Professional Documents
Culture Documents
National Income: Click To Edit Master Subtitle Style
Uploaded by
ashpakkhatikOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
National Income: Click To Edit Master Subtitle Style
Uploaded by
ashpakkhatikCopyright:
Available Formats
National Income
Click to edit Master subtitle style
5/13/12
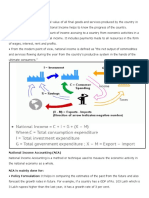
Gross Income Vs Net Income
During the process of production, machinery and equipment which is a part of gross capital formation usually wears out(depreciates) or becomes obsolete. This is called as Consumption of Fixed Capital. To the extent there is wear and tear and the amount produced is used for replacement. To get more accurate estimation of the output generated in an economy one needs to take account of the net value of investment or net capital formation.
5/13/12
Gross Income Vs Net Income Cont
Gross Fixed Capital Formation = Net Fixed Capital Formation + Depreciation. Gross Capital Formation (Gross Investment) = Gross Fixed Capital Formation + Change in Stock of Inventories. Net Fixed Capital Formation = Gross Fixed Capital Formation Depreciation. Net Capital Formation = Net Fixed Capital Formation + Change in Stock of Inventories.
5/13/12
Market Price Vs Factor Cost
The market price (mp) is the same as the factor cost (fc).These two prices would be the same if the government is neither imposing any tax on commodities nor providing any subsidy to the producer. Hence, the market price faced by the households while purchasing commodities is the same as the factor cost faced by the producers of these commodities. However, when government imposes taxes on commodities and provides subsidies to the producers the market price differs from factor 5/13/12 cost.
Market Price Vs Factor Cost Cont
The market value of goods and services includes indirect taxes in the form of sales tax and excise duties. These are indirect as they are levied on sellers and may be shifted to buyers in form of market prices for commodities. The market value also includes subsidies that are provided by the government to the producers for selling their products at lower prices. Thus, indirect taxes increase the price, whereas subsidies reduce the price of the commodity. In order to equate factor cost to market prices, 5/13/12
Domestic Income Vs National Income
Domestic output is the output generated within the domestic territory of the country which includes the output generated within the political territory including the territorial waters, income generated by the ships and aircrafts operated by the country and also the income generated by the embassies; government offices located abroad but excludes all the income generated by the foreign embassies and offices of international organizations located in the political territory. National income or output refers to the income or output produced by the normal residents of the country. Normal residents are those individuals who normally 5/13/12
Domestic Income Vs National Income
The normal residents of the country can generate income/output not only inside the domestic territory but also outside the domestic territory by supplying factor inputs abroad. For supply of these factor inputs they receive factor income from abroad. On the contrary , the normal residents of other countries also provide factor inputs to the domestic territory and thereby receive factor payments from them. This is referred to as the factor payments made abroad. National Income (Product) = Domestic (Product) + Net Factor Income From Abroad. Income
Net Factor Income From Abroad = Factor Income 5/13/12 Received From Abroad Factor Payment Made to the
Eight Possible Combinations of National Product Aggregates
GNPM P NNPMP GDPMP GNPF C
NNP FC NDPMP NDPFC
5/13/12
GDPFC
Eight Possible Combinations of National Product Aggregates Cont
Gross= Net + Depreciation Market Prices= Factor Cost + (Indirect taxes Subsidies) National= Domestic + Net Factor Income from Abroad (NFIA)
NDPFC = Compensation of the Employees (CoE) + Operating Surplus (OS) + Mixed Income of the Self Employed (MISE) NDPMP = Net Indirect Taxes + NDPFC GDPFC = Consumption of Fixed Capital + NDPFC GDPMP= Net Indirect Taxes + GDPFC 5/13/12
Eight Possible Combinations of National Product Aggregates Cont
There are four categories of factor incomes: Compensation of employees (CoE), rent interest and profit. CoE is the total remuneration in cash, kind and in term of social security contributions by employers to their employees. The sum of rent, interest and profit is called Operating Surplus (OS). Hence there are two basic categories of factor incomes: CoE and OS. Mixed Income is a mixture of CoE and OS. The sum total of factor payments (CoE + OS) by all the production units located within the 5/13/12
Eight Possible Combinations of National Product Aggregates Cont
Net Factor Income from Abroad (NFIA) is the difference between the income received from abroad by the residents for rendering factor services abroad and the income paid to the non residents for rendering services within the economic territory. The three component of NFIA are: Net CoE received from abroad (CoE received by residents from abroad - CoE paid to nonresidents) Net OS (OS received by residents from abroad OS paid to non-residents)
5/13/12
(a)
(b)
(c)
Net Retained Earnings of Resident Companies
National Income
Income of an individual is an important determinant of his/her consumption level, investment and standard of living in a given period of time. National income is the measurement of overall income generated in an economy. It represents the money value of all final goods and services (output) produced in a country in a given period of time especially during an accounting year (avoiding the problem of double counting).
5/13/12
National Income Cont.
Data on, and trend in national income and the related aggregates, such as gross domestic product, net domestic product , gross national product and net national product are placed in National Income Accounts. The collection and analysis of this data is referred to as National Income accounting. While estimating, collecting and analyzing of the data economists use various variables like flow variables and stock variables.
5/13/12
National Income Cont.
The flow variables are those variables which are estimated over a period of time like budget deficits, investment expenditure, and capital formation and income (household, national, per capita). Stock variables are those variables which are estimated at a particular point of time like wealth(accumulation of savings), debt (accumulation of borrowings), and capital stock (factories, machines and inventories).
5/13/12
National Income Cont.
Almost all countries have some form of official national income account. For example, in the U.S., the national income accounts are officially known as National Income and Product Account (NIPA) which are constructed quarterly by the government, economists and statisticians in the Bureau of Economic Analysis(BEA). In India the Central Statistical Organization (CSO) regularly compiles and publishes the National Account Statistics (NAS).
5/13/12
Types of National Income
National income at current prices: Goods and services included in national valued at the income
prices of the same year. It reflects changes in prices as well as physical Production. National income at constant prices: Goods and services included in national income valued at the prices of some chosen year, called the base year. It reflects changes
5/13/12
Measurement of National Income
There are three measurements of national income:
1.
Value added method Income method Expenditure method
2.
3.
5/13/12
Value Added Method
Classify production units into industrial sectors. Estimate Net Value Added at factor Cost (NVAFC) of each industrial sector which involves estimates of value of output, intermediate consumption, consumption of fixed capital, net indirect taxes. Calculate the sum of NVAFC arrive at NDPFC. Add NFIA to NDPFC to 5/13/12 National Income. by all sectors to
arrive at NNPFC
or
Income Method
Classify production units into industrial sectors. Estimate factor incomes (CoE, rent, interest, profit) paid out by each sector which equals to NVA FC. Calculate the sum of NVAFC arrive at NDPFC. Add NFIA to NDPFC to National Income.
5/13/12
by all
sectors to
arrive at NNPFC
or
Expenditure Method
Classify production units into industrial sectors. Estimate final expenditures on goods and services produced by these sectors - Private Final Consumption Expenditure, Government Final Consumption Expenditure, Gross Domestic Capital Formation and Net Exports. Calculate the sum of these final expenditures to get GDPMP. Estimate consumption of fixed capital and net indirect taxes and deduct from GDPMP to get 5/13/12
Problems in the Measurement of National Income
Exclusion of value of personal services rendered to oneself in the national product accounts. Non-market activities and imputation. Changes in the inventories valuation adjustment. and inventory
Final product-current and constant rupees.
5/13/12
Uses of National Income Estimates
Measures of economic growth Indicator of success or failure of planning Indicator of structural changes Measure of income inequalities Indicator of the pattern of consumption and investment International and spatial comparisons Measurement of business cycles
5/13/12
Transfer Payments
A transfer is a transaction in which the payer provides a good, service or an asset without receiving from the recipient any good, service or asset in return. Current Transfer: A transfer made out of current income of the payer and added to the current income of the recipient. Capital Transfer: A transfer made out of wealth or capital of the payer and added to the wealth or capital of the recipient.
5/13/12
National Income to Personal Outlays
The total income that is actually received by the households is known as Personal Income (PI) which represents the flow of aggregate income to the households from other sectors. Personal Income (PI) = NNPFC Undistributed Profits Corporate Taxes + Transfer Payments . Personal income differs from disposable income by the amount of direct taxes paid by the individuals.
5/13/12 Deducting personal income tax (a form of direct
The amount of disposable income that is left after total spending in a year is referred to as Personal Saving (PS).Thus, subtracting personal saving from disposable personal income one gets Personal Outlays (PO). PO = DPI - PS
National Income to Personal Outlays Cont
5/13/12
Thank You
5/13/12
You might also like
- Offices of Bank Holding Company Revenues World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryFrom EverandOffices of Bank Holding Company Revenues World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryNo ratings yet
- Module - 4 National IncomeDocument64 pagesModule - 4 National Incomelakshmi dileepNo ratings yet
- National Income Accounting: Economics, 7 Edition Boyes and Melvin Houghton Mifflin Company, 2008Document26 pagesNational Income Accounting: Economics, 7 Edition Boyes and Melvin Houghton Mifflin Company, 2008Asad NaseerNo ratings yet
- Nationalincome 141209072252 Conversion Gate02Document37 pagesNationalincome 141209072252 Conversion Gate02Simmi KhuranaNo ratings yet
- National Income Accounting (NIA)Document8 pagesNational Income Accounting (NIA)Mamta VermaNo ratings yet
- Macro Economics: National Income Fiscal Policy Monetary Policy Trade CyclesDocument48 pagesMacro Economics: National Income Fiscal Policy Monetary Policy Trade Cyclesusne902No ratings yet
- Macroeconomic Analysis For Management 1 - Chapter 3Document21 pagesMacroeconomic Analysis For Management 1 - Chapter 3dawsonNo ratings yet
- National Income-Concepts and MeasurementsDocument34 pagesNational Income-Concepts and MeasurementsSonali SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture TwoDocument49 pagesLecture TwoBilliee ButccherNo ratings yet
- NatioDocument16 pagesNatioNisar Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- National Income and Occupational Structure in IndiaDocument45 pagesNational Income and Occupational Structure in IndiaakshatNo ratings yet
- Ofp 015Document51 pagesOfp 015abdul ahmad kilimaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 NewDocument94 pagesUnit 5 NewrajapatnaNo ratings yet
- National Income: - by Shikha SinghDocument40 pagesNational Income: - by Shikha SinghPrashastiNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument18 pagesNational Incomepankajpatidar7440No ratings yet
- Measuring a Nation's Economy: An Introduction to National IncomeDocument13 pagesMeasuring a Nation's Economy: An Introduction to National IncomeRatika GuptaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 NewDocument94 pagesUnit 5 NewrajapatnaNo ratings yet
- A New Approach To National Income AccountingDocument8 pagesA New Approach To National Income AccountingDaodu Ladi BusuyiNo ratings yet
- National Income - ConceptsDocument21 pagesNational Income - ConceptsKunal GargNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument81 pagesNational IncomeGaurav gusaiNo ratings yet
- National Income Concept and MeasurementDocument33 pagesNational Income Concept and Measurementriteshlal100% (1)
- National Income: By-Roopak Malik & Raneesh ChoudharyDocument18 pagesNational Income: By-Roopak Malik & Raneesh Choudharyemin4No ratings yet
- Revision Notes For Class 12 Macro Economics Chapter 2 - Free PDF DownloadDocument17 pagesRevision Notes For Class 12 Macro Economics Chapter 2 - Free PDF DownloadVibhuti BatraNo ratings yet
- National Income-1Document17 pagesNational Income-1Ms. Vandana MohantyNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument24 pagesNational IncomePranay Sai Garepally100% (1)
- National IncomeDocument7 pagesNational IncomeFahadNo ratings yet
- MN 304 - National Accounting and Macro Economics - 7Document34 pagesMN 304 - National Accounting and Macro Economics - 7Nipuna Thushara WijesekaraNo ratings yet
- National Income: Presented by Asst - Prof Nimbolkar V.R. MBA Finance (SET)Document18 pagesNational Income: Presented by Asst - Prof Nimbolkar V.R. MBA Finance (SET)Atul BorbaneNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument32 pagesNational IncomeSona VermaNo ratings yet
- Concepts of National IncomeDocument35 pagesConcepts of National IncomeChitraksh MahajanNo ratings yet
- The National Income Accounting 1Document15 pagesThe National Income Accounting 1Kyle Kenneth GarciaNo ratings yet
- Measurement of National Income Types Methods Benefits and Problems Associated E6766766Document9 pagesMeasurement of National Income Types Methods Benefits and Problems Associated E6766766RohanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document40 pagesChapter 2Seamnia demoNo ratings yet
- Zica Accountancy Programme: Macro Economics (Zica) AccountingDocument163 pagesZica Accountancy Programme: Macro Economics (Zica) AccountingAmir MirNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument29 pagesNational IncomegipaworldNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument11 pagesEconomicsAMITNo ratings yet
- National Income AccountingDocument18 pagesNational Income AccountingDeepikaa PoobalarajaNo ratings yet
- Chap I National IncomeDocument34 pagesChap I National IncomeVAISALY S MBANo ratings yet
- National Income in India, Concept and MeasurementDocument87 pagesNational Income in India, Concept and MeasurementPreeti BajajNo ratings yet
- Measurement of National Income: Modula 4Document12 pagesMeasurement of National Income: Modula 4BHANU TYAGINo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument4 pagesNational Incomesubbu2raj3372No ratings yet
- Measuring National Income: Concepts and MethodsDocument17 pagesMeasuring National Income: Concepts and MethodsPradeep RaviNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument26 pagesNational IncomerajapatnaNo ratings yet
- Circular Flow of IncomeDocument66 pagesCircular Flow of IncomeAshish Tewani100% (3)
- National Income: Submitted To: - Dr. Hiranmoy RoyDocument30 pagesNational Income: Submitted To: - Dr. Hiranmoy RoyAbhishek ChopraNo ratings yet
- Measurement of National IncomeDocument13 pagesMeasurement of National IncomeSrinivasan KuppusamyNo ratings yet
- The Concepts of National IncomeDocument22 pagesThe Concepts of National IncomeHaren ShylakNo ratings yet
- Me Unit-5Document7 pagesMe Unit-5Anuj YadavNo ratings yet
- Economics IDocument34 pagesEconomics IKevin kayNo ratings yet
- Unit-V Managerial EconomicsDocument34 pagesUnit-V Managerial Economicsatulkumar.rise1No ratings yet
- Business Economics 2Document18 pagesBusiness Economics 2hassanNo ratings yet
- Macrounit 1Document11 pagesMacrounit 1AksshNo ratings yet
- National Income (Notes) IMBADocument27 pagesNational Income (Notes) IMBASubham .MNo ratings yet
- CFA Level 1 - Section 4 MacroEconomicsDocument30 pagesCFA Level 1 - Section 4 MacroEconomicsapi-3763138No ratings yet
- CH 6 Fundamental Concepts of MacroeconomicsDocument52 pagesCH 6 Fundamental Concepts of MacroeconomicsabelNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Circular FlowDocument62 pagesUnit 2 Circular FlowAnshumaan PatroNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Circular FlowDocument62 pagesUnit 2 Circular Flowk pradeepaNo ratings yet
- Nation S OutputDocument26 pagesNation S OutputStefano CHuaNo ratings yet
- Activities Related to Credit Intermediation Miscellaneous Revenues World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryFrom EverandActivities Related to Credit Intermediation Miscellaneous Revenues World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryNo ratings yet
- Deductions: Basic Rule The Aggregate Amount of Deductions Under Sections 80C To 80U Cannot Exceed The Gross Total IncomeDocument29 pagesDeductions: Basic Rule The Aggregate Amount of Deductions Under Sections 80C To 80U Cannot Exceed The Gross Total IncomeashpakkhatikNo ratings yet
- Circular Flow of Economic Activity-FinalDocument12 pagesCircular Flow of Economic Activity-FinalashpakkhatikNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology 1Document25 pagesResearch Methodology 1ashpakkhatikNo ratings yet
- Circular Flow of Economic Activity-FinalDocument12 pagesCircular Flow of Economic Activity-FinalashpakkhatikNo ratings yet
- DONE - Law1301 - Topic Law On Sales NADocument4 pagesDONE - Law1301 - Topic Law On Sales NAJosh Josh50% (2)
- BM & RUM PortionDocument2 pagesBM & RUM PortionAdarsh Jagannath NavaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Long Lived Assets - SolutionsDocument102 pagesChapter 8 Long Lived Assets - SolutionsKate SandersNo ratings yet
- Sales BudgetDocument8 pagesSales Budgetabhi7840100% (1)
- Agricultural InputsDocument94 pagesAgricultural InputsRAKSHIT JAINNo ratings yet
- WESTERN COALFIELDS BUYING PROCESSDocument4 pagesWESTERN COALFIELDS BUYING PROCESSDhiraj ThombareNo ratings yet
- ABSSAC Self Reversing ScrewDocument10 pagesABSSAC Self Reversing Screwrobert_lascuNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Our PresentationDocument26 pagesWelcome To Our Presentationnaimul_bariNo ratings yet
- Contract to Sell CarDocument3 pagesContract to Sell CarAljunBaetiongDiazNo ratings yet
- Accounting Concepts and ConventionsDocument4 pagesAccounting Concepts and ConventionsPrincess RubyNo ratings yet
- What Is Channel Conflict - Definition, Types, Causes, Consequences, Management, Example - The Investors Book PDFDocument10 pagesWhat Is Channel Conflict - Definition, Types, Causes, Consequences, Management, Example - The Investors Book PDFRaman KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Business-to-Business (B2B)Document6 pagesBusiness-to-Business (B2B)AMANSURI786No ratings yet
- Tire - City AnalysisDocument17 pagesTire - City AnalysisJustin HoNo ratings yet
- Service Recovery StrategiesDocument23 pagesService Recovery StrategiesAizat AmirNo ratings yet
- Caribbean Airlines SWOT, Value Chain and Growth Strategy AnalysisDocument3 pagesCaribbean Airlines SWOT, Value Chain and Growth Strategy AnalysisCherrell LynchNo ratings yet
- Global Marketing Assignment 1Document25 pagesGlobal Marketing Assignment 1Marcus TeeNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of The Circus IndustryDocument4 pagesThe Evolution of The Circus IndustryCarlii SaraviaNo ratings yet
- Customer Management: Market Planning & Research. Marketing Mix. Advertising & Brand ManagementDocument52 pagesCustomer Management: Market Planning & Research. Marketing Mix. Advertising & Brand ManagementAchin PrakashNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Strategic Role of ManagementDocument7 pagesLesson 6 Strategic Role of ManagementMilene BasanalNo ratings yet
- A 24Document1 pageA 24AnuranjanNo ratings yet
- Verizon Employee Discount FormDocument1 pageVerizon Employee Discount FormmuggsyNo ratings yet
- Turismo Receptivo Australia (Estudio)Document49 pagesTurismo Receptivo Australia (Estudio)Syluén GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Hospitality Math Test-Out Study Guide - 2015 - w-KEY-1 PDFDocument10 pagesHospitality Math Test-Out Study Guide - 2015 - w-KEY-1 PDFAlina-Alexandra PoschinăNo ratings yet
- Market Power: Monopoly and Monopsony: Prepared byDocument50 pagesMarket Power: Monopoly and Monopsony: Prepared byRamadhan Ihza31No ratings yet
- TESLA'S 3 BUSINESSES SEE REVENUE GROWTH IN AUTOMOTIVE, ENERGY AND SERVICESDocument19 pagesTESLA'S 3 BUSINESSES SEE REVENUE GROWTH IN AUTOMOTIVE, ENERGY AND SERVICESMuhammad Rifki PutraNo ratings yet
- A Theory of Market Segmentation - American Marketing AssociationDocument8 pagesA Theory of Market Segmentation - American Marketing AssociationAliya Raheel100% (1)
- ATC F7 - Rev Kit - June12Document150 pagesATC F7 - Rev Kit - June12Waseem Ahmad Qurashi75% (4)
- Invoice detailsDocument1 pageInvoice detailsDaniel DanNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument19 pagesBusiness Plansona_ktk100% (2)