Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Principles of Refrigeration
Uploaded by
Maneth Muñez Caparos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views9 pagesBasic Principles of Refrigeration in RAC - Industrial Arts
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBasic Principles of Refrigeration in RAC - Industrial Arts
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views9 pagesBasic Principles of Refrigeration
Uploaded by
Maneth Muñez CaparosBasic Principles of Refrigeration in RAC - Industrial Arts
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
Basic Principles of Refrigeration
The Principle of Refrigeration
The refrigeration cycle is also
known as a vapour compression
cycle. The cycle operates at two
pressures high and low, to
produces a continuous cooling
effect.
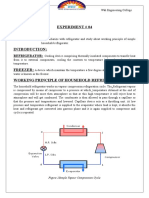
Refrigeration Cycle
Receiver or Condenser
The liquid is kept in a container namely condenser.
The refrigerant is under pressure.
Expansion Valve
It is a device, which controls the rate of flow of
refrigerant into the evaporator. Now high pressure
refrigerant enters low pressure zone.
Evaporator
It consist of coils, here the refrigerant evaporate by
absorbing heat from the space. The energy required
for this process is taken from the surrounding (space
which is too be cooled). In this step, liquid vapourises,
but some liquid still remains.
Liquid Trap
This is used to remove the traces of liquid refrigerant
and then returned to receiver (condenser).
Compressor
Saturated vapour is allowed to pass through the
compressor. The compression is adiabatic and it
produces supersaturated gas.
Condenser
The supersaturated gas (vapour) flows to the
condenser where the gas is liquefied. The condenser
can be air cooled (or) water cooled. Thus one cycle is
completed as shown above and process is continued.
You might also like
- Types of ChillerDocument13 pagesTypes of Chillerzakaria masud sonyNo ratings yet
- Functioning of ChillersDocument22 pagesFunctioning of ChillersAnonymous b9fcR5No ratings yet
- Vapor Compression Refrigeration SystemDocument6 pagesVapor Compression Refrigeration SystemGerson Paul BangoyNo ratings yet
- Basic Refrigeration CycleDocument2 pagesBasic Refrigeration CycleParvez Saif100% (1)
- Performance and Efficiency Test of A Refrigeration PlantDocument17 pagesPerformance and Efficiency Test of A Refrigeration Plantjun75% (4)
- Refrigeration CycleDocument5 pagesRefrigeration CycleLiezel Quijada LicupNo ratings yet
- Oral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseFrom EverandOral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseNo ratings yet
- 1,2 - Unit 1Document137 pages1,2 - Unit 1Saran T SNo ratings yet
- Performance and Efficiency Test of Refrigeration PlantDocument26 pagesPerformance and Efficiency Test of Refrigeration PlantGigi Sales100% (2)
- Building Services IV-hvac NotesDocument17 pagesBuilding Services IV-hvac NotessamairaNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning 2Document33 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning 2Christina OhNo ratings yet
- Different Refrigeration CyclesDocument11 pagesDifferent Refrigeration CyclesLester AngelesNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration SystemDocument37 pagesRefrigeration Systemdeepakdshenoy100% (1)
- Group 2 Basic Refrigerationsystem and ComponentsDocument25 pagesGroup 2 Basic Refrigerationsystem and ComponentsVipin VetriNo ratings yet
- The Refrigeration CycleDocument2 pagesThe Refrigeration CycleIvy Pearl TabagNo ratings yet
- Solar Automobile FridgeDocument4 pagesSolar Automobile FridgeRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.2: ObjectiveDocument5 pagesExperiment No.2: Objectiveمیاں اسامہ صفدرNo ratings yet
- Hvac Lab Report: Name: Ali Raza Roll No: 18-MCE-18 Submitted To: Sir Murawat Abbas Semester 6Document11 pagesHvac Lab Report: Name: Ali Raza Roll No: 18-MCE-18 Submitted To: Sir Murawat Abbas Semester 6AliNo ratings yet
- Vapour Compression CycleDocument5 pagesVapour Compression CycleNimra EhsanNo ratings yet
- SolarDocument6 pagesSolarMuneeb YounisNo ratings yet
- Basic Refrigeration Cycle: Presented by Therese SchutteDocument10 pagesBasic Refrigeration Cycle: Presented by Therese SchutteEugeneNo ratings yet
- Draft Basic AirconDocument37 pagesDraft Basic AirconcspolaNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration SystemDocument3 pagesRefrigeration SystemCamillus GulimNo ratings yet
- Working Principle of VRF SystemDocument11 pagesWorking Principle of VRF Systemghazanfarhayat456No ratings yet
- WATER COOLER 9235074-F935-49bc-90cc-08ed4ab8014dDocument3 pagesWATER COOLER 9235074-F935-49bc-90cc-08ed4ab8014dAmbika prasadNo ratings yet
- Major Elements of Refrigeration System and Their FunctionsDocument8 pagesMajor Elements of Refrigeration System and Their FunctionsXahid HasanNo ratings yet
- سمنار الثرموDocument14 pagesسمنار الثرموhussein alnasryNo ratings yet
- Reerigeation System Basics, Week 2 Part 1Document17 pagesReerigeation System Basics, Week 2 Part 1Musfirah AdeelNo ratings yet
- 588-Water Cooler Cum HeaterDocument6 pages588-Water Cooler Cum Heatersanu222100% (3)
- Hot and Cold Water DespensorDocument6 pagesHot and Cold Water DespensorMohamedFasilNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration CycleDocument12 pagesRefrigeration CycleVishalVaishNo ratings yet
- Unit 5.1 RefrigrationDocument11 pagesUnit 5.1 RefrigrationPalanichamy MuruganNo ratings yet
- Absorption RefrigerationDocument40 pagesAbsorption RefrigerationAniket MitraNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 04: ObjectiveDocument3 pagesExperiment # 04: ObjectiveAhsen NasimNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration System HarpalDocument19 pagesRefrigeration System HarpalVijay DawarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4RACDocument32 pagesChapter 4RACSameer AhmadNo ratings yet
- Mechanical-Compression Refrigeration SystemsDocument4 pagesMechanical-Compression Refrigeration Systemsaruna MoonNo ratings yet
- Basic Refrigeration CycleDocument14 pagesBasic Refrigeration Cyclehussein alnasryNo ratings yet
- Water Chillers 85Document2 pagesWater Chillers 85Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration CycleDocument29 pagesRefrigeration CycleShyam WanaskarNo ratings yet
- Mahika Saxena Refrigeartion.Document9 pagesMahika Saxena Refrigeartion.Warrior InsideNo ratings yet
- Figure 4-.2 Air Conditioning System ExampleDocument2 pagesFigure 4-.2 Air Conditioning System ExamplerohitNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - The Heat PumpDocument25 pagesUnit 4 - The Heat PumpShyam WanaskarNo ratings yet
- Cooling Mode: Principles of Heat Pump OperationDocument1 pageCooling Mode: Principles of Heat Pump OperationSushant MishraNo ratings yet
- RefrigerationDocument25 pagesRefrigerationAnoop SlathiaNo ratings yet
- BUILDING UTILITIES 2 Building HVAC SystemsDocument142 pagesBUILDING UTILITIES 2 Building HVAC Systemsjona serranoNo ratings yet
- Refregeration UnitDocument24 pagesRefregeration UnitEZWANNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual: RGPV University (Bhopal)Document6 pagesLab Manual: RGPV University (Bhopal)Pushpendra KushwahaNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Definition and Applications of Refrigeration: Thermal EquilibriumDocument59 pages3.1 Definition and Applications of Refrigeration: Thermal EquilibriumRosina AdhikariNo ratings yet
- RefrigerationDocument65 pagesRefrigerationyassinNo ratings yet
- Vapor Compression CycleDocument1 pageVapor Compression Cyclefreeky_sidNo ratings yet
- Absorption Refrigerator - WikipediaDocument5 pagesAbsorption Refrigerator - Wikipediaaravind grandhiNo ratings yet
- Part 3 Phase Change of The Refrigerant in The CycleDocument7 pagesPart 3 Phase Change of The Refrigerant in The CycleKenneth JameroNo ratings yet
- AUX2Document210 pagesAUX2KirsthyNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration CycleDocument4 pagesRefrigeration CycleRanjith KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Air Condition How Does It Works?Document10 pagesAir Condition How Does It Works?Gwapong CrisNo ratings yet
- HVAC Unit 1&2Document22 pagesHVAC Unit 1&2LOYOLA RS 200No ratings yet
- Vapour Absorption Refrigeration SystemDocument12 pagesVapour Absorption Refrigeration SystemHarshNo ratings yet
- Basic Air Conditioning System.2022 NotesDocument25 pagesBasic Air Conditioning System.2022 NotesKITSAO SAMUELNo ratings yet
- Refrigerator Revelations: A User's Guide to Operation and MaintenanceFrom EverandRefrigerator Revelations: A User's Guide to Operation and MaintenanceNo ratings yet
- TemperatureDocument7 pagesTemperatureManeth Muñez CaparosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To RefrigerationDocument7 pagesIntroduction To RefrigerationManeth Muñez CaparosNo ratings yet
- HEATDocument8 pagesHEATManeth Muñez CaparosNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric PressureDocument13 pagesAtmospheric PressureManeth Muñez CaparosNo ratings yet
- 6 COMPLETION and SHORT ANSWER ITEMSDocument17 pages6 COMPLETION and SHORT ANSWER ITEMSManeth Muñez CaparosNo ratings yet
- Multiple-choice-WPS OfficeDocument19 pagesMultiple-choice-WPS OfficeManeth Muñez CaparosNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument18 pagesMeasures of Central TendencyManeth Muñez CaparosNo ratings yet
- Checklist ReportDocument17 pagesChecklist ReportManeth Muñez CaparosNo ratings yet
- Altenate Choice ItemDocument15 pagesAltenate Choice ItemManeth Muñez CaparosNo ratings yet
- The MedianDocument18 pagesThe MedianManeth Muñez CaparosNo ratings yet
- Types of SeedlingsDocument13 pagesTypes of SeedlingsManeth Muñez CaparosNo ratings yet
- Republic Act 8550Document60 pagesRepublic Act 8550Maneth Muñez CaparosNo ratings yet
- Post Harvest ParametersDocument14 pagesPost Harvest ParametersManeth Muñez CaparosNo ratings yet
- Rectifiers: Reported By: Maneth M. CaparosDocument11 pagesRectifiers: Reported By: Maneth M. CaparosManeth Muñez CaparosNo ratings yet
- The Five Main Parts of A ComputerDocument5 pagesThe Five Main Parts of A ComputerManeth Muñez CaparosNo ratings yet