0% found this document useful (0 votes)
119 views11 pagesSolid Figures Lesson Presentation
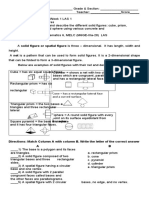
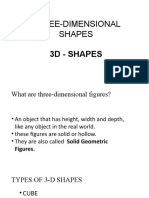
Solid figures are three-dimensional shapes characterized by faces, edges, and vertices. The document describes various types of solid figures including cubes, prisms, pyramids, cylinders, cones, and spheres, each with unique properties. These shapes can be found in everyday objects and are essential for understanding geometry.
Uploaded by
Jia TabioloCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
119 views11 pagesSolid Figures Lesson Presentation
Solid figures are three-dimensional shapes characterized by faces, edges, and vertices. The document describes various types of solid figures including cubes, prisms, pyramids, cylinders, cones, and spheres, each with unique properties. These shapes can be found in everyday objects and are essential for understanding geometry.
Uploaded by
Jia TabioloCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd