Template (Landscape) (修正版3) - 副本Document1 pageA1 GC Poster Template (Landscape) (修正版3) - 副本wanzhen0527No ratings yet
- 会议版本 - 副本Document1 page会议版本 - 副本wanzhen0527No ratings yet
- Topic 13 Full Doc j22 DDocument45 pagesTopic 13 Full Doc j22 DabdulwahabibnfayazNo ratings yet
- How Antibiotic Resistance Spreads - Boa ImagemDocument1 pageHow Antibiotic Resistance Spreads - Boa ImagemCinthia MadeiraNo ratings yet
- E-Poster Veena PillaiDocument1 pageE-Poster Veena PillaiVeena PillaiNo ratings yet
- 最终版本1 - 副本Document1 page最终版本1 - 副本wanzhen0527No ratings yet
- Laboratory 6 - AntimicrobialsDocument4 pagesLaboratory 6 - AntimicrobialsLuzzuvannaNo ratings yet
- B3 Full Revision Summary Broadsheet (Triple Only)Document2 pagesB3 Full Revision Summary Broadsheet (Triple Only)Jason akieNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics: Sana Husain & Rabia Mukaty FY-C3Document8 pagesAntibiotics: Sana Husain & Rabia Mukaty FY-C3sanNo ratings yet
- Microbial Insecticides: R. Weinzierl, T. Henn, P. G. Koehler and C. L. TuckerDocument13 pagesMicrobial Insecticides: R. Weinzierl, T. Henn, P. G. Koehler and C. L. TuckerRajesh MandarapuNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Persistence: Fundamentals and Clinical ImportanceDocument7 pagesBacterial Persistence: Fundamentals and Clinical ImportanceMathieu VigneauNo ratings yet
- AltinsecDocument76 pagesAltinsecAnggry SolihinNo ratings yet
- CommentsDocument1 pageCommentshussymian06No ratings yet
- Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing: NotesDocument12 pagesAntibiotic Susceptibility Testing: NotesKania Putri D 113No ratings yet
- Collective Antibiotic Resistance: Mechanisms and ImplicationsDocument7 pagesCollective Antibiotic Resistance: Mechanisms and ImplicationsWilfrido Jose Barrios AgamezNo ratings yet
- Carmilaa Introduction To AntimicrobialsDocument2 pagesCarmilaa Introduction To AntimicrobialsCARINA-ELENA-MIHAELA STANCUNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics and Resistance Activity Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesAntibiotics and Resistance Activity Lesson PlanbadrhashmiNo ratings yet
- Abigail Ann ADocument9 pagesAbigail Ann AAbigail Ann BinalayNo ratings yet
- Anti-Infective AgentsDocument7 pagesAnti-Infective AgentsAlyssaGrandeMontimor100% (1)
- Biological Warfare: Module - VDocument7 pagesBiological Warfare: Module - VDIVAS NEGINo ratings yet
- Antibiotics ResistanceDocument8 pagesAntibiotics ResistanceboredtarteelNo ratings yet
- ResistanceDocument1 pageResistanceisamat07No ratings yet
- Antibiotics & Analgesics in Dentistry: Dr. Hala Helmi A. HazzaaDocument69 pagesAntibiotics & Analgesics in Dentistry: Dr. Hala Helmi A. HazzaaPuchka IndurNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - MidtermDocument7 pagesPharmacology - MidtermEthel May AlabastroNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology - Chapter Six Antibiotics - Protein Synthesis, Nucleic Acid Synthesis and MetabolismDocument6 pagesBacteriology - Chapter Six Antibiotics - Protein Synthesis, Nucleic Acid Synthesis and MetabolismZeth MoturiNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1369527422001084 MainDocument13 pages1 s2.0 S1369527422001084 MainRobert StryjakNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing & Antimicrobial AgentsDocument18 pagesAntimicrobial Susceptibility Testing & Antimicrobial AgentsMayra FlorNo ratings yet
- MC 3 Lecture 05 ASTDocument3 pagesMC 3 Lecture 05 ASTJanna Niña ElementoNo ratings yet
- Microbial Control Sterilization & DisinfectionDocument10 pagesMicrobial Control Sterilization & DisinfectionMatt CloudNo ratings yet
- AMG Brochure R4Document20 pagesAMG Brochure R4exgeNo ratings yet
- Microbial InsecticidesDocument29 pagesMicrobial InsecticidesChandni V. AhujaNo ratings yet
- Prevention: What Is Antibiotic Resistance?Document1 pagePrevention: What Is Antibiotic Resistance?Verinice NañascaNo ratings yet
- Anti-Biotic: Click Icon To Add PictureDocument13 pagesAnti-Biotic: Click Icon To Add PictureahamedNo ratings yet
- CNSHQTK1 - G4 - IPM General ViewsDocument6 pagesCNSHQTK1 - G4 - IPM General ViewsTuan Huynh AnhNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Concepts Practice BookletDocument7 pagesBacteria Concepts Practice BookletEli GlassNo ratings yet
- Herbal Antibiotics and Antivirals: Herbal Medicine to Heal Yourself NaturallyFrom EverandHerbal Antibiotics and Antivirals: Herbal Medicine to Heal Yourself NaturallyNo ratings yet
- Human Defence PDFDocument13 pagesHuman Defence PDFDarrell CalabiaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic - Definition, Types, Side Effects, Resistance, Classification, & Facts - BritannicaDocument13 pagesAntibiotic - Definition, Types, Side Effects, Resistance, Classification, & Facts - Britannicaali khanNo ratings yet
- Pharma Week34 ReviewerDocument20 pagesPharma Week34 ReviewerDT1029No ratings yet
- Revisiting Antibiotic Resistance MechanisticDocument23 pagesRevisiting Antibiotic Resistance Mechanisticgembul31No ratings yet
- Lech 202Document26 pagesLech 202dongNo ratings yet
- Anti Hiv Using Nano RobotsDocument8 pagesAnti Hiv Using Nano RobotsBharadwaj Santhosh50% (2)
- LL1703 Antibiotics Review PDFDocument15 pagesLL1703 Antibiotics Review PDFAparna DwivediNo ratings yet
- Experiment 10Document2 pagesExperiment 10Mark Janssen CustodioNo ratings yet
- First Sem NotesDocument37 pagesFirst Sem NotesRose Anne AbivaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Resistance GameDocument3 pagesAntibiotic Resistance GamepooppfppNo ratings yet
- Evidence 5Document4 pagesEvidence 5api-527267271No ratings yet
- Kingdom Monera - AntibioticsDocument22 pagesKingdom Monera - AntibioticsCaleb TanNo ratings yet
- AST Part 2 1Document3 pagesAST Part 2 1anti romantic txtNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Resistance in BacteriaDocument16 pagesAntimicrobial Resistance in Bacteriamahveen balochNo ratings yet
- M.06 MISCELLANEOUS ANTIMICROBIALS (Part 1)Document3 pagesM.06 MISCELLANEOUS ANTIMICROBIALS (Part 1)PAUL ALINGKAYONNo ratings yet
- ChemoDocument7 pagesChemoZohaNo ratings yet
- Biocontrol of Insect PestsDocument8 pagesBiocontrol of Insect PestsnareshbutaniNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic and The Basis of Chemotherapy: Lecturer: Lubna KamilDocument12 pagesAntibiotic and The Basis of Chemotherapy: Lecturer: Lubna KamilZainab ZakiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Micro 303-محولDocument12 pagesChapter Two Micro 303-محولshimaa dewedarNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, DPA 200-2Document26 pagesAntimicrobial Chemotherapy, DPA 200-2Yeboah Kukudabi AsiamahNo ratings yet
- Antobiotics I NotesDocument11 pagesAntobiotics I NotesBayan AlsaadiNo ratings yet
- What Are TheyDocument1 pageWhat Are TheyDanna CruzNo ratings yet
- 3C Blood PhysiologyDocument11 pages3C Blood PhysiologyRen AlvNo ratings yet
- Vaccines Explained (Korean-English): Language Lizard Bilingual Explore SeriesFrom EverandVaccines Explained (Korean-English): Language Lizard Bilingual Explore SeriesNo ratings yet
- Example Poster 6Document1 pageExample Poster 6wanzhen0527No ratings yet
- BH - Example Poster 2Document1 pageBH - Example Poster 2wanzhen0527No ratings yet
- 会议版本 - 副本Document1 page会议版本 - 副本wanzhen0527No ratings yet
- 最终版本1 - 副本Document1 page最终版本1 - 副本wanzhen0527No ratings yet
- Chronic Wound Care Ch13 22Document86 pagesChronic Wound Care Ch13 22Chunti HuNo ratings yet
- 5.respiratory Distress Dental LectureDocument40 pages5.respiratory Distress Dental LecturehaneeneeNo ratings yet
- Overview of Mechanical Thrombectomy TechniquesDocument8 pagesOverview of Mechanical Thrombectomy Techniquesjaknews adminNo ratings yet
- Improving Patient Safety in The Operating Theatre and Perioperative Care: Obstacles, Interventions, and Priorities For Accelerating ProgressDocument14 pagesImproving Patient Safety in The Operating Theatre and Perioperative Care: Obstacles, Interventions, and Priorities For Accelerating ProgressKainat BaigNo ratings yet
- Post Mortem CareDocument5 pagesPost Mortem CareTaqwantrih SandiNo ratings yet
- COLD Vs FLU ChartDocument1 pageCOLD Vs FLU ChartAllysha VarugheseNo ratings yet
- Neurology II 6.04 Traumatic Brain Injury Dr. TanDocument10 pagesNeurology II 6.04 Traumatic Brain Injury Dr. TanAbi IgsNo ratings yet
- PharmakologyDocument43 pagesPharmakologyshezo4u100% (3)
- Using PICO & PEO:: Developing Your Research Question and Search StrategyDocument2 pagesUsing PICO & PEO:: Developing Your Research Question and Search StrategyDiego Marcelo Aragon Caqueo50% (2)
- Recall 139, Sum 2.3.13 AMC CLINICALDocument34 pagesRecall 139, Sum 2.3.13 AMC CLINICALAMMARA100% (4)
- Guía Clínica HTA 2011Document310 pagesGuía Clínica HTA 2011marcelagarciavNo ratings yet
- Correspondence: DR Dhananjaya Sabat Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, MaulanaDocument8 pagesCorrespondence: DR Dhananjaya Sabat Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, MaulanaDr Mohamed ShamaaNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic MonitoringDocument15 pagesHemodynamic MonitoringUno PrimoNo ratings yet
- CisPt TOP Dasari2014 PDFDocument15 pagesCisPt TOP Dasari2014 PDFJuanita Pulido TeutaNo ratings yet
- Brochure BI - FPP 2017Document2 pagesBrochure BI - FPP 2017donehealNo ratings yet
- Glasgow Coma Scale Canvas NCM 116 SkillsDocument6 pagesGlasgow Coma Scale Canvas NCM 116 Skillsbing bongNo ratings yet
- Cholesterol and HomeopathyDocument6 pagesCholesterol and Homeopathykuldip1951100% (2)
- Gambaran Klinis Dan Laboratorium Pada Pasien Pneumonia Di Icu Rsud Raden Mattaher JambiDocument7 pagesGambaran Klinis Dan Laboratorium Pada Pasien Pneumonia Di Icu Rsud Raden Mattaher JambigusdeNo ratings yet
- Transpersonal Perspectives On Mental Health and Mental IllnessDocument16 pagesTranspersonal Perspectives On Mental Health and Mental IllnessJacob KaminkerNo ratings yet
- Nursing Case StudyDocument21 pagesNursing Case StudyJeyser T. GamutiaNo ratings yet
- Grand Rounds Alumni MagazineSaint Louis University School of MedicineDocument13 pagesGrand Rounds Alumni MagazineSaint Louis University School of MedicineSlusom WebNo ratings yet
- Doh Standard For Emergency DepartmentsDocument21 pagesDoh Standard For Emergency DepartmentsMendero Medical CenterNo ratings yet
- Ozone Therapy Its Uses Benefits EffectsDocument7 pagesOzone Therapy Its Uses Benefits EffectsHello MisterNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Intervention For Bipolar Disorder:: Best Practices For School PsychologistsDocument29 pagesAssessment and Intervention For Bipolar Disorder:: Best Practices For School PsychologistswulanfarichahNo ratings yet
- Varicose Veins CaseDocument16 pagesVaricose Veins Casebenak shivalingappaNo ratings yet
- Excoriation (Skin-Picking) Disorder: A Systematic Review of Treatment OptionsDocument6 pagesExcoriation (Skin-Picking) Disorder: A Systematic Review of Treatment OptionsBecados PsiquiatriaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Scleral Staphyloma in A Dog Repaired With Preserved Homologous PeritoneumDocument3 pagesCongenital Scleral Staphyloma in A Dog Repaired With Preserved Homologous PeritoneumFelippe Correia100% (1)
- DOSAGE CHART - Acetaminophen, Tylenol, Tempra, FeveralDocument1 pageDOSAGE CHART - Acetaminophen, Tylenol, Tempra, FeveralElla Jane Manolos PaguioNo ratings yet