Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Photo
Photo
Uploaded by
victoria.huggins0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views19 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views19 pagesPhoto
Photo
Uploaded by
victoria.hugginsCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
Chapter 4
The Energy of Life
Photosynthesis
● Some organisms, known as producers, use energy
from the sun to make organic molecules
● Autotroph- organism that gets energy by making it
out of light or chemicals
● Heterotroph- organism that gets its energy by eating
other organisms
● Plants are producers and use energy from the sun to
make glucose out of atmospheric CO2
● Photosynthesis- process by which light energy is
converted to chemical energy
● Takes place in the chloroplast
● Chlorophyll- molecule that absorbs light energy in the
chloroplast
2 steps in photosynthesis
1. Light-dependent reactions- captures energy from
sunlight to make O2, energy carrying molecules, and
ATP
2. Light- independent reactions- use energy made in
light-dependent reactions to make sugars from CO2;
also called the Calvin cycle
I expect you to know where the processes happen,
what goes IN, and what goes OUT
Overall reaction:
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Notice how it is the cellular respiration equation
BACKWARDS!
● Plants are producers
● One of the main sources of energy for most organisms on Earth
● The energy for almost all organisms begins as sunlight
● Light energy comes from the sun
● Sunlight includes several kinds of energy, such as
ultraviolet radiation, microwaves, and the visible light
spectrum
● Visible light appears white but is made of several
colors/wavelengths of light
● The process that captures energy
from sunlight to make sugars that
store chemical energy is called
photosynthesis
● Photosynthesis- process by which
light energy is converted to
chemical energy; produces sugar
and oxygen from carbon dioxide
and water
● Plants absorb visible light for
photosynthesis
● Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplast of plant cells
● The molecule in the chloroplast that absorbs the
energy in visible light is called chlorophyll
● 2 types of chlorophyll in plants: chlorophyll a and
chlorophyll b
● Chlorophyll absorbs mostly red and blue wavelengths
of light, NOT green light
● The green color of plants comes from the reflection
of the wavelength of light that shows green
● Plants absorb red/blue light, reflect green light
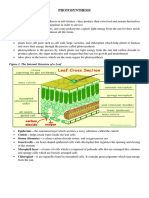
● Most chloroplasts are in leaf cells
● The 2 main parts of the chloroplast needed for photosynthesis are the
grana (singular: granum) and the stroma
● Grana are stacks of structures called thylakoids
● Thylakoids are coin shaped,
membrane-enclosed compartments
● Thylakoids contain chlorophyll,
light-absorbing molecules, and
proteins
● The inside of the thylakoid is
called the lumen
● Grana are surrounded by a fluid
called the stroma
Overall reaction for photosynthesis:
6CO2 + 6H2O + light → C6H12O6 + 6O2
1. Light-dependent reactions
● Depends on the presence of light to occur
● If there’s no light, there’s no light-dependent
reactions
● “Photo” part of photosynthesis
● Happens across the thylakoid membrane
● Chlorophyll captures energy from sunlight
● Water molecules are broken down to make hydrogen
ions, electrons, and oxygen gas
● Main function of the light-dependent reactions is to
capture and transfer energy
Summary of Light-dependent Reactions
● Energy is captured from sunlight by light-absorbing
molecules (chlorophyll). The energy is transferred to
electrons that enter the electron transport chain
● Water molecules are broken down into H+ ions, electrons,
and O2 molecules
● Energized electrons provide energy for H+ ion transport
and are added to NADP+ to form NADPH
● The flow of H+ ions through ATP synthase makes ATP
● Where is happens: across the thylakoid membrane
● What goes in: electrons and water
● What goes out: oxygen, NADPH, and ATP
2.Light-independent reactions
● Also called the Calvin Cycle
● Does not need sunlight to occur
● Can happen any time that energy from the light-
dependent reactions is available
● Energy sources are ATP and NADPH
● Uses carbon dioxide and energy to make simple
sugars
● “Synthesis” part of photosynthesis
Summary of Light-independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle)
● Carbon dioxide enters the Calvin cycle
● ATP and NADPH from the light-dependent reactions transfer
energy to the Calvin and keeps the cycle going
● One high-energy 3-carbon molecule is made for every three
molecules of carbon dioxide that enter the cycle
● Two high-energy 3-carbon molecules are bonded together to
make a sugar. 6 molecules of carbon dioxide must be added to
the Calvin cycle to make one 6-carbon sugar
● Where it happens: in the stroma
● What goes in: CO2, ATP, and NADPH
● What goes out: a sugar, NADP+, and ADP
You might also like
- Photosynthesis Interactive NotebookDocument26 pagesPhotosynthesis Interactive NotebookAshley Farnham67% (3)
- Crop Science PDFDocument7 pagesCrop Science PDFGowtham100% (1)
- Science - G9 - Week 7 (Lessons 19-20)Document19 pagesScience - G9 - Week 7 (Lessons 19-20)L.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology June 2011 P2Document17 pagesCSEC Biology June 2011 P2school yourschoolNo ratings yet
- Lect. 8Document21 pagesLect. 8أحمدشريفNo ratings yet
- GenBio - PhotosynthesisDocument3 pagesGenBio - PhotosynthesisHeaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument28 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular RespirationGlena MendozaNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument31 pagesPhotosynthesisnatheerohgamieldienNo ratings yet
- What Are The Parts of The Cell?Document31 pagesWhat Are The Parts of The Cell?Karl Wyndyll LambanNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Light Energy From The Sun Is Converted To Chemical Energy That Is Stored in SugarDocument47 pagesPhotosynthesis: Light Energy From The Sun Is Converted To Chemical Energy That Is Stored in Sugarpsamuel24No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular RespirationFatima DariaNo ratings yet
- BiomassNotes 2019Document155 pagesBiomassNotes 2019Jonathan WrightNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics: Is The Study of How Energy Flows Through Living CellsDocument49 pagesBioenergetics: Is The Study of How Energy Flows Through Living CellsRy CyNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Using Light To Make Food: UsuallyDocument12 pagesPhotosynthesis: Using Light To Make Food: UsuallyMARCO ANTONIO CONDOR CHAVEZNo ratings yet
- FotosintesisDocument51 pagesFotosintesisDwi HardianiNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument77 pagesPhotosynthesisapi-300804410No ratings yet
- BIO1 Lesson-12 PhotosynthesisDocument36 pagesBIO1 Lesson-12 PhotosynthesisCath Detoperez100% (1)
- Biology Unit 4 Part 1 Last Minute Revision ReallyacademicsDocument67 pagesBiology Unit 4 Part 1 Last Minute Revision ReallyacademicsWill AndyNo ratings yet
- BIOLS102-UOB-Chapter 7Document13 pagesBIOLS102-UOB-Chapter 7Noor JanahiNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis (Light Reaction)Document19 pagesPhotosynthesis (Light Reaction)hatimiNo ratings yet
- Energy TransformationDocument4 pagesEnergy TransformationAsh Nico BanquilloNo ratings yet
- SSGBIO1 - CM Week 7Document61 pagesSSGBIO1 - CM Week 7christine ManuelNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Humss Grade 11Document22 pagesEarth and Life Science: Humss Grade 11Micaela Castillo100% (4)
- The Basics of Photosynthesis: - Almost All Plants Are Photosynthetic Autotrophs, As Are Some Bacteria and ProtistsDocument43 pagesThe Basics of Photosynthesis: - Almost All Plants Are Photosynthetic Autotrophs, As Are Some Bacteria and ProtistsYesenia Shashi AnastaNo ratings yet
- BIOL101 Ch7 Pt1Document19 pagesBIOL101 Ch7 Pt1marwa haribNo ratings yet
- Class-Xi Biology Study Material 2022-23Document21 pagesClass-Xi Biology Study Material 2022-23devil luciferNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument48 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respirationharold carbonelNo ratings yet
- Hotosynthesis: Big PictureDocument3 pagesHotosynthesis: Big Picturehomamunfat100% (1)
- Photosynthesis Cellular RespirationDocument27 pagesPhotosynthesis Cellular RespirationSamantha De CastroNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument37 pagesPhotosynthesisRestuad TvNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration-0Document49 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respiration-0Zulhanif IdrisNo ratings yet
- 9 1photosynthesis-FinalDocument36 pages9 1photosynthesis-FinalHara Vienna ClivaNo ratings yet
- 4 Cell RespirationDocument20 pages4 Cell RespirationCristina MaquintoNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesisv 3Document40 pagesPhotosynthesisv 3Sofia CorderoNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Study Guide Photosynthesis Equation: 6CO2 + 6H2O - C6H12O6 + 6O2Document4 pagesPhotosynthesis: Study Guide Photosynthesis Equation: 6CO2 + 6H2O - C6H12O6 + 6O2vscolegit shoppeNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer.Document3 pagesScience Reviewer.harlanecarlsNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument24 pagesPhotosynthesisDexter Armamento Sulit100% (3)
- Light Dependent ReactionDocument11 pagesLight Dependent ReactionKarla InsoNo ratings yet
- GenBio 1 - 2nd Quarter ReviewerDocument8 pagesGenBio 1 - 2nd Quarter Reviewerjoshua tejadaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Energy TransformationsDocument49 pagesUnit 5 Energy TransformationsFiguracion, Zhass Naye D.No ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument25 pagesTrigonometryhadeelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5:genetic Control & Protein Synthesis (Week 10 & 11)Document58 pagesChapter 5:genetic Control & Protein Synthesis (Week 10 & 11)RabbitNo ratings yet
- Integrated ScienceDocument12 pagesIntegrated ScienceMalinda GreeneNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and RespirationDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis and RespirationChristian BaleNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument6 pagesPhotosynthesispwssewwandiNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Power Point NotesDocument22 pagesPhotosynthesis Power Point NotesJohn SchmidtNo ratings yet
- Biology 2.1: Electrical Energy (Electrons Become Excited (Energised) )Document3 pagesBiology 2.1: Electrical Energy (Electrons Become Excited (Energised) )Sel 7No ratings yet
- Q2 GenBio Reviewer 2Document21 pagesQ2 GenBio Reviewer 2Kaye BaloranNo ratings yet
- Utilizing Energy For LifeDocument41 pagesUtilizing Energy For LifeJOHN PAUL MACALLINGNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Unit 2 Study GuideDocument2 pagesAP Bio Unit 2 Study GuideRana MehaiNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument22 pagesPhotosynthesislaNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument23 pagesPhotosynthesisepick7No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis PDFDocument21 pagesPhotosynthesis PDFShegNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesispresentationbyme 120608123750 Phpapp01Document23 pagesPhotosynthesispresentationbyme 120608123750 Phpapp01Shaquille McdonaldNo ratings yet
- By The End of This Lecture You Will Be Able To:: Light-Dependent Reactions (I.e., Light Reactions)Document35 pagesBy The End of This Lecture You Will Be Able To:: Light-Dependent Reactions (I.e., Light Reactions)reziegeoNo ratings yet
- By The End of This Lecture You Will Be Able To:: Light-Dependent Reactions (I.e., Light Reactions)Document35 pagesBy The End of This Lecture You Will Be Able To:: Light-Dependent Reactions (I.e., Light Reactions)monica_elysabethNo ratings yet
- Form Carbohydrate That Is Usable by The BodyDocument5 pagesForm Carbohydrate That Is Usable by The BodyEmman RevillaNo ratings yet
- Plants and Other Autotrophs Are The Producers of The BiosphereDocument12 pagesPlants and Other Autotrophs Are The Producers of The Biosphereюрий локтионовNo ratings yet
- 10 Photosynthesis NotesDocument7 pages10 Photosynthesis NotesancientblackdragonNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Pathways: Chapter 6 and 7 From Text BookDocument46 pagesBiochemical Pathways: Chapter 6 and 7 From Text BookSnehal SinghNo ratings yet
- CS01-Chapter 2Document48 pagesCS01-Chapter 2AJ MoralesNo ratings yet
- 8.3 NotesDocument16 pages8.3 NotesEliazbethNo ratings yet
- Exampel ProjDocument3 pagesExampel Projvictoria.hugginsNo ratings yet
- Central DogmaDocument37 pagesCentral Dogmavictoria.hugginsNo ratings yet
- Homology & Convergent EvolutionDocument4 pagesHomology & Convergent Evolutionvictoria.hugginsNo ratings yet
- Butterflies - 9wks ExDocument21 pagesButterflies - 9wks Exvictoria.hugginsNo ratings yet
- DNA RaceDocument28 pagesDNA Racevictoria.hugginsNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 1 Term 1 2 3 Schemes of Work Lg2fcyDocument14 pagesBiology Form 1 Term 1 2 3 Schemes of Work Lg2fcySamson OdhiamboNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis Assignment - PhotosynthesisDocument1 pageData Analysis Assignment - PhotosynthesisJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- ODB - Bio (Botany)Document1 pageODB - Bio (Botany)aloevera1994No ratings yet
- SHS Core - Earth and Life Science CG - 0Document10 pagesSHS Core - Earth and Life Science CG - 0Jhullienne Jabat100% (1)
- Plant and Animal Organ Systems and Their Functions: (Nutrient Procurement and Processing, and Gas Exchange)Document28 pagesPlant and Animal Organ Systems and Their Functions: (Nutrient Procurement and Processing, and Gas Exchange)Ica A TorioNo ratings yet
- O LEVEL BIOLOGY O/N 2020 PAPER 11 (5090 - w20 - QP - 11)Document20 pagesO LEVEL BIOLOGY O/N 2020 PAPER 11 (5090 - w20 - QP - 11)ImanNo ratings yet
- Bioprime'sDocument46 pagesBioprime'sINKPAT & CO.No ratings yet
- Form Carbohydrate That Is Usable by The BodyDocument5 pagesForm Carbohydrate That Is Usable by The BodyEmman RevillaNo ratings yet
- DLL SHS STEM Science Grade 11 - Earth & Life Quarter2 Week3 (Palawan Division)Document10 pagesDLL SHS STEM Science Grade 11 - Earth & Life Quarter2 Week3 (Palawan Division)Dalgo Spplies100% (2)
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument20 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary Levelrashmi_harryNo ratings yet
- Assertion and Reason Biology Selina 2025 Edition-1Document6 pagesAssertion and Reason Biology Selina 2025 Edition-1Joy KakodkarNo ratings yet
- The Living Earth - Lost Creatures of The Earth PDFDocument273 pagesThe Living Earth - Lost Creatures of The Earth PDFAna MantillaNo ratings yet
- Plant PigmentsDocument12 pagesPlant PigmentsvazsonzijuliaNo ratings yet
- PLB 101Document9 pagesPLB 101shishirchemNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2 - Module 7 Components of An Ecosystem: Biotic and AbioticDocument15 pagesScience: Quarter 2 - Module 7 Components of An Ecosystem: Biotic and AbioticPinky Vitalicio SeñaNo ratings yet
- Rwamagana District Exam 2023 S4 BiologyDocument15 pagesRwamagana District Exam 2023 S4 BiologyMutaganda Ami fidele100% (1)
- Mock 2 IRDocument3 pagesMock 2 IRWendell Kim LlanetaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Exam-Sample Paper 1Document19 pagesCambridge Exam-Sample Paper 1Pon KrithikhaNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS Proving PhotosynthesisDocument10 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESIS Proving PhotosynthesisMadhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- Leafy Matters 1: Name ClassDocument1 pageLeafy Matters 1: Name ClassElsa MartinezNo ratings yet
- ExcerptDocument10 pagesExcerptIsini sehansa amarathungaNo ratings yet
- Focus Batch PCB Test 25Document72 pagesFocus Batch PCB Test 25Aditya rajNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Paper 6 Practical Notes - Cattaystudies - 220825 - 183805Document11 pagesIGCSE Biology Paper 6 Practical Notes - Cattaystudies - 220825 - 183805Eydie WongNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Cellular Energy Worksheet With AnswersDocument2 pagesUnit 5 Cellular Energy Worksheet With AnswersJohn Daniel AntolinNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/22Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/22yevajainnNo ratings yet
- Introduction - What Is An Ecosystem?Document9 pagesIntroduction - What Is An Ecosystem?Gaurav YadavNo ratings yet