Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pa Tho Physiology of Dengue
Uploaded by
Maria Ivy Mendoza0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views2 pagesCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views2 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Dengue
Uploaded by
Maria Ivy MendozaCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
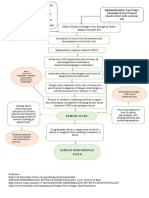
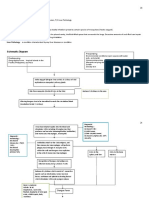
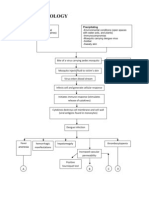
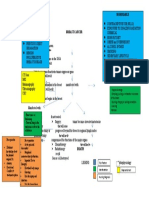
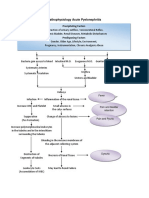
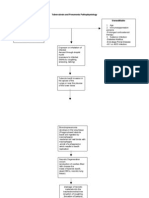
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF DENGUE
Bite of a virus carrying Aedes mosquito
Mosquito injects fluid into victim’s skin
Virus enters blood stream
Infects cells and generate cellular response
Initiates immune response
(Stimulates release of cytokines)
Cytokines destroys cell membrane and cell wall
(Viral Antigens found in monocytes)
Fluid Shift
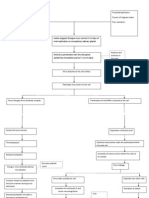
When treated early with doctor prescribed medications and When illness becomes severe
managed to prevent the appearance of other symptoms
IVF and electrolyte replacements and precautions Damage cells due to cytokines and virus
Patient recovers Fluid shift from ICF- ECF
Manifest evanescent rashes rashes in several areas in the body
Bloody vomittus, urine and stool
Circulatory collapse
Shock
DEATH
You might also like
- DengueDocument4 pagesDengueKathleen DimacaliNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument1 pagePathophysiology Dengue Hemorrhagic Fevershiramu33% (3)
- Pathophysiology DengueDocument1 pagePathophysiology DengueKevin50% (2)
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever Pathophysiology DiagramDocument4 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic Fever Pathophysiology DiagramAni MarlinaNo ratings yet
- Geographical Area - Tropical Islands in Thepacific (Philippines) and AsiaDocument1 pageGeographical Area - Tropical Islands in Thepacific (Philippines) and AsiaGenevang SeaweedsNo ratings yet
- DEngue FlowchartDocument2 pagesDEngue FlowchartJelly Cruz100% (3)
- Dengue PoathoDocument6 pagesDengue PoathoCleobebs Agustin100% (1)
- Pathophysiology Dengue 2Document4 pagesPathophysiology Dengue 2KatherineNo ratings yet
- Malaria PathophysiologyDocument1 pageMalaria Pathophysiologykaye040375% (4)
- Patho DengueDocument3 pagesPatho DengueKayshey Christine ChuaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Dengue FeverDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Dengue FeverApple Mae100% (1)
- Pathophsyiology of AGEDocument1 pagePathophsyiology of AGEmariaNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument2 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY of Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverMaynelle Caspe100% (2)
- Case Presentation (Age) NG Grp. A2 FinalDocument43 pagesCase Presentation (Age) NG Grp. A2 Finaljean therese83% (6)
- Breast Cancer Concept MapDocument1 pageBreast Cancer Concept MapKeepItSecret100% (1)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of DENGUEDocument2 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY of DENGUEKenrick Randell IbanaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of TuberculosisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of TuberculosisLeikkaNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic Fever Pathophysiologyteddydeclines1483% (18)
- Amoebiasis PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesAmoebiasis PathophysiologyApril CornejoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of CholeraDocument1 pagePathophysiology of CholeraFarr Krizha Tangkusan67% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Dengue Fever 1Document2 pagesPathophysiology of Dengue Fever 1Dominique Lim Yañez88% (8)
- Pathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating Factorsgodwinkent888No ratings yet
- Dengue PathophysiologyDocument1 pageDengue PathophysiologyRafael Miguel Alon Protacio50% (2)
- Measles PathoDocument1 pageMeasles PathoAin JamelaNo ratings yet
- B. Diagram: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors EtiologyDocument3 pagesB. Diagram: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors EtiologyKenneth Torres100% (1)
- Neonatal Pneumonia Case StudyDocument2 pagesNeonatal Pneumonia Case StudyAngel Villamor0% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever - Doc (Phil)Document8 pagesPathophysiology of Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever - Doc (Phil)Firenze Fil0% (1)
- Pathophy (Age)Document1 pagePathophy (Age)Michelle Ann CasamayorNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever Pathophysiology DiagramDocument4 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic Fever Pathophysiology DiagramGuia Rose Sibayan0% (1)
- Pcap Pathophysiology PDFDocument3 pagesPcap Pathophysiology PDFMikaela RamosNo ratings yet
- Age With Moderate Dehydration New 1Document74 pagesAge With Moderate Dehydration New 1Jhade Relleta100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of TuberculosisDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of TuberculosisMonica Marie Morales86% (14)
- Dengue Fever Case StudyDocument5 pagesDengue Fever Case StudyJen Faye Orpilla100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Koch's Disease (Tuberculosis) : Primary InfectionDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Koch's Disease (Tuberculosis) : Primary InfectionStephanie GapuzNo ratings yet
- Patho DengueDocument3 pagesPatho DengueLindy Shane BoncalesNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology AGEDocument2 pagesPathophysiology AGEMareeze Hatta100% (1)
- Group 3 Pathophysiology-of-BREAST-CANCERDocument1 pageGroup 3 Pathophysiology-of-BREAST-CANCERArisa VijungcoNo ratings yet
- Acute Glomrulonephritis PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesAcute Glomrulonephritis PathophysiologyJai - HoNo ratings yet
- Rabies PathophysiologyDocument1 pageRabies PathophysiologyMichael Urrutia100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Septic Shock Secondary To PyelonephritisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Septic Shock Secondary To PyelonephritisShirlyn100% (1)
- PathophysiologyDocument6 pagesPathophysiologyElbert Hermogino ﭢNo ratings yet
- Chickenpox 1Document7 pagesChickenpox 1Nica Joy CandelarioNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic Fever PathophysiologyKirk Espanol BigstoneNo ratings yet
- DiarrheaDocument24 pagesDiarrheaash ashNo ratings yet
- Inflammation & Repair: Tim Dosen PatologiDocument32 pagesInflammation & Repair: Tim Dosen PatologiNdaru SetyaningrumNo ratings yet
- Pathology ReviewDocument26 pagesPathology ReviewSafiya James100% (1)
- Pathophysiology: Predisposing PrecipitatingDocument3 pagesPathophysiology: Predisposing PrecipitatinggizelleNo ratings yet
- Aureus. It Can Be Either Acute or ChronicDocument7 pagesAureus. It Can Be Either Acute or ChronicfortunelobsterNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Pathophysiology of Osteomyelitis DiagramDocument1 pageDokumen - Tips Pathophysiology of Osteomyelitis DiagramRodriguez, Joyce Ann G.No ratings yet
- Acute & Chronic Inflammation: Bethy S HernowoDocument61 pagesAcute & Chronic Inflammation: Bethy S HernowodhifaNo ratings yet
- Inflamation2Document61 pagesInflamation2Andi Tri NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument1 pagePathophysiology Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverShiella Heart Malana100% (1)
- Dr. H. Soekimin, Sppa: Bagian Patologi Anatomi Fakultas KedokteranDocument45 pagesDr. H. Soekimin, Sppa: Bagian Patologi Anatomi Fakultas KedokteranRommy Kurniawan DeskyNo ratings yet
- Abses InguinalDocument7 pagesAbses Inguinalmuhammad azharanNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever Pathophysiology: Precipitating Factors Predisposing FactorsDocument2 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic Fever Pathophysiology: Precipitating Factors Predisposing FactorsAl-Mujib TanogNo ratings yet
- InflammationDocument2 pagesInflammationAndrew BonusNo ratings yet
- Inflammation and WOund HealingDocument122 pagesInflammation and WOund HealingDeb SNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Lower Urinary Tract InfectionDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Lower Urinary Tract InfectionSTORAGE FILENo ratings yet
- ST 20200509 Ftcovidtoe 5655233Document1 pageST 20200509 Ftcovidtoe 5655233Muhammad ArifinNo ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis Definition: Infection of The Bone and Surrounding Tissues, Most Commonly Caused byDocument3 pagesOsteomyelitis Definition: Infection of The Bone and Surrounding Tissues, Most Commonly Caused byAngelie_Elvamb_8952No ratings yet
- Grp25 Rivera, Mikhail Bien.. MICU Drug StudyDocument11 pagesGrp25 Rivera, Mikhail Bien.. MICU Drug Studysinister17No ratings yet
- Endocrine and Respiratory System DisordersDocument5 pagesEndocrine and Respiratory System Disorderssinister17No ratings yet
- A. Historical Perspectives in Nursing: I. Personal and Professional Growth and DevelopmentDocument67 pagesA. Historical Perspectives in Nursing: I. Personal and Professional Growth and Developmentsinister17No ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolytes ImbalancesDocument7 pagesFluids and Electrolytes Imbalancessinister17No ratings yet
- NCP WeaknessDocument1 pageNCP Weaknesssinister17100% (5)
- NCP Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument1 pageNCP Impaired Skin Integritysinister17No ratings yet
- NCP HypertensionDocument2 pagesNCP Hypertensionsinister1781% (27)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- NCP FeverDocument3 pagesNCP Feversinister1785% (48)
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studysinister17No ratings yet