Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 05
Uploaded by
Sakshi SharmaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 05
Uploaded by
Sakshi SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
5-1
Chapter
EXCEL BOOKS
HUMAN RESOURCE PLANNING
5-2
ANNOTATED OUTLINE
INTRODUCTION
HRP offers an accurate estimate of the number of employees required with matching skill requirements to meet organisational objectives. HRP is a forward looking function as human resource estimates are made well in advance. It is, of course, subject to revision.
Human Resource Planning
5-3
Objective
The basic purpose of HRP is to decide what positions the organisation will have to fill and how to fill them.
Objectives of human resource planning
Forecast personnel requirements
Cope with changes Use existing manpower productively Promote employees in a systematic way
Human Resource Planning
5-4
Importance
Organisations use HRP to meet future challenges, cut costs, and achieve greater effectiveness
Importance of human resource planning
Create a talent pool Prepare people for future Cope with organisational changes Cut costs Help succession planning
Human Resource Planning
5-5
The Process Of HRP
The HRP is a four step process: demand forecasting, supply forecasting, estimating manpower gaps and formulating HR plans. The demand for human resources is influenced by several factors
Forecasting the demand for human resources
External challenges Economic developments Political, legal, social, technological changes Competition Organisational decisions Workforce factors
Human Resource Planning
5-6
The Process Of HRP
External Challenges: Liberalisation, privatisation and globalisation (LPG era) have created huge demand for people in software, finance marketing, and manufacturing fields. Policy towards reserving certain jobs for different communities, army etc. Organisational Decisions: Decisions such as expansion, diversification, and relocation leading to demand for people possessing requisite skills Workforce Factors: Such as retirement, termination etc creating manpower gaps. resignation, and
Companies Production operations policy, trade unions( no.of working hours per week, recruitment sources)
Human Resource Planning
5-7
Forecasting Techniques
HR forecasts are an attempt to find out an organisation's future demand for employees
Forecasting techniques
Expert forecasts Trend analysis Workforce analysis Workload analysis
Human Resource Planning
5-8
Forecasting techniques
Expert Forecasts: These are based on the judgements of those who possess good knowledge of future human resource needs
Trend Analysis: This is based on the assumption that the future is an extrapolation from the past. Human resource needs, as such, can be estimated by examining past trends.
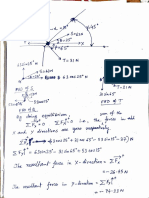
An example of trend analysis
2001-02 2002-03 Production of Units 5,000 No. of Workers 100 Ratio 100:5000 2003-04 Estimated Production 8,000 : : : :
100 5000
No. Human Resource Planning of Workers required
5-9
Forecasting techniques
Workforce Analysis: All relevant factors in planning manpower flows in a firm such as transfers, promotions, new recruitments, retirement, resignation, dismissal etc are taken into account while estimating HR needs
Manpower flows in a bank
Promotions out Transfers In > > > > > Recruits In > > > > Promotions In > > > Job Hopping Transfers Out Retirement VRS Scheme (Golden handshake) Discharge or Dismissal T erminations Resignations Retrenchment Attractions in Other Banks, etc.
Human Resource Planning
5-10
Forecasting techniques
Workload analysis: Based on the planned output, a firm tires to calculate the number of persons required for various jobs.
An example of workload analysis
Planned output for the year Standard hours per piece 10,000 pieces 3 hours
Planned hours required
Productive hours per person per year (allowing for absenteeism, turnover, idle time etc.) No. of workers required
30,000 hours
1,000 hours (estimated on annual basis)
30
If span of control in the unit is 10 per officer, then 3 officers are also required.
Human Resource Planning
5-24
Limitations Of Human Resource Planning
HR professionals are basically confronted with three problems while preparing and administering HR plans: accuracy, inadequate top management support, lopsided focus on quantitative aspects.
Human Resource Planning
5-25
Effective Human Resource Planning
HR plans must fit in with overall objectives of a firm. They must get consistent support from top management. Computerised human resource information systems must be used for applicant tracking, succession planning, building skills inventories etc. The whole exercise must be carried out in coordination with operating managers.
Human Resource Planning
You might also like
- Graffiti Model Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesGraffiti Model Lesson Planapi-286619177100% (1)
- Techniques-Of-Attitude-Scale-Construction FullDocument344 pagesTechniques-Of-Attitude-Scale-Construction FullLuthfi fharuq Al Fairuz67% (3)
- Assembly Transmission Volvo A40GDocument52 pagesAssembly Transmission Volvo A40GNanang SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Aims of Human Resource PlanningDocument6 pagesAims of Human Resource PlanningZalkif Ali100% (2)
- UNIT 3 - HR Inventory PDFDocument15 pagesUNIT 3 - HR Inventory PDFPurnima Singh67% (6)
- Unit-3 Human Resource Planning ProcessDocument5 pagesUnit-3 Human Resource Planning ProcessSujan Chaudhary100% (1)
- Human Resource PlanningDocument21 pagesHuman Resource Planningincpatna100% (2)
- Catering Reserving and Ordering System with MongoDB, Express, Node.js (39Document5 pagesCatering Reserving and Ordering System with MongoDB, Express, Node.js (39radha krishnaNo ratings yet
- FMBXXX Quick Manual v3.5Document18 pagesFMBXXX Quick Manual v3.5AMNo ratings yet
- Chalk & TalkDocument6 pagesChalk & TalkmathspvNo ratings yet
- 2 - HR PlanningDocument23 pages2 - HR PlanningSushant ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- HRP Chapter 2 SummaryDocument10 pagesHRP Chapter 2 SummaryAbhinav SinghNo ratings yet
- HR Planning & Analysis: A GuideDocument60 pagesHR Planning & Analysis: A GuideSunita MehtaNo ratings yet
- Human Resource PlanningDocument18 pagesHuman Resource PlanningSreenidhi R BBA LLB HNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Planning (H R P)Document31 pagesHuman Resource Planning (H R P)Chingith RamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HRPDocument21 pagesIntroduction To HRPAmruta KapoorNo ratings yet
- HR Planning: Forecast Staffing Needs with Gallagher Model and Cohort AnalysisDocument19 pagesHR Planning: Forecast Staffing Needs with Gallagher Model and Cohort Analysisdsravani50% (2)
- Chapter - 5 Human Resource PlanningDocument37 pagesChapter - 5 Human Resource Planningmoni314No ratings yet
- Models and Techniques of Manpower Demand and Supply ForecastingDocument27 pagesModels and Techniques of Manpower Demand and Supply ForecastingReetika DadheechNo ratings yet
- Class TesDocument6 pagesClass TesZul HashimNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management - Unit 2 (B.com) - 2024Document26 pagesHuman Resource Management - Unit 2 (B.com) - 2024Shrey BankaNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management - Unit 2 (B.com) - 2024Document19 pagesHuman Resource Management - Unit 2 (B.com) - 2024Shrey BankaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - HRPDocument23 pagesChapter 2 - HRPElla MoonstoneNo ratings yet
- Human Resources Planning (HRP)Document65 pagesHuman Resources Planning (HRP)Huneza ShahNo ratings yet
- Man Power Plann & Re-Sourcin Set1Document9 pagesMan Power Plann & Re-Sourcin Set1Rajini GrNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document13 pagesModule 4Sreejith C S SreeNo ratings yet
- Manpower Planning - Setting The ToneDocument31 pagesManpower Planning - Setting The TonePreeti TanejaNo ratings yet
- HR Planning.1Document24 pagesHR Planning.1Avro KhanNo ratings yet
- HR PlanningDocument26 pagesHR Planningjohnrovietbauat41No ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument33 pagesHuman Resource Managementhewia1921No ratings yet
- RVU Part 2Document33 pagesRVU Part 2Hiwot NimanieNo ratings yet
- HRP - HRRDocument12 pagesHRP - HRRDeepak SharmaNo ratings yet
- HRM - Unit-II - 16 MarksDocument17 pagesHRM - Unit-II - 16 MarksRam KumarNo ratings yet
- HRM Unit IiDocument67 pagesHRM Unit IivjagatheeshNo ratings yet
- HRM - 2nd Week - Lecture NotesDocument8 pagesHRM - 2nd Week - Lecture NotesProf. Jomar MariquitNo ratings yet
- A Note On Manpower PlanningDocument6 pagesA Note On Manpower PlanningDarel WizNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Resource PlanningDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Human Resource Planningharish_100_inNo ratings yet
- HRM Unit 2Document47 pagesHRM Unit 2vamsibuNo ratings yet
- HR PlanningDocument6 pagesHR PlanningYash SonkarNo ratings yet
- MBA Sem 3 AssignmentsDocument6 pagesMBA Sem 3 AssignmentsRajini GrNo ratings yet
- People Resourcing Strategy...Document50 pagesPeople Resourcing Strategy...ابوعركي عثمانNo ratings yet
- HR1Document22 pagesHR1Hashar RashidNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document10 pagesModule 5meet daftaryNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Planning Can Be Defined As A Process by Which An Organization Ensures That It Has The Right Number and Kinds of PeopleDocument35 pagesHuman Resource Planning Can Be Defined As A Process by Which An Organization Ensures That It Has The Right Number and Kinds of PeoplekiranaishaNo ratings yet
- HRM2L2 HumanResPlanningDocument15 pagesHRM2L2 HumanResPlanningGloria Compound Youth OrganizationNo ratings yet
- HRM Investment Perspectives and Demand ForecastingDocument17 pagesHRM Investment Perspectives and Demand ForecastingSai PrabhasNo ratings yet
- HR Planning Guide for Strategic Workforce ManagementDocument36 pagesHR Planning Guide for Strategic Workforce ManagementDheeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Session 2 HR PlanningDocument17 pagesSession 2 HR PlanningFebrianti FebriNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Manpower PlanningDocument30 pagesUnit 3 Manpower PlanningSmit ShahNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Human Resources Management in Canada Twelfth Canadian Edition Plus Mymanagementlab With Pearson Etext Package 12 e Gary Dessler Nita Chhinzer Nina D ColeDocument18 pagesSolution Manual For Human Resources Management in Canada Twelfth Canadian Edition Plus Mymanagementlab With Pearson Etext Package 12 e Gary Dessler Nita Chhinzer Nina D ColeRobertLynchwxey100% (34)
- Human Resource Planning: Definition of HRP Importance of HRP Process of HRP Factors Affecting HRP Barriers To HRPDocument24 pagesHuman Resource Planning: Definition of HRP Importance of HRP Process of HRP Factors Affecting HRP Barriers To HRPvipin goyal83% (6)
- Manpower Planning StrategiesDocument38 pagesManpower Planning Strategiesmonojg_mjNo ratings yet
- Module 1-Part 3 - Human Resource PlanningDocument76 pagesModule 1-Part 3 - Human Resource PlanningUma Devi AnanthNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document23 pagesLecture 2ALIS VERİSNo ratings yet
- HRM - Unit-2Document17 pagesHRM - Unit-2noobda gamerNo ratings yet
- HR Planning & Recruitment Process OverviewDocument37 pagesHR Planning & Recruitment Process OverviewShivam KhannaNo ratings yet
- Outline - Demand Planning (Slide 14 Resource)Document6 pagesOutline - Demand Planning (Slide 14 Resource)wootenr2002No ratings yet
- Human Resource PlanningDocument25 pagesHuman Resource Planningjoginder GrewalNo ratings yet
- Planning Is A Management FunctionDocument6 pagesPlanning Is A Management FunctionMd Fahim Muntasir HeavenNo ratings yet
- Mba Human Resource PlanningDocument13 pagesMba Human Resource PlanningtchoumbaprincessNo ratings yet
- HRP Importance and StepsDocument38 pagesHRP Importance and StepsyonataNo ratings yet
- HRM Report - Human Resource PlanningDocument32 pagesHRM Report - Human Resource PlanningKeith Amor100% (1)
- Human Resource PlanningDocument16 pagesHuman Resource PlanningMitali AroraNo ratings yet
- HRP & Job Analysis - Module 2Document61 pagesHRP & Job Analysis - Module 2Dr-Shefali GargNo ratings yet
- Solutions for Forecasting Manpower Needs in an Organization!From EverandSolutions for Forecasting Manpower Needs in an Organization!No ratings yet
- Introducing The Phenomenon To Be Discussed: Stating Your OpinionDocument8 pagesIntroducing The Phenomenon To Be Discussed: Stating Your OpinionRam RaghuwanshiNo ratings yet
- Advanced Blueprint 1Document3 pagesAdvanced Blueprint 1api-728237431No ratings yet
- Kerala University 2013 Admission ProspectusDocument50 pagesKerala University 2013 Admission ProspectusMuneer SainulabdeenNo ratings yet
- Soft Computing Techniques Assignment1 PDFDocument14 pagesSoft Computing Techniques Assignment1 PDFshadan alamNo ratings yet
- The historical evolution of organizational behavior and how it shaped modern managementDocument3 pagesThe historical evolution of organizational behavior and how it shaped modern managementSaravanan Swagger100% (1)
- Topic 3Document28 pagesTopic 3Ashraf YusofNo ratings yet
- Basic Facts For Homebooks Stage 7Document3 pagesBasic Facts For Homebooks Stage 7api-311857762No ratings yet
- 10 ExtSpringsDocument27 pages10 ExtSpringsresh27No ratings yet
- Sigmund Freud and His Main TheoriesDocument5 pagesSigmund Freud and His Main TheoriesNguyen HarryNo ratings yet
- IIT BOMBAY RESUME by SathyamoorthyDocument1 pageIIT BOMBAY RESUME by SathyamoorthySathyamoorthy VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Renal Angina Index in Pediatric Septic Patients As A Predictor of Acute Kidney Injury in Remote AreaDocument9 pagesRenal Angina Index in Pediatric Septic Patients As A Predictor of Acute Kidney Injury in Remote AreaFarhanNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual Series 854 XTG Level GaugeDocument60 pagesInstruction Manual Series 854 XTG Level GaugeJandri JacobNo ratings yet
- Kunduz Tutor Job Apply Question 1Document2 pagesKunduz Tutor Job Apply Question 1anirbanNo ratings yet
- T38N/T48N: Suffix Code Instruction ManualDocument1 pageT38N/T48N: Suffix Code Instruction ManualaliNo ratings yet
- Electronics Today 1977 10Document84 pagesElectronics Today 1977 10cornel_24100% (3)
- Keynote Proficient End-Of-Course Test BDocument7 pagesKeynote Proficient End-Of-Course Test Bana maria csalinasNo ratings yet
- Sample of Application Letter (Updated)Document4 pagesSample of Application Letter (Updated)Mizpah Sarah BautistaNo ratings yet
- TM-1870 AVEVA Everything3D - (2.1) Draw Administration (CN)Document124 pagesTM-1870 AVEVA Everything3D - (2.1) Draw Administration (CN)yuehui niuNo ratings yet
- Calmark - Birtcher 44 5 10 LF L DatasheetDocument2 pagesCalmark - Birtcher 44 5 10 LF L DatasheetirinaNo ratings yet
- Methanol Technical Data Sheet FactsDocument1 pageMethanol Technical Data Sheet FactsmkgmotleyNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Thermodynamics 1Document28 pages1.1 Thermodynamics 1Lyan SantosNo ratings yet
- Eccsa Five Year (2014 15 - 2018 19) Strategic PlanDocument95 pagesEccsa Five Year (2014 15 - 2018 19) Strategic Planyayehyirad100% (1)
- Query Operation 2021Document35 pagesQuery Operation 2021Abdo AbaborNo ratings yet
- Training Needs Analysis (Managing Training & Development)Document78 pagesTraining Needs Analysis (Managing Training & Development)Henrico Impola100% (1)