0% found this document useful (0 votes)
106 views27 pagesRadiographic Object Localization Techniques
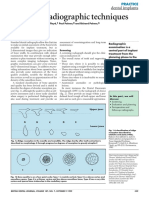
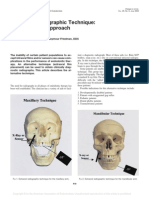
Object localization is a method used to locate the position of tooth or foreign object present inside the jaws. This document discusses techniques for localizing objects using radiography. Two basic techniques are used to localize objects: the buccal object rule and the right-angle technique
Uploaded by
immortalneoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
106 views27 pagesRadiographic Object Localization Techniques
Object localization is a method used to locate the position of tooth or foreign object present inside the jaws. This document discusses techniques for localizing objects using radiography. Two basic techniques are used to localize objects: the buccal object rule and the right-angle technique
Uploaded by
immortalneoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd