Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gradients and Straight Line Graphs: © Oxford University Press 2016
Uploaded by
Muminah DorayOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gradients and Straight Line Graphs: © Oxford University Press 2016
Uploaded by
Muminah DorayCopyright:
Available Formats
GRADIENTS AND STRAIGHT LINE
GRAPHS
© Oxford University Press 2016
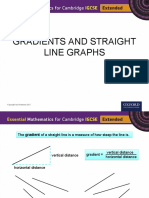
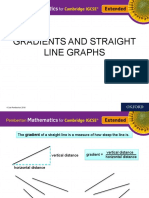
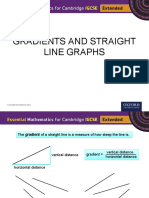
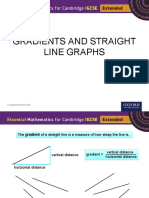
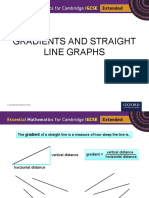
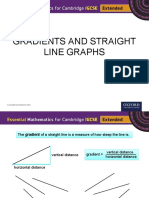
The gradient of a straight line is a measure of how steep the line is.
vertical distance
vertical distance gradient =
horizontal distance
horizontal distance
These lines have negative gradient. These lines have positive gradient.
© Oxford University Press 2016
1 Find the gradient of the line.
Gradient = 5
5 4
© Oxford University Press 2016
2 Find the gradient of the line.
Gradient = 3 = 1
6 2
3
© Oxford University Press 2016
3 Find the gradient of the line.
Gradient = 5 =1
5 5
© Oxford University Press 2016
4 Find the gradient of the line.
Gradient = − 6 = − 3
2
6
© Oxford University Press 2016
5 Find the gradient of the line.
Gradient = − 4 = − 2
4 6 3
© Oxford University Press 2016
6 Find the gradient of the line joining the points (−2, 1) and (4, 5).
y
Gradient = 4 = 2
4 6 3
6
x
© Oxford University Press 2016
7 Find the gradient of the line joining the points (−1, 3) and (2, −3).
y
Gradient = − 6 = −2
x 3
6
© Oxford University Press 2016
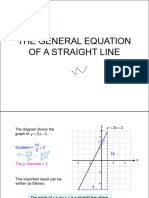
The gradient of a line passing through two points can also be
calculated using a formula.
If the points are (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) then the gradient (m) is
given by y y1
m 2
x2 x1
Examples
1 Find the gradient of the line joining the points (2, 1) and (8, 7).
(x1, y1) (x2 , y 2 )
y 2 y1 7 1 6
Gradient = m 1
x2 x1 82 6
© Oxford University Press 2016
2 Find the gradient of the line joining the points (−2, 1) and (4, 5).
(x1, y1) (x2 , y 2 )
y 2 y1 5 1 4 2
Gradient = m
x2 x1 4 2 6 3
3 Find the gradient of the line joining the points (−1, 3) and (2, −3).
(x1, y1) (x2 , y 2 )
y 2 y1 3 3 6
Gradient = m 2
x2 x1 2 1 3
© Oxford University Press 2016
Straight line graphs of the form y = ax + b
1 Draw the graph of y = 2x + 1.
y
Choose 3 values of x and work
out the corresponding y values. x
4 y = 2x + 1
When x = 0, y = 2 × 0 + 1 = 1 x
When x = 1, y = 2 × 1 + 1 = 3 2
x
When x = 2, y = 2 × 2 + 1 = 5
x
-4 -2 2 4
Put the results into a table.
-2
x 0 1 2
y 1 3 5 -4
Plot the points on a graph and
join with a straight line.
© Oxford University Press 2016
2 Draw the graph of y 2 31 x.
y 2 31 x 4
When x = 3, y = 2 - ⅓ × 3 = 1 x
When x = 0, y = 2 - ⅓ × 0 = 2 2x
When x = −3, y = 2 - ⅓ × -3 = 3 x
x
-4 -2 2 4
-2
x −3 0 3
y 3 2 1 -4
© Oxford University Press 2016
Straight line graphs of the form ax + by = c
1 Draw the graph of 3x + 4y = 12.
y
The easiest method is to find the
axis crossing points. 4
x
When x = 0, 4y = 12 so y = 3. 3x + 4y = 12
2
When y = 0, 3x = 12 so x = 4.
x x
-4 -2 2 4
Put the results into a table.
-2
x 0 4
y 3 0 -4
Plot the points on a graph and
join with a straight line.
© Oxford University Press 2016
2 Draw the graph of 2x - 3y = 6.
y
The easiest method is to find the
axis crossing points. 4
When x = 0, −3y = 6 so y = −2.
2
When y = 0, 2x = 6 so x = 3.
x x
-4 -2 2 4
Put the results into a table.
-2x
x 0 3 2x - 3y = 6
y −2 0 -4
Plot the points on a graph and
join with a straight line.
© Oxford University Press 2016
You might also like
- Introduction To Differentiation - SolutionsDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Differentiation - Solutionswolfretonmaths0% (1)
- Ethics Appn FormDocument14 pagesEthics Appn FormMuminah Doray0% (1)
- HW 9514 6751 G9Unit10GraphicalSolutionsDocument54 pagesHW 9514 6751 G9Unit10GraphicalSolutionsmidnightgamer375No ratings yet
- 5-Straight Line GraphsDocument15 pages5-Straight Line GraphsSameh SalahNo ratings yet
- A5-Gradients and Straight Line GraphsDocument15 pagesA5-Gradients and Straight Line GraphsAlis AcademicNo ratings yet
- Graphs of Functions NoteDocument51 pagesGraphs of Functions NoteJJMBNo ratings yet
- Gradients and Straight Line GraphsDocument15 pagesGradients and Straight Line GraphsMayhem1105 kNo ratings yet
- Gradients and Straight Line GraphsDocument15 pagesGradients and Straight Line GraphsMayhem1105 kNo ratings yet
- Gradients and Straight Line GraphsDocument15 pagesGradients and Straight Line GraphsMayhem1105 kNo ratings yet
- Gradients and Straight Line GraphsDocument15 pagesGradients and Straight Line GraphsMayhem1105 kNo ratings yet
- Gradients and Straight Line GraphsDocument15 pagesGradients and Straight Line GraphsMayhem1105 kNo ratings yet
- Gradients and Straight Line GraphsDocument15 pagesGradients and Straight Line GraphsMayhem1105 kNo ratings yet
- The General Equation of A Straight Line y MX+CDocument9 pagesThe General Equation of A Straight Line y MX+Crewaayaqub2013No ratings yet
- The General Equation of A Straight LineDocument9 pagesThe General Equation of A Straight LineKupakwashe KampiniNo ratings yet
- Equation of Straight LineDocument9 pagesEquation of Straight LineMeiying LeeNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry Topic 6: AB X X y yDocument4 pagesCoordinate Geometry Topic 6: AB X X y ySyed Abdul Mussaver ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Simultaneous Equations: Worked Example 3.1Document8 pagesChapter 3: Simultaneous Equations: Worked Example 3.1monicaNo ratings yet
- Normal and Tangent LineDocument2 pagesNormal and Tangent LineJohn SumastreNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics: Simultaneous EquationsDocument10 pagesAdditional Mathematics: Simultaneous EquationsmdmemaNo ratings yet
- 703 Algebraic - Equations.in - One.UnknownDocument11 pages703 Algebraic - Equations.in - One.UnknownKelvin LauNo ratings yet
- Eew - ps1 - Sol (Logarithms and Exponents)Document3 pagesEew - ps1 - Sol (Logarithms and Exponents)James WigtonNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Simultaneous EquationsDocument3 pagesModule 3 - Simultaneous EquationsMohd Rizalman Mohd AliNo ratings yet
- Practice: Slopes of Parallel and Perpendicular LinesDocument2 pagesPractice: Slopes of Parallel and Perpendicular LinesLinda Yurani Carvajal AngaritaNo ratings yet
- Ap15 Calculus Ab q6Document8 pagesAp15 Calculus Ab q6Muse MusthafaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - : Precalculus - BDocument1 pageChapter 1 - : Precalculus - BRecord BouquetNo ratings yet
- 6.5 Parallel and Perpendicular LinesDocument20 pages6.5 Parallel and Perpendicular LinesAlvie Mae MagparocNo ratings yet
- Linearfunctionslopes Math 8Document26 pagesLinearfunctionslopes Math 8Misha Dela Cruz CallaNo ratings yet
- 9:05 Gradient-Intercept Form: ExerciseDocument1 page9:05 Gradient-Intercept Form: ExercisesNo ratings yet
- Math 8 Unit 3 Lesson 4 Module Slope - InterceptDocument6 pagesMath 8 Unit 3 Lesson 4 Module Slope - Interceptmary joy buliagNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce Vs Commerce - 1Document21 pagesE-Commerce Vs Commerce - 1rizwan ziaNo ratings yet
- SPM Format PracticeDocument150 pagesSPM Format Practicechunhsienwc68338711100% (1)
- Slope and Equations of LinesDocument10 pagesSlope and Equations of LinesBryle WizardNo ratings yet
- Characteristic of Linear Graphs: Linear Graph Equations Are Normally Written in The FormDocument17 pagesCharacteristic of Linear Graphs: Linear Graph Equations Are Normally Written in The Formlucybaik24No ratings yet
- Notes Slope, Distance, MidpointDocument6 pagesNotes Slope, Distance, MidpointAbhilash Reddy100% (1)
- CoordinateDocument9 pagesCoordinateGabriel ChicasNo ratings yet
- 2CA Maths Unit03 Graphs Rev2 19nov09Document25 pages2CA Maths Unit03 Graphs Rev2 19nov09ankitNo ratings yet
- 2022 - T1 - WK5 - Linear Relationship L3Document6 pages2022 - T1 - WK5 - Linear Relationship L3cha0tic.cookiemxnsterNo ratings yet
- Skema Trial PHG p2 2013Document11 pagesSkema Trial PHG p2 2013Hazuriada HanafiNo ratings yet
- Sri Sri Ravishankar Vidya Mandir, Indore Subject - Mathematics Date: 12/08/2023 Worksheet:-Vrctors and 3-D Class - XiiDocument4 pagesSri Sri Ravishankar Vidya Mandir, Indore Subject - Mathematics Date: 12/08/2023 Worksheet:-Vrctors and 3-D Class - XiiJatin MoolchandaniNo ratings yet
- Linear Functions Review 20-50Document9 pagesLinear Functions Review 20-50Alberto EcheverriNo ratings yet
- 9:06 Point-Gradient Form: ExerciseDocument1 page9:06 Point-Gradient Form: ExercisesNo ratings yet
- Solution P 1 Jan 19Document16 pagesSolution P 1 Jan 19hasan zaidiNo ratings yet
- C3 Modulus Functions PDFDocument5 pagesC3 Modulus Functions PDFatul kumarNo ratings yet
- C3 Modulus FunctionsDocument5 pagesC3 Modulus Functionsatul kumarNo ratings yet
- Co-Ordinate GeometryDocument7 pagesCo-Ordinate GeometryHugh IngramNo ratings yet
- Part II Conic SectionsDocument23 pagesPart II Conic SectionsicbbattadNo ratings yet
- 2018 Additional Mathematics PamphletDocument127 pages2018 Additional Mathematics PamphletJacklim NdhlovuNo ratings yet
- Relations and Functions (Mathematics) : Relation Domain Abscissae Range OrdinatesDocument4 pagesRelations and Functions (Mathematics) : Relation Domain Abscissae Range Ordinatesarnab_rc_007No ratings yet
- 4th Gradient SheetDocument1 page4th Gradient SheetNazir RashidNo ratings yet
- Aga A1 0204 Ap AkDocument1 pageAga A1 0204 Ap Akdeepaksharma1976No ratings yet
- Help Sheet For Week 3Document12 pagesHelp Sheet For Week 3Kira L. MorrisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4,5 &6Document12 pagesLesson 4,5 &6zyx xyzNo ratings yet
- 3-Graph 0Document7 pages3-Graph 0CSP EDUNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary LevelDocument4 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary LevelEema AminNo ratings yet
- Parabols and QuadraticsDocument5 pagesParabols and QuadraticsJohn ManciaNo ratings yet
- Autumn Break Home Work Class 12-2023Document2 pagesAutumn Break Home Work Class 12-2023Ramya ChandraNo ratings yet
- CG-1 (Basic) : Xis EducationDocument5 pagesCG-1 (Basic) : Xis EducationAbrar ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- 08 Apr MorningDocument18 pages08 Apr Morninganujku9245No ratings yet
- 2Document1 page2api-44813426250% (2)
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- Solving Linear Equations: © Oxford University Press 2016Document21 pagesSolving Linear Equations: © Oxford University Press 2016Muminah DorayNo ratings yet
- Averages and Range: © Oxford University Press 2016Document7 pagesAverages and Range: © Oxford University Press 2016Muminah DorayNo ratings yet
- Direct and Inverse Proportion: © Oxford University Press 2016Document9 pagesDirect and Inverse Proportion: © Oxford University Press 2016Muminah DorayNo ratings yet
- Symmetry: © Oxford University Press 2016Document27 pagesSymmetry: © Oxford University Press 2016Muminah DorayNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document57 pagesModule 4Muminah DorayNo ratings yet
- 6 Resource and Material Development3Document29 pages6 Resource and Material Development3Muminah DorayNo ratings yet
- Work Very Near Others, Within A Few Feet or Less. ... Are Exposed To Loud Sounds and High Noise Levels On A WeeklyDocument1 pageWork Very Near Others, Within A Few Feet or Less. ... Are Exposed To Loud Sounds and High Noise Levels On A WeeklyMuminah DorayNo ratings yet
- Ethics Application TemplateDocument6 pagesEthics Application TemplateMuminah DorayNo ratings yet
- As Level Biology Summary Notes (2022-2024 Syllabus)Document5 pagesAs Level Biology Summary Notes (2022-2024 Syllabus)ElisaNo ratings yet
- Omniclass: Description and Illustration: Rajan F CDocument22 pagesOmniclass: Description and Illustration: Rajan F CTomas SirusasNo ratings yet
- BFC3042 BFC31802Document13 pagesBFC3042 BFC31802Zuliyah ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Alfred Sds ProjectDocument10 pagesAlfred Sds ProjectMr TuchelNo ratings yet
- BS Iso 21573-1-2014Document32 pagesBS Iso 21573-1-2014Salafi MhmdNo ratings yet
- Beam Number: Project Name: 17-Mar-20 Engr. Mark Christian D. Esguerra Passed Engineer: DateDocument1 pageBeam Number: Project Name: 17-Mar-20 Engr. Mark Christian D. Esguerra Passed Engineer: DateMark Christian EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Regular Expressions in Perl::-KLK Mohan, 200841011, M.Tech, VLSIDocument18 pagesRegular Expressions in Perl::-KLK Mohan, 200841011, M.Tech, VLSISudheer PrasadNo ratings yet
- Exambank HigherDocument62 pagesExambank HigherJust WadeNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study On Partial Replacement of Fine Aggregate With Quarry Dust and Saw DustDocument13 pagesExperimental Study On Partial Replacement of Fine Aggregate With Quarry Dust and Saw DustPerarasan MNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Manual Training Presentation - R.ADocument232 pagesMaintenance Manual Training Presentation - R.AYasir Ammar100% (3)
- Prosthetic Arm For AmputeesDocument6 pagesProsthetic Arm For AmputeesPratik ParsewarNo ratings yet
- 84 Cómo Crear Una User Exit para Activos Fijos ANLUDocument8 pages84 Cómo Crear Una User Exit para Activos Fijos ANLUPedro Francisco GomezNo ratings yet
- Group 3 (Seksyen4) (1) (Repaired)Document15 pagesGroup 3 (Seksyen4) (1) (Repaired)alnzNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument11 pagesPhysics ProjectDimpySurya44% (25)
- Power World Simulator 8 TutorialDocument8 pagesPower World Simulator 8 TutorialMauricio VargasNo ratings yet
- 2014oct FE PM QuestionDocument34 pages2014oct FE PM QuestionShwe Yee Win ThantNo ratings yet
- ISODRAFT Reference ManualDocument248 pagesISODRAFT Reference Manualgabi_nanaNo ratings yet
- Thanh Huyen - Week 5 - Final Test AnswerDocument3 pagesThanh Huyen - Week 5 - Final Test AnswerNguyễn Sapphire Thanh HuyềnNo ratings yet
- IET DAVV 2014 Com2Document12 pagesIET DAVV 2014 Com2jainam dudeNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document6 pagesBook 1Team UnitedNo ratings yet
- g484 Physics Newtonian World Notes Ocr Robbie PeckDocument10 pagesg484 Physics Newtonian World Notes Ocr Robbie Peckapi-236179294No ratings yet
- FMS 304 Research Methodology - 0 PDFDocument188 pagesFMS 304 Research Methodology - 0 PDFvicky100% (2)
- AL8860EV2 User GuideDocument8 pagesAL8860EV2 User GuideHans ClarinNo ratings yet
- Business Magazine SOFIA FABALDocument4 pagesBusiness Magazine SOFIA FABALSofia FabalNo ratings yet
- 785 Truck Electrical System: 8GB418-UPDocument2 pages785 Truck Electrical System: 8GB418-UPEdwin Ruiz VargasNo ratings yet
- Summit X670 Series: Product OverviewDocument10 pagesSummit X670 Series: Product OverviewAlex KramerNo ratings yet
- Dexxum TDocument15 pagesDexxum Tfrancisco mugica quintanaNo ratings yet
- Website Layout Design in Corel DrawDocument111 pagesWebsite Layout Design in Corel DrawFathoni WangsadranaNo ratings yet
- AC Resistance and Impedance in An AC Circuit PDFDocument20 pagesAC Resistance and Impedance in An AC Circuit PDFKamal CharbelNo ratings yet
- Difference Between DWA and TEB Local PlannersDocument2 pagesDifference Between DWA and TEB Local PlannersChandrajit GangulyNo ratings yet