Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ram
Uploaded by
sonsfhsdlfhsadhCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ram
Uploaded by
sonsfhsdlfhsadhCopyright:
Available Formats
An Introduction To
Two Port Networks
The University of Tennessee
Electrical and Computer Engineering
Knoxville, TN
wlg
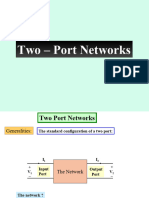
Two Port Networks
Generalities: The standard configuration of a two port:
The Network
Input
Port
Output
Port
+
_ _
+
V
1
V
2
I
1
I
2
The network ?
The voltage and current convention ?
* notes
Two Port Networks
Network Equations:
V
1
= z
11
I
1
+ z
12
I
2
V
2
= z
21
I
1
+ z
22
I
2
I
1
= y
11
V
1
+ y
12
V
2
I
2
= y
21
V
1
+ y
22
V
2
V
1
= AV
2
- BI
2
I
1
= CV
2
- DI
2
V
2
= b
11
V
1
- b
12
I
1
I
2
= b
21
V
1
b
22
I
1
V
1
= h
11
I
1
+ h
12
V
2
I
2
= h
21
I
1
+ h
22
V
2
I
1
= g
11
V
1
+ g
12
I
2
V
2
= g
21
V
1
+ g
22
I
2
Impedance
Z parameters
Admittance
Y parameters
Transmission
A, B, C, D
parameters
Hybrid
H parameters
* notes
Two Port Networks
Z parameters:
1
1
11 I
V
z !
0
2
! I
2
1
12 I
V
z !
0
1
! I
1
2
21 I
V
z !
0
2
! I
2
2
22 I
V
z !
0
1
! I
z
11
is the impedance seen looking into port 1
when port 2 is open.
z
12
is a transfer impedance. It is the ratio of the
voltage at port 1 to the current at port 2 when
port 1 is open.
z
21
is a transfer impedance. It is the ratio of the
voltage at port 2 to the current at port 1 when
port 2 is open.
z
22
is the impedance seen looking into port 2
when port 1 is open.
* notes
Two Port Networks
Y parameters:
1
1
11 V
I
y !
0
2
! V
2
1
12 V
I
y !
0
1
! V
1
2
21 V
I
y !
0
2
! V
2
2
22 V
I
y !
0
1
! V
y
11
is the admittance seen looking into port 1
when port 2 is shorted.
y
12
is a transfer admittance. It is the ratio of the
current at port 1 to the voltage at port 2 when
port 1 is shorted.
y
21
is a transfer impedance. It is the ratio of the
current at port 2 to the voltage at port 1 when
port 2 is shorted.
y
22
is the admittance seen looking into port 2
when port 1 is shorted.
* notes
Two Port Networks
Z parameters: Example 1
Given the following circuit. Determine the Z parameters.
8
20 20 ;
; ;
;
10
+
_
+
_
V
1
V
2
I
1
I
2
Find the Z parameters for the above network.
Two Port Networks
Z parameters: Example 1 (cont 1)
For z
11
:
Z
11
= 8 + 20||30 = 20 ;
For z
22
:
For z
12
:
Z
22
= 20||30 = 12 ;
2
1
12 I
V
z !
0
1
! I
8
20 20 ;
; ;
;
10
+
_
+
_
1 2
I
1
I
2
2
2
1
8
30 20
20 20
xI
x xI
V !
!
Therefore:
8
8
2
2
12
! !
I
xI
z
;
=
21
z
Two Port Networks
Z parameters: Example 1 (cont 2)
The Z parameter equations can be expressed in
matrix form as follows.
2
1
2
1
12 8
8 20
I
I
V
V
2
1
22 21
12 11
2
1
I
I
z z
z z
V
V
Two Port Networks
Z parameters: Example 2 (problem 18.7 Alexander & Sadiku)
You are given the following circuit. Find the Z parameters.
1;
1;
4 ;
2 ;
2
x
+
-
x
+ +
_
_
1 2
I
1
I
2
Two Port Networks
Z parameters: Example 2 (continue p2)
1
1
11 I
V
z !
0
2
! I
1;
1;
4 ;
2 ;
2
+
-
+ +
_
_
1 2
I
1
I
2
6
2 6
6
2
1
1
x x x x x x
V V V V V V
I
+ +
!
+
+ !
2
3
1
x
V
I !
; but
1 1
I V V
x
!
Substituting gives;
)
2
3
1 1
1
I V
I
!
or
; ! !
3
5
11
1
1
z
I
V
Z
21
= -0.667 ;
Z
12
= 0.222 ;
Z
22
= 1.111 ;
Other Answers
Two Port Networks
Transmission parameters (A,B,C,D):
The defining equations are:
2
2
1
1
I
V
D C
B A
I
V
2
1
V
V
A!
I
2
= 0
2
1
I
V
B
!
V
2
= 0
2
1
V
I
C !
I
2
= 0
2
1
I
I
!
V
2 =
0
Two Port Networks
Transmission parameters (A,B,C,D):
Example Given the network below with assumed voltage polarities and
Current directions compatible with the A,B,C,D parameters.
+
_
+
_
R
1
R
2
V
1
V
2
I
1
-I
2
We can write the following equations.
V
1
= (R
1
+ R
2
)I
1
+ R
2
I
2
V
2
= R
2
I
1
+ R
2
I
2
It is not always possible to write 2 equations in terms of the Vs and Is
Of the parameter set.
1
1
R
2
1
R
2
2 1
R
R R +
Two Port Networks
Transmission parameters (A,B,C,D):
Example (cont.)
V
1
= (R
1
+ R
2
)I
1
+ R
2
I
2
V
2
= R
2
I
1
+ R
2
I
2
From these equations we can directly evaluate the A,B,C,D parameters.
2
1
V
V
A!
I
2
= 0
2
1
I
V
B
!
V
2
= 0
2
1
V
I
!
I
2
= 0
2
1
I
I
!
V
2 =
0
=
=
=
=
Later we will see how to interconnect two of these networks together for a final answer
* notes
Two Port Networks
Hybrid Parameters:
The equations for the hybrid parameters are:
2
1
22 21
12 11
2
1
V
I
h h
h h
I
V
1
1
11
I
V
h !
V
2
= 0
2
1
12
V
V
h !
I
1
= 0
1
2
21
I
I
h !
V
2
= 0
2
2
22
V
I
h !
I
1
= 0
* notes
Two Port Networks
Hybrid Parameters:
The following is a popular model used to represent
a particular variety of transistors.
+ +
_ _
1 2
+
_
1
4
3
V
1
2
V
2
I
1
I
2
We can write the following equations:
D
V
CI I
BV AI V
2
1 2
2 1 1
+ !
+ !
* notes
4
1
K
K
2
K
3
K
1
Two Port Networks
Hybrid Parameters:
D
V
I I
V I V
2
1 2
2 1 1
!
!
We want to evaluate the H parameters from the above set of equations.
1
1
11
I
V
!
V
2
= 0
2
1
12
V
V
!
I
1
= 0
1
2
21
I
I
h !
V
2
= 0
2
2
22
V
I
h !
I
1
= 0
=
=
=
=
2
1
R
1
- 1
1
R
Two Port Networks
Hybrid Parameters:
Another example with hybrid parameters.
Given the circuit below.
+
_
+
_
R
1
2
V
1
V
2
I
1
-I
2
The equations for the circuit are:
V
1
= (R
1
+ R
2
)I
1
+ R
2
I
2
V
2
= R
2
I
1
+ R
2
I
2
The H parameters are as follows.
1
1
11
I
V
h !
2
1
12
V
V
h !
1
2
21
I
I
h !
2
2
22
V
I
!
V
2
=0
V
2
=0
I
1
=0
I
1
=0
=
=
=
=
Two Port Networks
Modifying the two port network:
Earlier we found the z parameters of the following network.
8
20 20 ;
; ;
;
10
+
_
+
_
V
1
V
2
I
1
I
2
2
1
2
1
12 8
8 20
I
I
V
V
* notes
Two Port Networks
Modifying the two port network:
We modify the network as shown be adding elements outside the two ports
8
20 20 ;
; ;
;
10
+
_
+
_
V
1
V
2
I
1
I
2
+
_
10 v
6;
4 ;
We now have:
V
1
= 10 - 6I
1
V
2
= - 4I
2
Two Port Networks
Modifying the two port network:
We take a look at the original equations and the equations describing
the new port conditions.
2
1
2
1
12 8
8 20
I
I
V
V
V
1
= 10 - 6I
1
V
2
= - 4I
2
So we have,
10 6I
1
= 20I
1
+ 8I
2
-4I
2
= 8I
1
+ 12I
2
* notes
-0.2273
0.4545
0
10
16 8
8 26
Two Port Networks
Modifying the two port network:
Rearranging the equations gives,
2
1
I
I
1
2
1
I
I
Two Port Networks
Y Parameters and Beyond:
Given the following network.
+
_
+
_
V
1
V
2
I
1
I
2
s
1
1 ;
1 ;
s
(a) Find the Y parameters for the network.
(b) From the Y parameters find the z parameters
Two Port Networks
1
1
11 V
I
y !
0
2
! V
2
1
12 V
I
y !
0
1
! V
1
2
21 V
I
y !
0
2
! V
2
2
22 V
I
y !
0
1
! V
I
1
= y
11
V
1
+ y
12
V
2
I
2
= y
21
V
1
+ y
22
V
2
+
_
+
_
V
1
V
2
I
1
I
2
s
1
1 ;
1 ;
s
To find y
11
!
1 2
2
)
1 2
2
(
1 1 1
s
I
s
s
I V
so
= s + 0.5
1
1
11 V
I
y !
0
2
! V
We use the above equations to
evaluate the parameters from the
network.
Y Parameter Example
short
Two Port Networks
Y Parameter Example
1
2
21
V
I
y !
0
2
! V
+
_
+
_
V
1
V
2
I
1
s
1
1 ;
1 ;
s
I
2
2 1
2I V !
We see
= 0.5 S
1
2
21 V
I
y !
Two Port Networks
Y Parameter Example
+
_
+
_
V
1
V
2
I
1
s
1
1 ;
1 ;
s
I
2
2
1
12 V
I
y !
0
1
! V
2
1
12
V
I
y !
1 2
2I V !
We have
= 0.5 S
short
2
2
22 V
I
y !
0
1
! V
We have
) 2 (
2
2 2
!
s
s
I V
s
y
1
5 . 0
22
!
To find y
12
and y
21
we reverse
things and short V
1
Two Port Networks
Y Parameter Example
Summary:
Y
=
+
+
!
s
s
y y
y y
1 5 . 0 5 . 0
5 . 0 5 . 0
22 21
12 11
Now suppose you want the Z parameters for the same network.
Two Port Networks
Going From Y to Z Parameters
For the Y parameters we have:
V Y I !
For the Z parameters we have:
I Z V !
From above;
I Z I Y V ! !
1
!
( (
! !
Y
y
Y
y
Y
y
Y
y
z z
z z
Y Z
11 21
12 22
22 21
12 11
1
Y
Y
et ! (
Therefore
where
Two Port Parameter Conversions:
Two Port Parameter Conversions:
To go from one set of parameters to another, locate the set of parameters
you are in, move along the vertical until you are in the row that contains
the parameters you want to convert to then compare element for element
22
11
h
z
H
(
!
Interconnection Of Two Port Networks
Three ways that two ports are interconnected:
* Parallel
* Series
* Cascade
? A ? A ? A
b a
y y y + !
? A ? A ? A
b a
z z z + !
? A ? A? A
b a
T T T !
y
a
y
b
z
a
z
b
T
a
T
b
parameters Y
parameters Z
parameters ABCD
Interconnection Of Two Port Networks
Consider the following network:
R
1
R
2
R
1
R
2
T
1
T
2
Referring to slide 13 we have;
+
_
+
_
V
1
V
2
I
1
I
2
1
2
V
V
Find
2
2
2
1
2 1
2
1
2
2 1
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
I
V
R
R
R
R R
R
R
R
R R
I
V
+
!
2
2
2
1
2 1
2
1
2
2 1
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
I
V
R
R
R
R R
R
R
R
R R
I
V
Interconnection Of Two Port Networks
Multiply out the first row:
'
+
'
+
+
'
+
'
+
! ) (
2 1 1
2
2 1
2
2
1
2
2
2 1
1
I R R
R
R R
V
R
R
R
R R
V
Set I
2
= 0 ( as in the diagram)
2
2 2 1 1
2
2
1
2
3
2
R R R R
R
V
V
!
Can be verified directly
by solving the circuit
End of Lesson
Basic Laws of Circuits
Two-Port Networks
You might also like
- ch19 Two-Port Networks PDFDocument19 pagesch19 Two-Port Networks PDFRohit Gandhi0% (1)
- Devices & Circuits RLC CircuitsDocument28 pagesDevices & Circuits RLC CircuitsANJALI DEORENo ratings yet
- Application of ABCDDocument15 pagesApplication of ABCDSantanu Nath50% (4)
- Multistage AmplifierDocument22 pagesMultistage AmplifierVijay AnandhNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics: Single Phase AC-AC ConvertersDocument18 pagesPower Electronics: Single Phase AC-AC ConvertersMaruti MohiteNo ratings yet
- Unijunction TransistorDocument12 pagesUnijunction TransistorGogoi LeftoverNo ratings yet
- Lab#2B: Half-Wave Rectifier Circuit Without and With FilterDocument5 pagesLab#2B: Half-Wave Rectifier Circuit Without and With FilterHemanth GedelaNo ratings yet
- Voltage Multipliers: Half-Wave Voltage DoublerDocument5 pagesVoltage Multipliers: Half-Wave Voltage DoublerKade Ben100% (1)
- Common Emitter UnbypassedDocument38 pagesCommon Emitter Unbypassedaliffuden 123No ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics Measurements and Instrumentation-77-Đã Chuyển ĐổiDocument9 pagesElectrical and Electronics Measurements and Instrumentation-77-Đã Chuyển ĐổiNguyên Nguyễn SơnNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Uncontrolled RectifiersDocument15 pagesThree Phase Uncontrolled RectifiersAnonymous 78iAn6100% (1)
- Unijunction Transistor: By: Smridhi ChawlaDocument27 pagesUnijunction Transistor: By: Smridhi Chawlasmridhi chawla100% (1)
- Power Semiconductor DevicesDocument11 pagesPower Semiconductor DevicesBhavesh Kaushal100% (1)
- EM-I Lab Viva Questions Updated OnDocument6 pagesEM-I Lab Viva Questions Updated OnNagamohan BilluNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 PN Junction Diode Complete Notes BEEDocument12 pagesUNIT 4 PN Junction Diode Complete Notes BEESomesh Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- EDC-II Unit-4 Part 1 SCR, Diac, Triac, SCS, GTO, & LASCRDocument39 pagesEDC-II Unit-4 Part 1 SCR, Diac, Triac, SCS, GTO, & LASCRsamarthNo ratings yet
- ELECTRON DEVICES AND CIRCUITS: 2 Marks Q & ADocument28 pagesELECTRON DEVICES AND CIRCUITS: 2 Marks Q & Ag jagadeesan83% (6)
- Merz Price Differential Protection For TransformerDocument2 pagesMerz Price Differential Protection For TransformerapjbalamuruganNo ratings yet
- S6 PE Lab Manual 2018 MATLAB PDFDocument27 pagesS6 PE Lab Manual 2018 MATLAB PDFhariNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics - 2 MARKSDocument30 pagesPower Electronics - 2 MARKSkarthik kumar50% (4)
- Power Electronics Lab ManualDocument47 pagesPower Electronics Lab Manualshaan_patil100% (1)
- Unit-3 3. Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument31 pagesUnit-3 3. Bipolar Junction TransistorshivaniNo ratings yet
- Clippers and ClamersDocument15 pagesClippers and ClamersThilaga MohanNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.3-Voltage Regulation of A 3-Phase Alternator by ZPF and ASA MethodDocument6 pagesExperiment No.3-Voltage Regulation of A 3-Phase Alternator by ZPF and ASA Method61EEPrabhat Pal100% (1)
- Chap 1 Single PhaseTransformerDocument37 pagesChap 1 Single PhaseTransformerKritika MehtaNo ratings yet
- Experiment - Feedback Amplifiers: 3.2.1 ObjectiveDocument13 pagesExperiment - Feedback Amplifiers: 3.2.1 ObjectiveskmrajkumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Three Phase TransformerDocument30 pagesChapter 10 - Three Phase TransformerWarez Ali0% (1)
- LabSheet Experiments - Giatutinhyeu14 - 2Document176 pagesLabSheet Experiments - Giatutinhyeu14 - 2Nhi OtNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits Question Bank PDFDocument8 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits Question Bank PDFVenkata SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document13 pagesChapter 6aregawi weleabezgiNo ratings yet
- Ec8261 Lab ManualDocument94 pagesEc8261 Lab ManualJayamani Krishnan0% (1)
- Magnetization Characteristics of A D.C. Shunt Generator: Exp. No: DateDocument60 pagesMagnetization Characteristics of A D.C. Shunt Generator: Exp. No: DateSuyash SinghNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Series and Parallel Inverter FinalDocument19 pagesSingle Phase Series and Parallel Inverter Finalmazza23467% (3)
- 3 ChopperDocument63 pages3 ChopperFaida HamidNo ratings yet
- Ac DrivesDocument36 pagesAc Drivesaswardi50% (2)
- Lecture 1 - Mesh and Nodal AnalysisDocument50 pagesLecture 1 - Mesh and Nodal AnalysisCindy KoechNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument67 pagesChapter Threeetayhailu80% (5)
- EEET 205 Lab - 102Document53 pagesEEET 205 Lab - 102Franch Maverick Arellano LorillaNo ratings yet
- BJT Biasing (DC Analysis)Document10 pagesBJT Biasing (DC Analysis)Mozibor RahmanNo ratings yet
- Buet Eee 08Document15 pagesBuet Eee 08kalamhassan33% (3)
- Power Electronics Lab Manual With LogoDocument69 pagesPower Electronics Lab Manual With LogoPunith Gowda M BNo ratings yet
- Half Wave Rectification Experiment - 3: TheoryDocument10 pagesHalf Wave Rectification Experiment - 3: TheoryLakshayNo ratings yet
- Transformer Lab ManualDocument68 pagesTransformer Lab ManualRolando Cruz100% (1)
- Power Electronics (Ques - Ch2 - Rectifiers) PDFDocument44 pagesPower Electronics (Ques - Ch2 - Rectifiers) PDFmadivala nagaraja0% (1)
- Em Lab-II ManualDocument45 pagesEm Lab-II Manualrkadiraj701150% (4)
- Circuitrix EventDocument6 pagesCircuitrix EventNikhil KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Three-Phase TransformersDocument4 pagesLecture 7 Three-Phase TransformersShahrim MohdNo ratings yet
- Op Amp IntegratorDocument14 pagesOp Amp IntegratorMuhammad Haroon50% (2)
- Power BJTDocument14 pagesPower BJTJahangeer SoomroNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab Manual1Document72 pagesPower Electronics Lab Manual1Harish SvNo ratings yet
- Two Port NetworksDocument34 pagesTwo Port Networksvijayalakshmiv VEMURINo ratings yet
- NA Unit-IVDocument33 pagesNA Unit-IVvijayalakshmiv VEMURINo ratings yet
- Two Port NetworksDocument33 pagesTwo Port Networkskumiko580No ratings yet
- Two Port Networks PPT 1 B TECH 3RDDocument32 pagesTwo Port Networks PPT 1 B TECH 3RDEuthecas KipkiruiNo ratings yet
- Two Port networks-NEODocument30 pagesTwo Port networks-NEOAntaredja KartasasmitaNo ratings yet
- Ec2 Chpter 1Document54 pagesEc2 Chpter 1Leet CyberwormNo ratings yet
- Elena Jaringan 2 PortDocument15 pagesElena Jaringan 2 PortFarid AlhasanNo ratings yet
- Andersen CH 19 Final R1Document19 pagesAndersen CH 19 Final R1utpNo ratings yet
- LMH Chapter5Document58 pagesLMH Chapter5Nguyen Son N NguyenNo ratings yet
- Two Port 2021Document34 pagesTwo Port 2021Paidamoyo MuzvidziwaNo ratings yet
- ELEN 127 - Lab 4Document1 pageELEN 127 - Lab 4ajaypalNo ratings yet
- Document 2Document1 pageDocument 2ajaypalNo ratings yet
- Elen 104 - HW 3Document2 pagesElen 104 - HW 3ajaypalNo ratings yet
- Linear Voltage Regulator ProjectDocument14 pagesLinear Voltage Regulator ProjectajaypalNo ratings yet
- IEEE Branch Leadership Training P G: Rahim Khoie, PH.DDocument56 pagesIEEE Branch Leadership Training P G: Rahim Khoie, PH.DajaypalNo ratings yet
- Katha June 1984Document8 pagesKatha June 1984tempsabyNo ratings yet
- Prelab 4Document3 pagesPrelab 4ajaypalNo ratings yet
- Gopalsingh Resume2Document1 pageGopalsingh Resume2ajaypalNo ratings yet
- Eng1 - Annotated Analytical BibliographyDocument3 pagesEng1 - Annotated Analytical BibliographyajaypalNo ratings yet
- SCTR 19 - Annotated BibDocument2 pagesSCTR 19 - Annotated BibajaypalNo ratings yet
- Working Hard or Hardly WorkingDocument2 pagesWorking Hard or Hardly WorkingajaypalNo ratings yet
- Eng1 - Writing Assingment 2nd DraftDocument5 pagesEng1 - Writing Assingment 2nd DraftajaypalNo ratings yet
- Heart of ChocolateDocument5 pagesHeart of ChocolateajaypalNo ratings yet
- G CH 16Document5 pagesG CH 16ajaypalNo ratings yet
- G CH 10Document4 pagesG CH 10ajaypalNo ratings yet
- Undergraduate Bulletin Class 2008Document229 pagesUndergraduate Bulletin Class 2008ajaypalNo ratings yet
- Gill 1Document4 pagesGill 1ajaypalNo ratings yet
- G CH 13Document4 pagesG CH 13ajaypalNo ratings yet
- G CH 4Document3 pagesG CH 4ajaypalNo ratings yet
- Gill 1Document3 pagesGill 1ajaypalNo ratings yet
- G CH 11Document4 pagesG CH 11ajaypalNo ratings yet
- G CH 8Document4 pagesG CH 8ajaypalNo ratings yet
- G CH 5Document4 pagesG CH 5ajaypalNo ratings yet
- We Are DarkDocument4 pagesWe Are DarkajaypalNo ratings yet
- PygmalionDocument10 pagesPygmalionajaypal100% (4)
- An Enhanced RFID-Based Authentication Protocol Using PUF For Vehicular Cloud ComputingDocument18 pagesAn Enhanced RFID-Based Authentication Protocol Using PUF For Vehicular Cloud Computing0dayNo ratings yet
- Coping Mechanism and Academic Performance Among FiDocument14 pagesCoping Mechanism and Academic Performance Among FiMary Margaret MorillaNo ratings yet
- Applications PDFDocument90 pagesApplications PDFahmedNo ratings yet
- The Politics of GenreDocument21 pagesThe Politics of GenreArunabha ChaudhuriNo ratings yet
- Poster PresentationDocument3 pagesPoster PresentationNipun RavalNo ratings yet
- Tablet Time - Student GuideDocument5 pagesTablet Time - Student GuideAyesha BaigNo ratings yet
- Chapter5A TorqueDocument32 pagesChapter5A TorqueShuq Faqat al-FansuriNo ratings yet
- You'Re My Everything - Glenn FredlyDocument2 pagesYou'Re My Everything - Glenn FredlyTommy Juliansyah MarsenoNo ratings yet
- Mat101 w12 Hw6 SolutionsDocument8 pagesMat101 w12 Hw6 SolutionsKonark PatelNo ratings yet
- Attitude of Tribal and Non Tribal Students Towards ModernizationDocument9 pagesAttitude of Tribal and Non Tribal Students Towards ModernizationAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNo ratings yet
- CD4 12-P374493Document30 pagesCD4 12-P374493suraj_savant1No ratings yet
- E Business - Module 1Document75 pagesE Business - Module 1Kannan V KumarNo ratings yet
- PCZ 1503020 CeDocument73 pagesPCZ 1503020 Cedanielradu27No ratings yet
- Vehicles 6-Speed PowerShift Transmission DPS6 DescriptionDocument3 pagesVehicles 6-Speed PowerShift Transmission DPS6 DescriptionCarlos SerapioNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: DR - Wasfi Dhahir Abid AliDocument9 pagesPathophysiology: DR - Wasfi Dhahir Abid AliSheryl Ann PedinesNo ratings yet
- Porifera and CnidariaDocument16 pagesPorifera and CnidariaMichaelNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris: ButterflyDocument4 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris: ButterflyRiyadi TeguhNo ratings yet
- Ton Miles Calculation 1Document17 pagesTon Miles Calculation 1Alexander Armando Clemente Andrade100% (1)
- ActivityDocument2 pagesActivityShaira May SalvadorNo ratings yet
- E WiLES 2021 - BroucherDocument1 pageE WiLES 2021 - BroucherAshish HingnekarNo ratings yet
- VRealize Operations Manager Installation and Configuration Guide For Linux and WindowsDocument98 pagesVRealize Operations Manager Installation and Configuration Guide For Linux and Windowsamdusias67No ratings yet
- LG) Pc-Ii Formulation of Waste Management PlansDocument25 pagesLG) Pc-Ii Formulation of Waste Management PlansAhmed ButtNo ratings yet
- Weather Prediction Using Machine Learning TechniquessDocument53 pagesWeather Prediction Using Machine Learning Techniquessbakiz89No ratings yet
- Ancient To Roman EducationDocument10 pagesAncient To Roman EducationAnonymous wwq9kKDY4100% (2)
- ESG Conundrum PDFDocument30 pagesESG Conundrum PDFVijay Kumar SwamiNo ratings yet
- Prelims CB em Ii5Document21 pagesPrelims CB em Ii5Ugaas SareeyeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For AIDS HIVDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For AIDS HIVFARAH MAE MEDINA100% (2)
- ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Sample Mock Paper Term 2 Exam 2021 22Document5 pagesICSE Class 10 Chemistry Sample Mock Paper Term 2 Exam 2021 22dhruv sharmaNo ratings yet
- Curry PowderDocument8 pagesCurry PowderMahendar Vanam100% (1)
- Embraer ERJ-170: Power PlantDocument5 pagesEmbraer ERJ-170: Power Plantபென்ஸிஹர்No ratings yet