Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FIFO Depth Calculation
FIFO Depth Calculation
Uploaded by
Ashik GhonaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FIFO Depth Calculation
FIFO Depth Calculation
Uploaded by
Ashik GhonaCopyright:
Available Formats
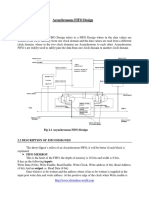
FIFO Depth Calculation: Basically we use FIFO for synchronizing two clock domains (different frequencies) so we need a device
which has some tolerance power to hold the data that device is called FIFO .By using FIFO we can easily avoid overflow and underflow conditions The scenario can be two of following l l Writing is faster than reading then there is possibility of overflow Writing is slower than reading then there is possibility of underflow
In FIFO depth calculation we always have to consider worst cast .size of FIFO basically implies that how much data is required to buffer . And it is totally depend on data rate of reading and writing. Data rate = Number of Data x Time Period Difference = DRFAST DRSLOW Depth = Difference / Higher Freq. Time Period
Writing side is Source and Reading Side is Sink. If the data rate of writing is higher then the reading sides data rate then the FIFO will now overflow. Another Type of depth calculation can be done by this method: Consider F1 is writing frequency and F2 is reading frequency (F1>F2) and Data Size is D (Data Words) Time taken to write to FIFO = DATA/F1 Data Read from the FIFO in the same time = (DATA/F1) xF2 Excess Data is FIFO (Backlog) = DATA-((DATA/F1) x F2 Read side will take more time to read the data so that time is called mop-up time. Following is the calculation of mop-up time Mop-up time = Backlog/F2 = DATA-(DATA/F1 F2) Fwrite = Clock Frequency of Write Clock Domain Depth= Wmax {Wmax x Fread x Wread} Fread = Clock Frequency of Read Clock Domain Fwrite x Wwrite Wmax= Maximum number of worlds can be Written Wwrite = Number of Writes in Per Clock Wread = Number of reads in Per Clock Following are some cases of FIFO depth calculation with perfect explanation. Case: 1 Writing Side Reading Side Solution: Consider the data size is = 10 Data Rate of Writing = 10 x (1/30) =333.33 ns Data Rate of Reading = 10 x (1/40) =250.0 ns. Difference between Data Rates = 333.33 250.0 = 83.33 Now divide with highest frequency time period = 83.33/25ns = 3.3332 = 4 (Aprox) Depth of FIFO Should be 4 = 30 MHz => 33.33 ns Time Period = 40 MHz = > 25.0 ns Time Period
Case: 2 Writing Side Reading Side = 80 Data/100 Clock = 100 MHz => 10ns Time Period = 80 Data/80 Clock = 80 MHz => 12ns Time Period
No Randomization Solution: Data Size is = 80 Data Rate of Writing =80*10=800ns Data Rate of Reading=80*12=900ns Difference = 960-800=160ns Now divide with highest frequency time period = 160/10ns=16 Depth of FIFO Should be 16 Case: 3 Writing Side Reading Side Word Size Solution: Data Rate of Writing =100*2=200ns Data Rate of Reading=400*2=800ns Difference = 800-200=600 Now Divide by the lowest frequency time period = 600/400 = 1.5 = 2 Case: 4 Writing Data = 80 DATA/100 Clock (Randomization of 20 Datas) Outgoing Data= 8 DATA/10 Clock Solution: Above shows that the Writing Frequency is equal to reading frequency We will consider worst case = 10 MHz => 100 ns = 2.5 MHz=>400 ns =2
20 Data
80 Valid Data
80 Valid Data
20 Data
So we will consider 200 Cycles. In 200 Cycle 160 Data is written. it means 160 data continuously written in 160 clock it is the worst case . At the reading side we will Read 8x16=128 data in 16x10=160 Clock Cycle. So the Difference between Written Data and Read Back Data is = 160-128=32
You might also like
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect - Associate Exam Dumps With PDF and VCE Download (1-50)Document11 pagesAWS Certified Solutions Architect - Associate Exam Dumps With PDF and VCE Download (1-50)Jatin Kumar69% (16)
- PALO ALTO - Standard Operation ProcedureDocument49 pagesPALO ALTO - Standard Operation ProcedureTofan SofiansahNo ratings yet
- PerspectiveDocument2 pagesPerspectivePatrick Joseph0% (1)
- p13 - Behavioral Modeling of LDO PDFDocument10 pagesp13 - Behavioral Modeling of LDO PDFTitan FredNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous FIFO Design Using VerilogDocument15 pagesAsynchronous FIFO Design Using Verilogkakaricardo2008No ratings yet
- Sram Part1Document36 pagesSram Part1api-285860375No ratings yet
- LTC 5Document2 pagesLTC 5Sharmet SolarzNo ratings yet
- BobCAD-CAM V22 Milling GSM 7-24-08 WEBDocument85 pagesBobCAD-CAM V22 Milling GSM 7-24-08 WEBsuveriNo ratings yet
- ASIC Verification - FIFODocument4 pagesASIC Verification - FIFOprodip7No ratings yet
- Fifo Depth Calculation Made EasyDocument8 pagesFifo Depth Calculation Made EasyGAURAV KUMARNo ratings yet
- FIFO Depth Calculation ?Document1 pageFIFO Depth Calculation ?AbhNo ratings yet
- F If o Depth Calculation Made Easy 2Document8 pagesF If o Depth Calculation Made Easy 2kotra devinagaphanindraNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous FIFO FinalDocument16 pagesAsynchronous FIFO FinalAyush Katyal100% (1)
- Advanced Digital FifoDocument68 pagesAdvanced Digital FifoPromit MandalNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of First in First Out MemoryDocument64 pagesDesign and Implementation of First in First Out MemoryMustafa NasserNo ratings yet
- Setup and Hold Time Definition PDFDocument5 pagesSetup and Hold Time Definition PDFRaghuNo ratings yet
- ASIC Interview Question & Answer: Memory Interface QuestionsDocument5 pagesASIC Interview Question & Answer: Memory Interface QuestionsRajendra PrasadNo ratings yet
- Metastability and CDC-1Document32 pagesMetastability and CDC-1tejaNo ratings yet
- Design of An Efficient FIFO Buffer For Network On Chip RoutersDocument4 pagesDesign of An Efficient FIFO Buffer For Network On Chip RoutersAmityUniversity IIcNo ratings yet
- Understanding Synchronous Fifos: Author: Cypress Associated Part FamilyDocument10 pagesUnderstanding Synchronous Fifos: Author: Cypress Associated Part FamilySainadh YerrapragadaNo ratings yet
- Cache DesignDocument59 pagesCache DesignChunkai HuangNo ratings yet
- Design of Asynchronous FIFODocument5 pagesDesign of Asynchronous FIFOSakshi GandhewarNo ratings yet
- BGRDocument30 pagesBGRMohammad Ayatullah MaktoomNo ratings yet
- Tips To Optimize Your Verilog HDL CodeDocument9 pagesTips To Optimize Your Verilog HDL CodeZaheer AbbasNo ratings yet
- Structural Data Types: Wire and RegDocument25 pagesStructural Data Types: Wire and RegRAGUL RAJ SNo ratings yet
- Igital Elay Ocked OOP Esign: Yun Lan ECG 721 11/18/2015Document29 pagesIgital Elay Ocked OOP Esign: Yun Lan ECG 721 11/18/2015Meshcheryakov SlavaNo ratings yet
- DDR Memory Design and TestDocument13 pagesDDR Memory Design and TestKevin_INo ratings yet
- Design of Synchronous FifoDocument18 pagesDesign of Synchronous Fifoprasu440No ratings yet
- RTL Coding Styles That Yield Simulation and Synthesis MismatchesDocument15 pagesRTL Coding Styles That Yield Simulation and Synthesis Mismatchesajaysimha_vlsiNo ratings yet
- Systemc-Ams Tutorial: Institute of Computer Technology Vienna University of Technology Markus DammDocument26 pagesSystemc-Ams Tutorial: Institute of Computer Technology Vienna University of Technology Markus DammAamir HabibNo ratings yet
- CMOS Power Dissipation and Trends: R. AmirtharajahDocument60 pagesCMOS Power Dissipation and Trends: R. AmirtharajahmarshaldvtNo ratings yet
- Io MultiplexingDocument19 pagesIo Multiplexingsubramanyam62No ratings yet
- Low Power Uart DeviceDocument19 pagesLow Power Uart DeviceparnabmasterNo ratings yet
- Power Distribution and Clock Design: R. Saleh Dept. of ECE University of British Columbia Res@ece - Ubc.caDocument55 pagesPower Distribution and Clock Design: R. Saleh Dept. of ECE University of British Columbia Res@ece - Ubc.caSiva RaoNo ratings yet
- Design and Modeling of I2C Bus ControllerDocument49 pagesDesign and Modeling of I2C Bus ControllerAmareshChaligeriNo ratings yet
- TCL Awk Xgraph BasicsDocument73 pagesTCL Awk Xgraph BasicsVinay ChalluruNo ratings yet
- Axi DmaDocument62 pagesAxi DmaSrinivas DangetiNo ratings yet
- Analog-To-Digital Conversion Btech IIIDocument50 pagesAnalog-To-Digital Conversion Btech IIILisa BhagatNo ratings yet
- Power Reduction Through RTL Clock GatingDocument10 pagesPower Reduction Through RTL Clock GatingAishwarya TekkalakotaNo ratings yet
- Interview QuestionsDocument29 pagesInterview Questionspritam044100% (1)
- Digital Design Interview Questions & AnswersDocument6 pagesDigital Design Interview Questions & AnswersSucharitha ReddyNo ratings yet
- GPIO Design, Layout, Simulation and ESD Clamp Placement Calculator PDFDocument200 pagesGPIO Design, Layout, Simulation and ESD Clamp Placement Calculator PDFVăn CôngNo ratings yet
- Understanding DDR - DDR Protocol - Truechip VIPsDocument9 pagesUnderstanding DDR - DDR Protocol - Truechip VIPssantosh soodNo ratings yet
- SVTBDocument222 pagesSVTBsandeepNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Questions PDFDocument34 pagesVlsi Questions PDFp gangadhar KumarNo ratings yet
- Palestra 4 Abram BelkDocument143 pagesPalestra 4 Abram BelkThiago Rafael PrettoNo ratings yet
- Clock Dividers Made EasyDocument25 pagesClock Dividers Made Easykumarbsnsp100% (2)
- 10-Coding Guidelines 07Document16 pages10-Coding Guidelines 07sckidNo ratings yet
- Verilog Interview Questions Part 1Document7 pagesVerilog Interview Questions Part 1radhakodirekka8732No ratings yet
- ASIC Interview Question & Answer - ASIC Timing Interview QuestionsDocument4 pagesASIC Interview Question & Answer - ASIC Timing Interview QuestionsHarry singhNo ratings yet
- Equalization Ffe, Dfe - Lect - 27Document42 pagesEqualization Ffe, Dfe - Lect - 27Bichon OttawaNo ratings yet
- Full Custom IC DesignDocument100 pagesFull Custom IC DesignZA IzatNo ratings yet
- Cadence Uv M Debug SlidesDocument34 pagesCadence Uv M Debug SlidesBharathwajan ParthasarathyNo ratings yet
- Implementation of DDR4 Using System Verilog: GuideDocument16 pagesImplementation of DDR4 Using System Verilog: GuideDhanya KNo ratings yet
- Design of CMOS Fully Differential Operational Transconductance AmplifierDocument24 pagesDesign of CMOS Fully Differential Operational Transconductance AmplifierAbhijit Kuvar100% (2)
- Overview of 3D Architecture Design Opportunities and TechniquesDocument6 pagesOverview of 3D Architecture Design Opportunities and TechniquesPramod Reddy RNo ratings yet
- VHDL Bram BromDocument9 pagesVHDL Bram BromGmit MandyaNo ratings yet
- TCL LangaugeDocument28 pagesTCL LangaugeLokesh Sharma100% (1)
- Interfacing and Some Common Building Blocks: Coe 111: Advanced Digital DesignDocument35 pagesInterfacing and Some Common Building Blocks: Coe 111: Advanced Digital DesignFrancisNo ratings yet
- TCLDocument101 pagesTCLBasavaraj KoppadNo ratings yet
- Millimicrosecond Pulse Techniques: International Series of Monographs on Electronics and InstrumentationFrom EverandMillimicrosecond Pulse Techniques: International Series of Monographs on Electronics and InstrumentationNo ratings yet
- Controles Empresariales SAS NetworkassmtV2 NetworkHealthAndOutagesDocument280 pagesControles Empresariales SAS NetworkassmtV2 NetworkHealthAndOutagesLuisa BaqueroNo ratings yet
- Utl FileDocument14 pagesUtl FilebhargavNo ratings yet
- PA Controls Software EngineerDocument1 pagePA Controls Software Engineerrajkumar396239No ratings yet
- Compact Planar Ultra Wideband Antenna For On-Body ApplicationsDocument5 pagesCompact Planar Ultra Wideband Antenna For On-Body ApplicationsHussien HagiNo ratings yet
- Hipo LectureDocument12 pagesHipo LectureJenny Sison-Wilson100% (7)
- B1 UDO Trace LogDocument5 pagesB1 UDO Trace Logpepb13No ratings yet
- Tomb - ManualDocument4 pagesTomb - Manualtelengard_tNo ratings yet
- Info Iec61439-2 (Ed3.0) enDocument6 pagesInfo Iec61439-2 (Ed3.0) enjueunNo ratings yet
- Rest API Python GuideDocument13 pagesRest API Python GuidehabibNo ratings yet
- Ifs Pub Onefs Release Notes 9700 en UsDocument11 pagesIfs Pub Onefs Release Notes 9700 en UsjanNo ratings yet
- Taller Practica ChurnDocument6 pagesTaller Practica ChurnLuis Medina50% (2)
- Realtime Procedural Terrain Generation PDFDocument20 pagesRealtime Procedural Terrain Generation PDFMdainNo ratings yet
- 12CSQuestion BankMYSQLDocument33 pages12CSQuestion BankMYSQLpeehutyagi06No ratings yet
- Kanakadhaarastotram MalayalamDocument5 pagesKanakadhaarastotram MalayalamithaqnNo ratings yet
- Low-Cost Inkjet Process For 3-D PrintingDocument53 pagesLow-Cost Inkjet Process For 3-D PrintingDeepak SoroutNo ratings yet
- Rajeev Murali - Project ManagerDocument3 pagesRajeev Murali - Project ManagerNuclear WifeNo ratings yet
- TD04803001E - Visual Designer Driver ListDocument8 pagesTD04803001E - Visual Designer Driver Listrogermantilla08No ratings yet
- A PROJECT REPORT by Justin MathewDocument61 pagesA PROJECT REPORT by Justin MathewRakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Openbridge Designer: Practice WorkbookDocument249 pagesIntroduction To Openbridge Designer: Practice WorkbookSteffy Catharina100% (1)
- Grundfosliterature 6119667Document22 pagesGrundfosliterature 6119667najkulimeNo ratings yet
- 1412PCDFCADocument55 pages1412PCDFCAEmanuel HeráclioNo ratings yet
- ATV/Motorcycle Computer: ACE-2XX User ManualDocument3 pagesATV/Motorcycle Computer: ACE-2XX User ManualtheunnoneNo ratings yet
- ANN - Perceptron - AdalineDocument15 pagesANN - Perceptron - AdalineDhanushMKuberNo ratings yet
- Connect HANA To SLD and Solution Manager - SCN PDFDocument7 pagesConnect HANA To SLD and Solution Manager - SCN PDFbasis445No ratings yet
- GTmetrix Report WWW - Fixya.com 20180515T163154 PtPcoy35 FullDocument27 pagesGTmetrix Report WWW - Fixya.com 20180515T163154 PtPcoy35 FullAdiumvirNo ratings yet