Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Scavenging Blowers
Uploaded by
Gargee ChavanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Scavenging Blowers
Uploaded by
Gargee ChavanCopyright:
Available Formats
Gargee Chavan Roll no- 608
Since
the piston of a 2 stroke engine cannot carry out the pumping action, a separate pumping mechanism called SCAVENGING PUMP is needed to supply scavenging air to the cylinder. performance of the 2 stroke engine largely depends upon the characteristics of the scavenging pump.
The
2s- 4s cycle engine must have a blower to fill the cylinder with fresh air at a pressure above the atmospheric pressure, before the compression event starts. Basically the function of a scavenging blower is to deliver large volume of air at a low pressure.
The
2 main types of scavenging blowers are as follows-
DISPLACEMENT BLOWERBLOWER-
usually gear driven directly by the engine.
CENTRIFUGAL
usually driven by an exhaust gas turbine
There
are two types of displacement blowers-
CRANKCASE
COMPRESSION BLOWER ROOT BLOWER
The
area below the piston ,the charging pump known as crankcase blower. A crankcase blower is generally used in smaller engines (up to 50kW per cylinder) Its used in both SI gas engines and CI oil engines The volumetric efficiency of such a pump is low (about 55-65%) due to presence of a large dead space in the crankcase.
In
crankcase scavenging pump , the crank case compression of air (in CI engine)or air fuel mixture (in SI engine) accrues in the crankcase. The medium is introduced at atmospheric pressure into the space below the piston through a one way valve. The power stroke of the piston compresses the medium as well as pushes the compressed medium through an inlet port into the combustion chamber.
Its
designed for efficient diesel operation. It supplies fresh air for combustion and scavenging. The air volume needed for the engine to perform scavenging is about 40 times greater than the cylinder volume. The location of the blower on the engine depends on the cylinder arrangement.
A Roots blower with twolobed rotors. Most real Roots blowers' rotors have three or four lobes. Key: 1 Rotary vane 1 2. Pump body 3. Rotary vane 2 a. Intake b. Pumping c. Forced air or air-fuel mixture into intake manifold
The
operation of the blower is similar to that of a gear-type pump. Two hollow 3lobe rotors revolve in opposite directions When the rotors turn, air is drawn in the space between the lobes at the inlet, is trapped, and is carried around to the discharge side. The meshing lobes at the discharge side force the air out of the lobe pockets and into the air box, where the air is then available for use. The sides of the lobes are helical surfaces in order to give uniform motion and to reduce air noise
It is preferred for large and high output engines With the centrifugal pump mass flow rate is highly influenced by the engine and exhaust system resistance. Thus scavenging with this pump is satisfactory provided the resistance of flow system is not sharply affected by carbon deposits in the ports, restricted exhausts or by long exhaust piping which may develop adverse pressure waves at certain speeds
Engines
equipped with centrifugal scavenging pumps will be more sensitive to the effect of pressure waves in the inlet and exhaust system than those equipped with displacement pumps, as in latter case the quantity of air flowing through the pump is not seriously affected by pump discharge pressure.
You might also like
- The Jet Engine, 5th EditionDocument306 pagesThe Jet Engine, 5th Editionmilad100% (3)
- Trouble Shooting in Vacuum PumpDocument12 pagesTrouble Shooting in Vacuum Pumpj172No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document16 pagesChapter 2Mohammed Algendy100% (1)
- 01.introduction To CorrosionDocument18 pages01.introduction To CorrosionIndah ArdiantiNo ratings yet
- History of CompressorDocument24 pagesHistory of CompressorHaryNo ratings yet
- Instructions BAH 6/10 to BAH 40/60 DI 6H to DI 40H BlowersDocument40 pagesInstructions BAH 6/10 to BAH 40/60 DI 6H to DI 40H BlowersvictoraghiNo ratings yet
- Lobe Pump Research PaperDocument10 pagesLobe Pump Research PaperReview DragonsNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Cycle 1Document66 pagesLab Manual Cycle 1Kaustubh SatheNo ratings yet
- 8.chapter 5 Compressed Air SystemDocument17 pages8.chapter 5 Compressed Air SystemAbdullah TalibNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal PumpDocument39 pagesCentrifugal PumpGogot Pantja ParijogoNo ratings yet
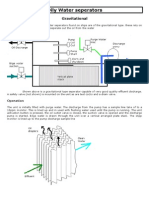
- An Oily Water SeparatorDocument3 pagesAn Oily Water SeparatorMin SoeNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating Air Compressor GuideDocument15 pagesReciprocating Air Compressor Guide2AG19ME411 JagadeeshNo ratings yet
- 3 Axis Modern TrailerDocument24 pages3 Axis Modern TrailerRATHANNo ratings yet
- General 1Document80 pagesGeneral 1Sachu S100% (1)
- Sample Problem - Pump Power Calculations - EnggcyclopediaDocument6 pagesSample Problem - Pump Power Calculations - EnggcyclopediaMuhammadObaidullahNo ratings yet
- Topic Wise Gme Interview Questions (Great Eastern) : NoteDocument2 pagesTopic Wise Gme Interview Questions (Great Eastern) : NoteAthul P PNo ratings yet
- Efficient Screw Compressors for Dry Air DeliveryDocument10 pagesEfficient Screw Compressors for Dry Air DeliverySaeedAkbarzadehNo ratings yet
- Pumps: Operations and MaintenanceDocument141 pagesPumps: Operations and Maintenanceissam elmoharirNo ratings yet
- Compressor (Disambiguation)Document54 pagesCompressor (Disambiguation)nelsonNo ratings yet
- An Investigation of The Volumetric. Efficiency of A Roots BlowerDocument9 pagesAn Investigation of The Volumetric. Efficiency of A Roots BlowershreemugNo ratings yet
- Pump Cavitation and NPSHDocument10 pagesPump Cavitation and NPSHshiel175No ratings yet
- Aux Mach 1 Air CompressorDocument86 pagesAux Mach 1 Air CompressorConrado Sta Ines100% (1)
- Water FilterDocument15 pagesWater FilterTEO ZHEN YINo ratings yet
- Express orDocument36 pagesExpress orkr_abhijeet72356587100% (1)
- Reciprocating Air CompressorsDocument20 pagesReciprocating Air CompressorsAshleen MarshallNo ratings yet
- Oil Water Separator (OWS)Document11 pagesOil Water Separator (OWS)api-3701567100% (1)
- Perfect Chloro Systems - Gas ..Document6 pagesPerfect Chloro Systems - Gas ..nazar750No ratings yet
- At AssignmentDocument3 pagesAt AssignmentYogesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Influence of The Nature of The Roots Blower On Pressure Fluctuations in A Fluidized BedDocument13 pagesInfluence of The Nature of The Roots Blower On Pressure Fluctuations in A Fluidized BedcoolcupidguyNo ratings yet
- V&T Hydrocyclone enDocument4 pagesV&T Hydrocyclone enIon_RiswanNo ratings yet
- Computer Assisted Design of Thermal Systems: Actual Compressor CalculationsDocument6 pagesComputer Assisted Design of Thermal Systems: Actual Compressor CalculationsmrinalbhadurioNo ratings yet
- IC Engine FormulaDocument5 pagesIC Engine FormulaKarthikeyan Gnanasekaran0% (1)
- Compressor Vs PumpDocument7 pagesCompressor Vs Pump'Izzad AfifNo ratings yet
- C Module-5 Reciprocating Air Compressors. Reciprocating Compressors - Construction - WorkingDocument48 pagesC Module-5 Reciprocating Air Compressors. Reciprocating Compressors - Construction - WorkingJasraj Gill100% (1)
- Jar Testing - How To Design and Perform Representative Jar Tests For A SWTPDocument101 pagesJar Testing - How To Design and Perform Representative Jar Tests For A SWTPYesica Alexandra Salcedo VelandiaNo ratings yet
- Sewage Treatment PlantDocument3 pagesSewage Treatment PlantGaurav WaliaNo ratings yet
- Zero Liquid Discharge Tirupur TextileDocument23 pagesZero Liquid Discharge Tirupur TextileAswin ABNo ratings yet
- Graham-Air Ejector Cheaper Than Steam PDFDocument5 pagesGraham-Air Ejector Cheaper Than Steam PDFJungmuk LeeNo ratings yet
- A C Engines and Jet Propulsion3Document152 pagesA C Engines and Jet Propulsion3Mukesh Kumar100% (1)
- U-type open-loop scrubber system layout, screens and alarm listsDocument21 pagesU-type open-loop scrubber system layout, screens and alarm listshein chanNo ratings yet
- Pump CalculationsDocument6 pagesPump CalculationsAshenafi Gebremeskel MezgeboNo ratings yet
- Rotary Screw ProcessDocument9 pagesRotary Screw ProcessEagle WingsNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1Ziyad Awali100% (1)
- Hydraulic Brake System Full ReportDocument3 pagesHydraulic Brake System Full ReportGautam VatsNo ratings yet
- Dorner 3200 Vacuum ConveyorDocument8 pagesDorner 3200 Vacuum ConveyorBobKatNo ratings yet
- MI-106 Tut ThermoDocument37 pagesMI-106 Tut ThermoDhananjayLekshmiNarayan100% (7)
- Impellers Information: Show All Impellers ManufacturersDocument6 pagesImpellers Information: Show All Impellers ManufacturersAbdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- Oily Water SeperatorsDocument2 pagesOily Water SeperatorsJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 24: Applications of Pneumatics and HydraulicsDocument15 pagesUnit 24: Applications of Pneumatics and HydraulicsEmad ElsaidNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating & Rotary CompressorDocument64 pagesReciprocating & Rotary Compressorraghu.entrepreneur100% (1)
- Examples On Hydraulic Jump PDFDocument3 pagesExamples On Hydraulic Jump PDFSylvester WafulaNo ratings yet
- Exhaust Systems in Tractors and Its EmissionsDocument11 pagesExhaust Systems in Tractors and Its EmissionsSimmonds100% (1)
- The Effect of Venturi Design On Jet Pump PerformanceDocument6 pagesThe Effect of Venturi Design On Jet Pump PerformanceJournal 4 ResearchNo ratings yet
- Basic Maintenance Tips To Retain Efficient Operation of Compressed Air SystemsDocument4 pagesBasic Maintenance Tips To Retain Efficient Operation of Compressed Air Systemskarthikraja21No ratings yet
- Comparing Pneumatic Spring Diaphragm and Cylinder ActuatorsDocument3 pagesComparing Pneumatic Spring Diaphragm and Cylinder ActuatorsVivi Oktavianti100% (1)
- Design & Control Smart Automatic Water Monitoring SystemDocument3 pagesDesign & Control Smart Automatic Water Monitoring SystemRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Air Drying ProcessDocument2 pagesAir Drying Processmarcoo8No ratings yet
- Assignment 2: Name: Levitaran A/L Sager MATRICS: A0000623 Lecture: Sir. Azni Bin MonDocument12 pagesAssignment 2: Name: Levitaran A/L Sager MATRICS: A0000623 Lecture: Sir. Azni Bin MonlevitranNo ratings yet
- 3.1 - ScavengingDocument6 pages3.1 - ScavengingPrafull TripathiNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Gas Turbine EngineDocument11 pagesAircraft Gas Turbine Engineখালিদহাসান100% (1)
- 4d GP One (Inlet&Comp)Document16 pages4d GP One (Inlet&Comp)BookMaggotNo ratings yet
- Skittlestack Earrings EDocument1 pageSkittlestack Earrings EGargee ChavanNo ratings yet
- 75mm Square Purse Frame Pattern No HolesDocument1 page75mm Square Purse Frame Pattern No HolesGargee ChavanNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines 1 2008 December Engineering Mechanical Engineering (Mech) Beng Semester 4 University Exam University of MumbaiDocument3 pagesTheory of Machines 1 2008 December Engineering Mechanical Engineering (Mech) Beng Semester 4 University Exam University of MumbaiGargee ChavanNo ratings yet
- VIMP Question Banks (Chapter 5 & 6) Dec 2011 ExamDocument4 pagesVIMP Question Banks (Chapter 5 & 6) Dec 2011 ExamAshique BaruaNo ratings yet
- Tallpoppycraft Tube PurseDocument3 pagesTallpoppycraft Tube PurseGargee ChavanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesChapter 3 - Lecture NotesGargee ChavanNo ratings yet
- MatrixDocument7 pagesMatrixGargee ChavanNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Problem Solutions Involving Generation Rates, Distributions, FluxesDocument18 pagesHeat Transfer Problem Solutions Involving Generation Rates, Distributions, FluxesFuriNo ratings yet
- - शाला.com - Shaalaa means School in Sanskrit - Fluid Mechanics - 2012 June - Engineering Mechanical Engineering (MECH) BE - Semester 5 - University Exam - University of Mumbai - - 2012-09-06Document4 pages- शाला.com - Shaalaa means School in Sanskrit - Fluid Mechanics - 2012 June - Engineering Mechanical Engineering (MECH) BE - Semester 5 - University Exam - University of Mumbai - - 2012-09-06Gargee ChavanNo ratings yet
- - शाला.com - Shaalaa means School in Sanskrit - Fluid Mechanics - 2011 May - Engineering Mechanical Engineering (MECH) BEng - Semester 5 - University Exam - University of Mumbai - - 2012-02-29Document3 pages- शाला.com - Shaalaa means School in Sanskrit - Fluid Mechanics - 2011 May - Engineering Mechanical Engineering (MECH) BEng - Semester 5 - University Exam - University of Mumbai - - 2012-02-29Gargee ChavanNo ratings yet
- Orthographic Projection and SectioningDocument8 pagesOrthographic Projection and SectioningGargee ChavanNo ratings yet
- - शाला.com - Shaalaa means School in Sanskrit - Fluid Mechanics - 2011 December - Engineering Mechanical Engineering (MECH) BE - Semester 5 - University Exam - University of Mumbai - - 2012-09-06Document3 pages- शाला.com - Shaalaa means School in Sanskrit - Fluid Mechanics - 2011 December - Engineering Mechanical Engineering (MECH) BE - Semester 5 - University Exam - University of Mumbai - - 2012-09-06Gargee ChavanNo ratings yet
- Production Process I d11Document1 pageProduction Process I d11Gargee ChavanNo ratings yet
- E-R ModelDocument3 pagesE-R ModelGargee ChavanNo ratings yet
- API Vs Ansi PumpsDocument6 pagesAPI Vs Ansi PumpsMarcos Martínez SánchezNo ratings yet
- Basic Information TJ100 - AJ Revision 5Document12 pagesBasic Information TJ100 - AJ Revision 5Mohammad Lavasani100% (1)
- PVG 120 SpecificationsDocument6 pagesPVG 120 Specificationsgonzalo andres HernandezNo ratings yet
- Split AC Guide: How They Work & System ComponentsDocument8 pagesSplit AC Guide: How They Work & System ComponentssadNo ratings yet
- SOLAR POWER SYSTEM (AC) SETUP GUIDEDocument15 pagesSOLAR POWER SYSTEM (AC) SETUP GUIDEHARKULVINDER SINGHNo ratings yet
- A. M. Buri Steam Power Plant Having A Forced Flow Steam Generator Filed May 28, 1956Document4 pagesA. M. Buri Steam Power Plant Having A Forced Flow Steam Generator Filed May 28, 1956Anonymous KzJcjGCJbNo ratings yet
- Apho2018 Theory Q3 Thermoelectricity Solution & Marking SchemeDocument6 pagesApho2018 Theory Q3 Thermoelectricity Solution & Marking SchemempecthNo ratings yet
- Uop Benfield Datasheet PDFDocument2 pagesUop Benfield Datasheet PDFArya YudistiraNo ratings yet
- TE-2 Unit - 4 &5 NotesDocument110 pagesTE-2 Unit - 4 &5 NotesKrishna VamsiNo ratings yet
- CPV10 14 PSI US Valve ManifoldDocument2 pagesCPV10 14 PSI US Valve ManifoldAmir AlibegovićNo ratings yet
- Cutting G Off of Turboc Charger (Temp Porary) : Ro Tor Locking Proce EdureDocument6 pagesCutting G Off of Turboc Charger (Temp Porary) : Ro Tor Locking Proce EdurepcatruongNo ratings yet
- CH 5 PDFDocument24 pagesCH 5 PDFМихаил МироновNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3. Refrigeration Cycles 2Document37 pagesLecture 3. Refrigeration Cycles 2addisudagneNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Calc 1 and 2 PDFDocument7 pagesActivity 1 Calc 1 and 2 PDFonyxNo ratings yet
- Industrial Visit ReportDocument8 pagesIndustrial Visit ReportPraa DeepNo ratings yet
- Flare Gas Ignition System: For Oil and Gas Producing Facilities and Petrochemical PlantsDocument2 pagesFlare Gas Ignition System: For Oil and Gas Producing Facilities and Petrochemical Plantsdebasish bhowmickNo ratings yet
- Board and PillarDocument1 pageBoard and PillarKRISHNA MOHANNo ratings yet
- Data 9x Containerized Gas Engine JGS 320 GS - SLDocument2 pagesData 9x Containerized Gas Engine JGS 320 GS - SLBalast MetheeNo ratings yet
- Valve Samson Model 3241 Serial 470 132 B347W701 ENDocument1 pageValve Samson Model 3241 Serial 470 132 B347W701 ENClaudio StadelmannNo ratings yet
- Sabroe PPDocument28 pagesSabroe PPGPNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas Production and OperationsDocument2 pagesNatural Gas Production and OperationsHossam M. Abd El RahmanNo ratings yet
- Ione-Aa00-Pe-Cm-0032 Mechanical Run-In Test Procedure - Rev. ADocument20 pagesIone-Aa00-Pe-Cm-0032 Mechanical Run-In Test Procedure - Rev. AYusuf100% (1)
- Innio Jenbacher j420 Brochure 210x297mm RZ Screen Ijb-122001-EnDocument5 pagesInnio Jenbacher j420 Brochure 210x297mm RZ Screen Ijb-122001-EnOwais JatoiNo ratings yet
- Steam Jet Refrigeration: How it WorksDocument6 pagesSteam Jet Refrigeration: How it WorksbbaytlNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine Operation and ControlsDocument75 pagesGas Turbine Operation and Controlskajaiqu100% (3)
- Fast Reference: CompressorDocument8 pagesFast Reference: CompressorJUNFERNNo ratings yet
- Model: Puhy-P450Tka (-BS) : 14-Ton Outdoor VRF Heat Pump SystemDocument4 pagesModel: Puhy-P450Tka (-BS) : 14-Ton Outdoor VRF Heat Pump SystemJesus SacramentoNo ratings yet
- New Stator Core Manufacturing ConceptsDocument22 pagesNew Stator Core Manufacturing ConceptsL Mahender ReddyNo ratings yet